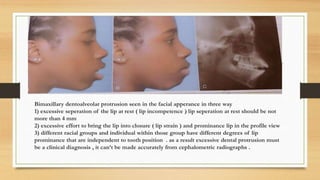
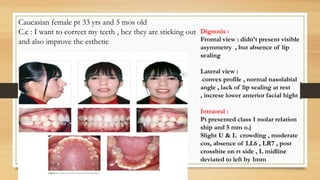
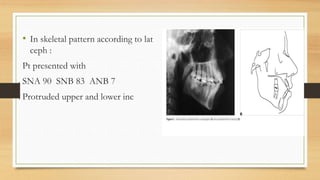
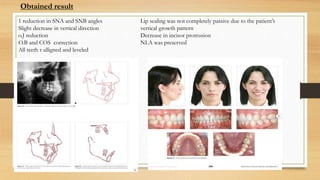
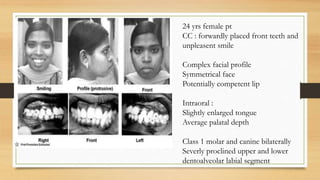
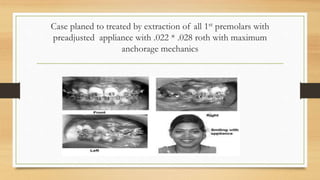
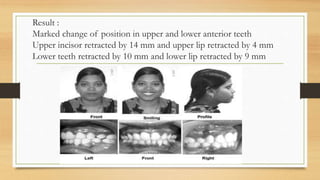
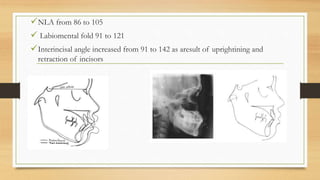
Bimaxillary proclination is a condition characterized by protrusive and proclined upper and lower incisors. It is most common in Afro-Caribbean populations and also seen in some Asian and Arab groups. Skeletal, soft tissue, dental, and habit-related factors can all contribute to the development of bimaxillary proclination. Treatment depends on the severity and may involve nonextraction for mild cases or extraction of first premolars with orthodontic alignment in moderate to severe cases. Stability can be improved with permanent retention like bonded lingual retainers.