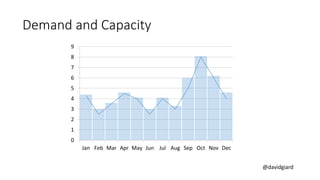
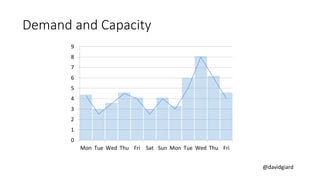
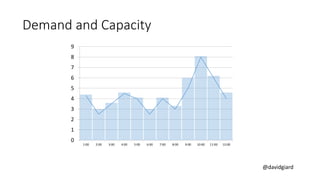
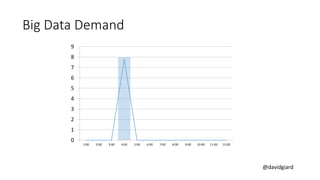
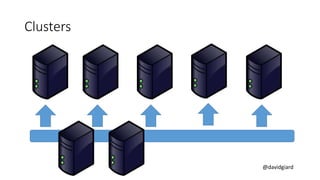
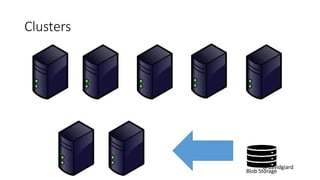
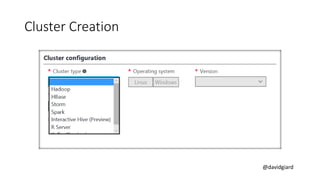
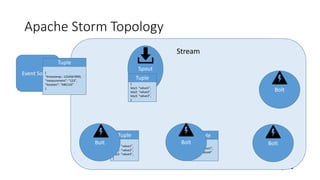
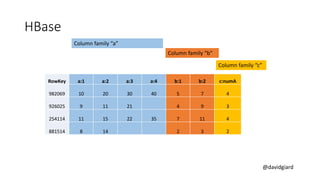
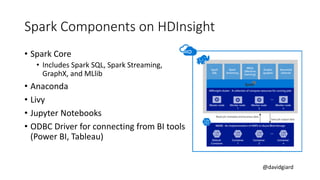
The document discusses Big Data on Azure and provides an overview of HDInsight, Microsoft's Apache Hadoop-based data platform on Azure. It describes HDInsight cluster types for Hadoop, HBase, Storm and Spark and how clusters can be automatically provisioned on Azure. Example applications and demos of Storm, HBase, Hive and Spark are also presented. The document highlights key aspects of using HDInsight including storage integration and tools for interactive analysis.