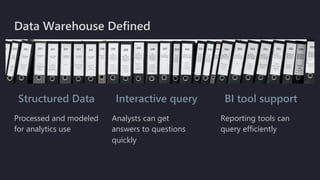
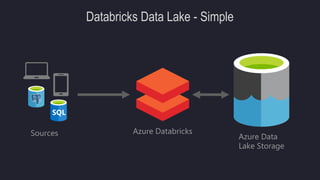
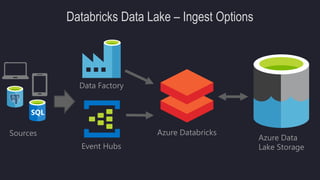
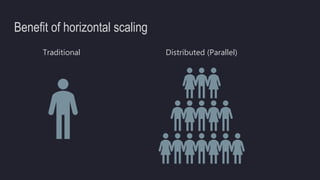
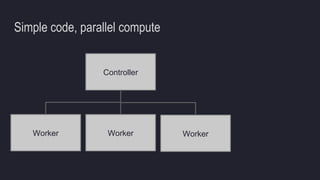
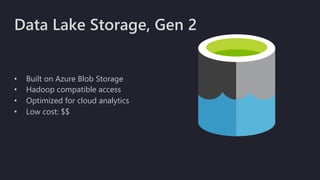
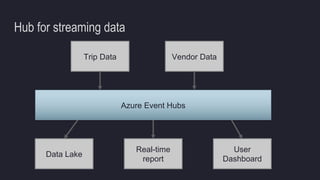
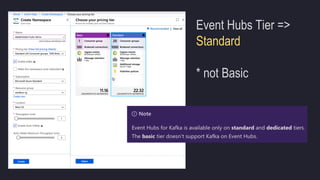
The document outlines the essentials of building data lakes using Azure Databricks, emphasizing the importance of big data storage and analytics. It discusses data lake structures, querying capabilities, and the benefits of using Apache Spark for scalable data processing. Additionally, it highlights best practices for data storage and management, including the use of Delta Lake for improved performance and compliance.