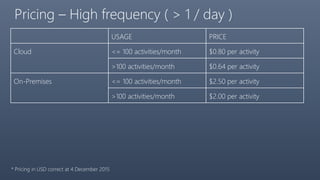
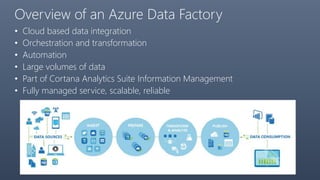
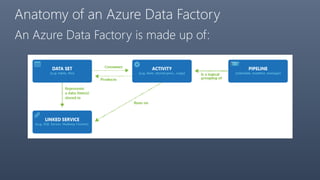
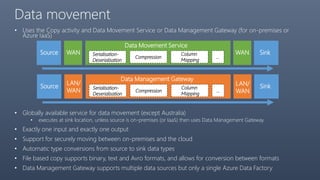
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Azure Data Factory, a cloud-based service for data integration and transformation. It details its components, such as linked services, data sets, and pipelines, alongside data movement and analysis functionalities. Additionally, pricing information and best practices for development and monitoring are included, making it a resource for understanding Azure Data Factory's capabilities and usage scenarios.











![Functions
• Rich set of functions to
• Specify data selection queries
• Specify input data set dependencies
• [startTime, endTime] – data set slice
• [f(startTime, endTime), g(startTime, endTime)] – dependency
period
• Use system variables as parameters
• Functions for text formatting and date/time selection
• Text.Format('{0:yyyy}',WindowStart)
• Date.AddDays(SliceStart, -7 - Date.DayOfWeek(SliceStart))](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alaparoundazuredatafactory-151208062230-lva1-app6891/85/A-lap-around-Azure-Data-Factory-14-320.jpg)



![Data analysis and transformation
TRANSFORMATION ACTIVITY COMPUTE ENVIRONMENT
Hive HDInsight [Hadoop]
Pig HDInsight [Hadoop]
MapReduce HDInsight [Hadoop]
Hadoop Streaming HDInsight [Hadoop]
Machine Learning activities: Batch Execution and
Update Resource
Azure VM
Stored Procedure Azure SQL Database
Data Lake Analytics U-SQL Azure Data Lake Analytics
DotNet HDInsight [Hadoop] or Azure Batch](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/alaparoundazuredatafactory-151208062230-lva1-app6891/85/A-lap-around-Azure-Data-Factory-19-320.jpg)