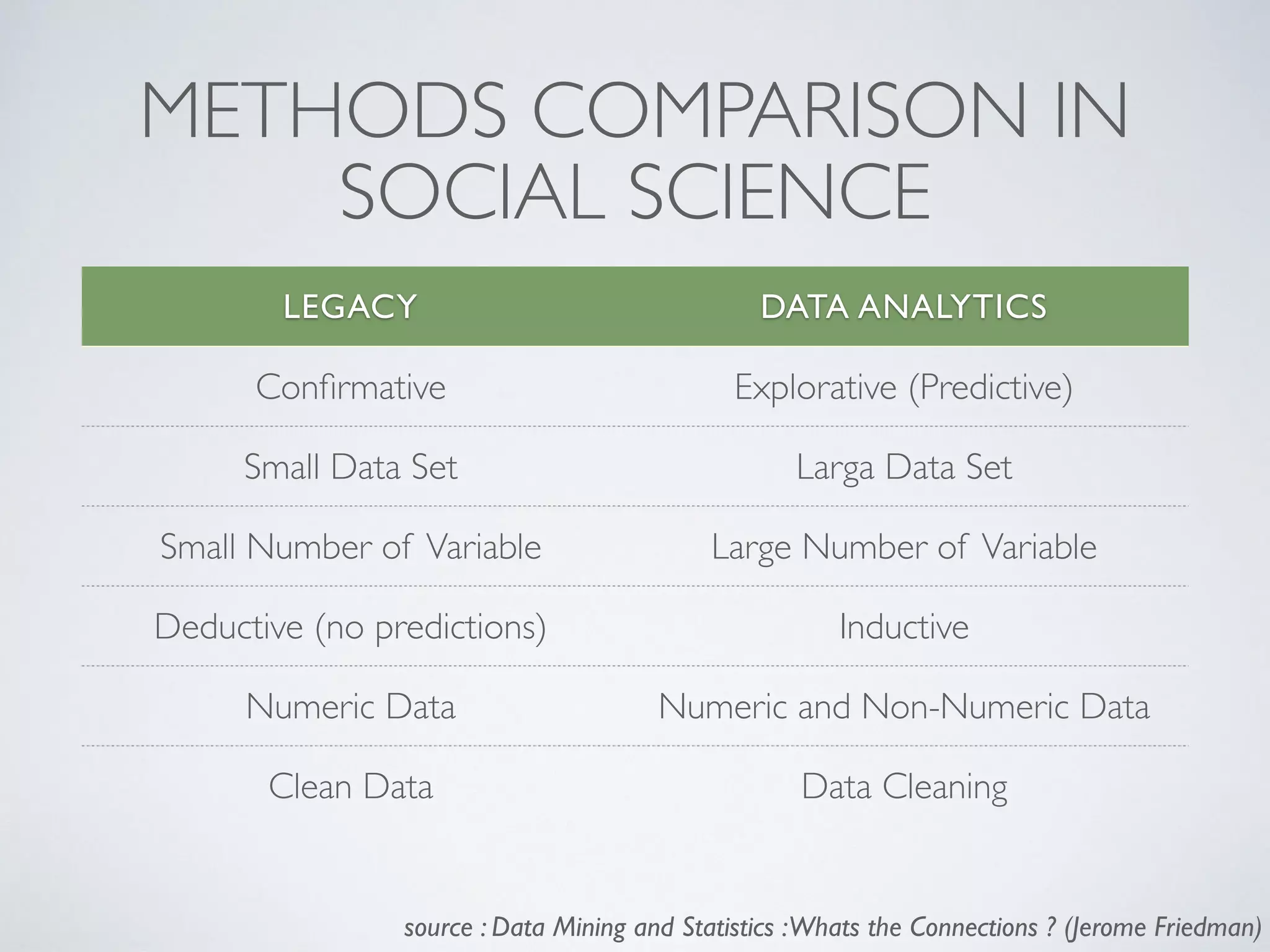
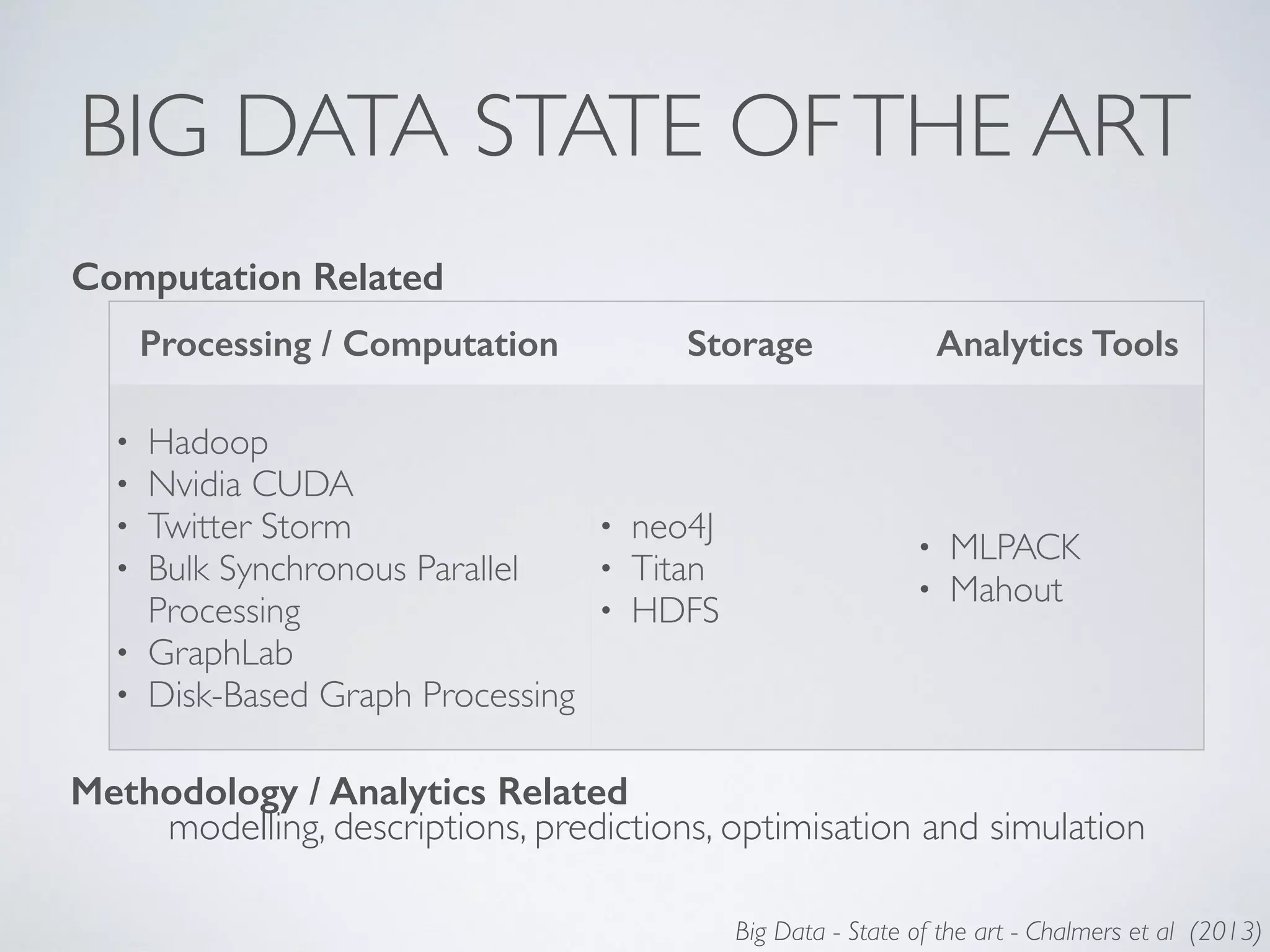
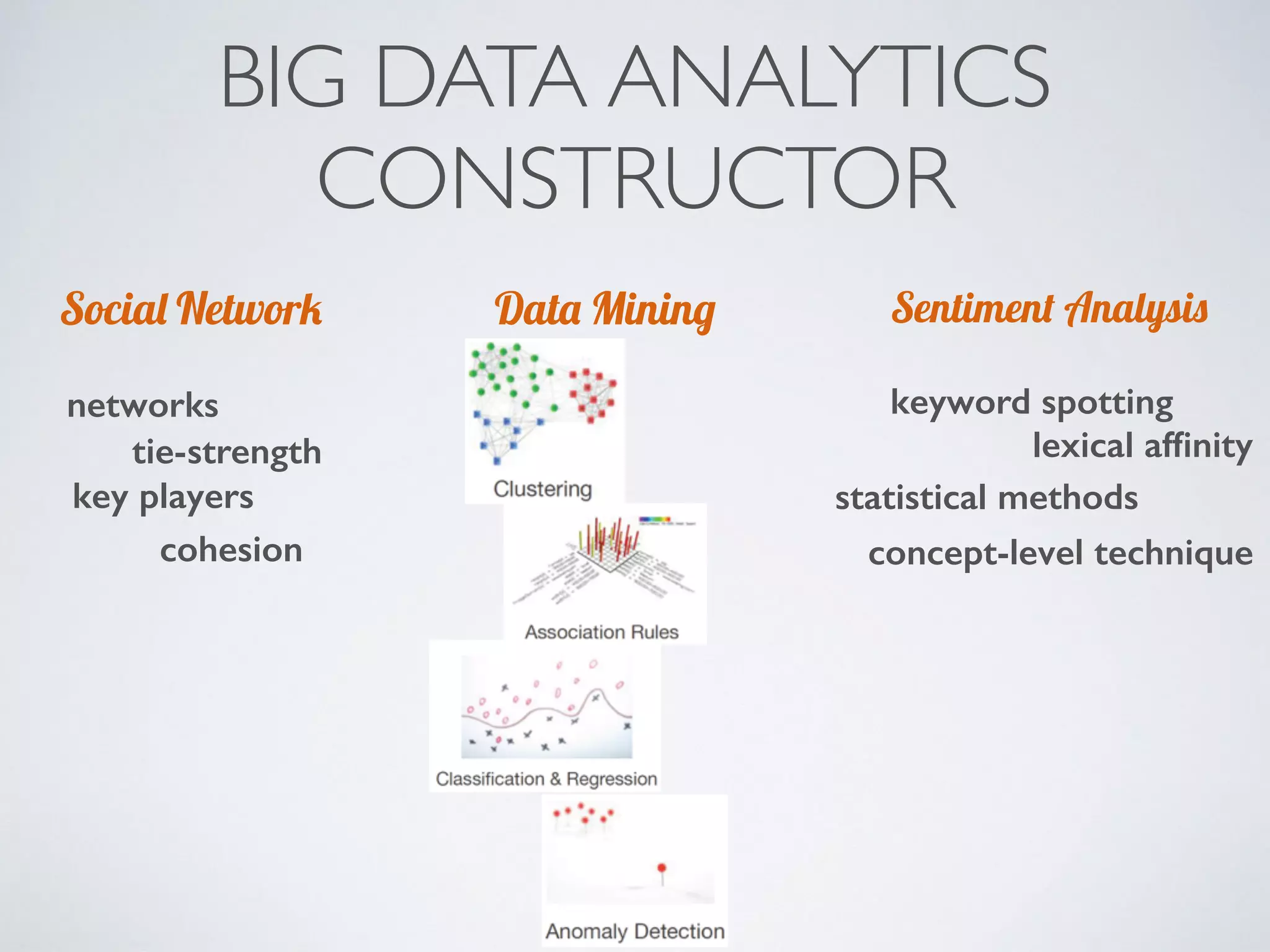
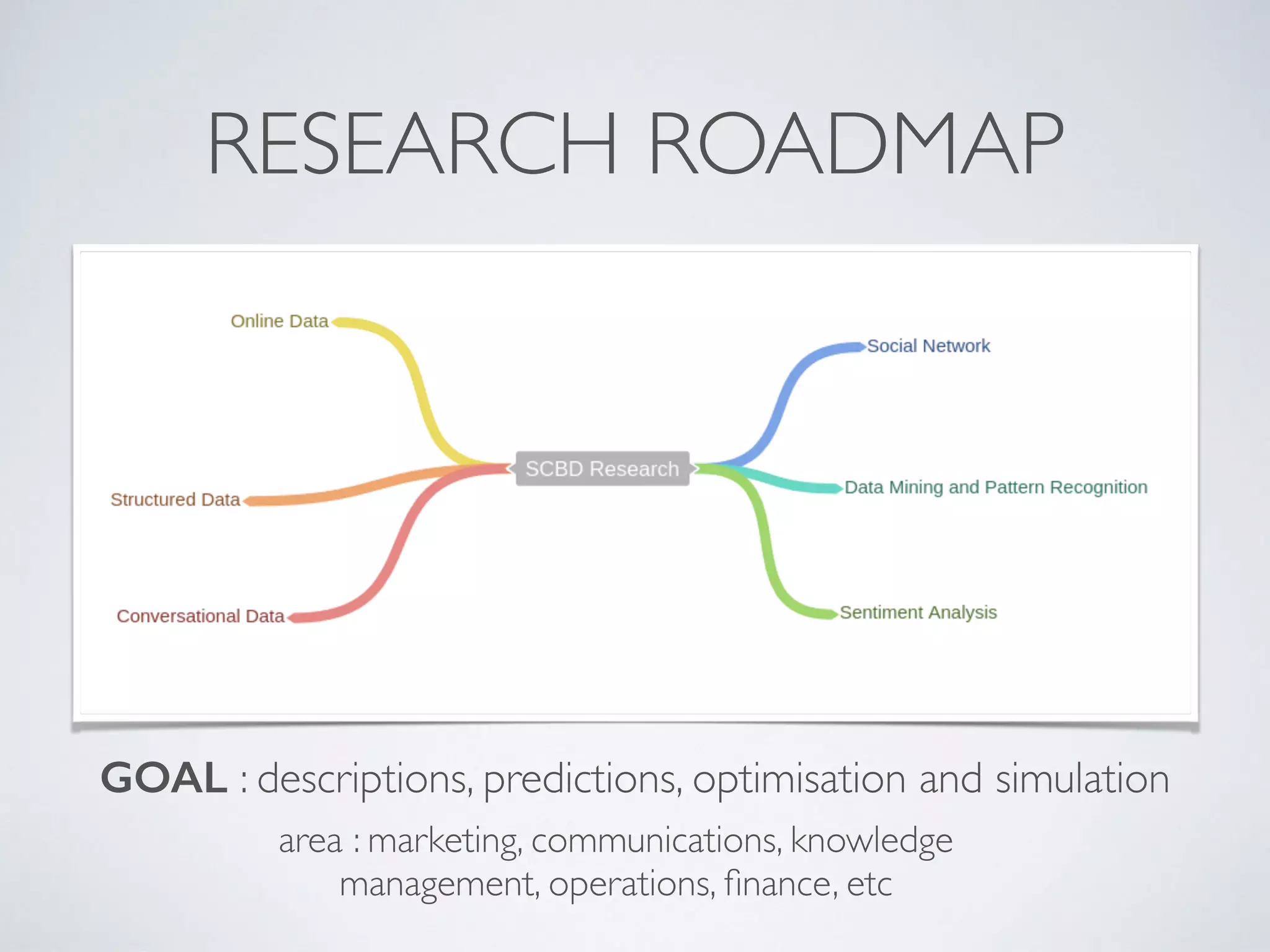
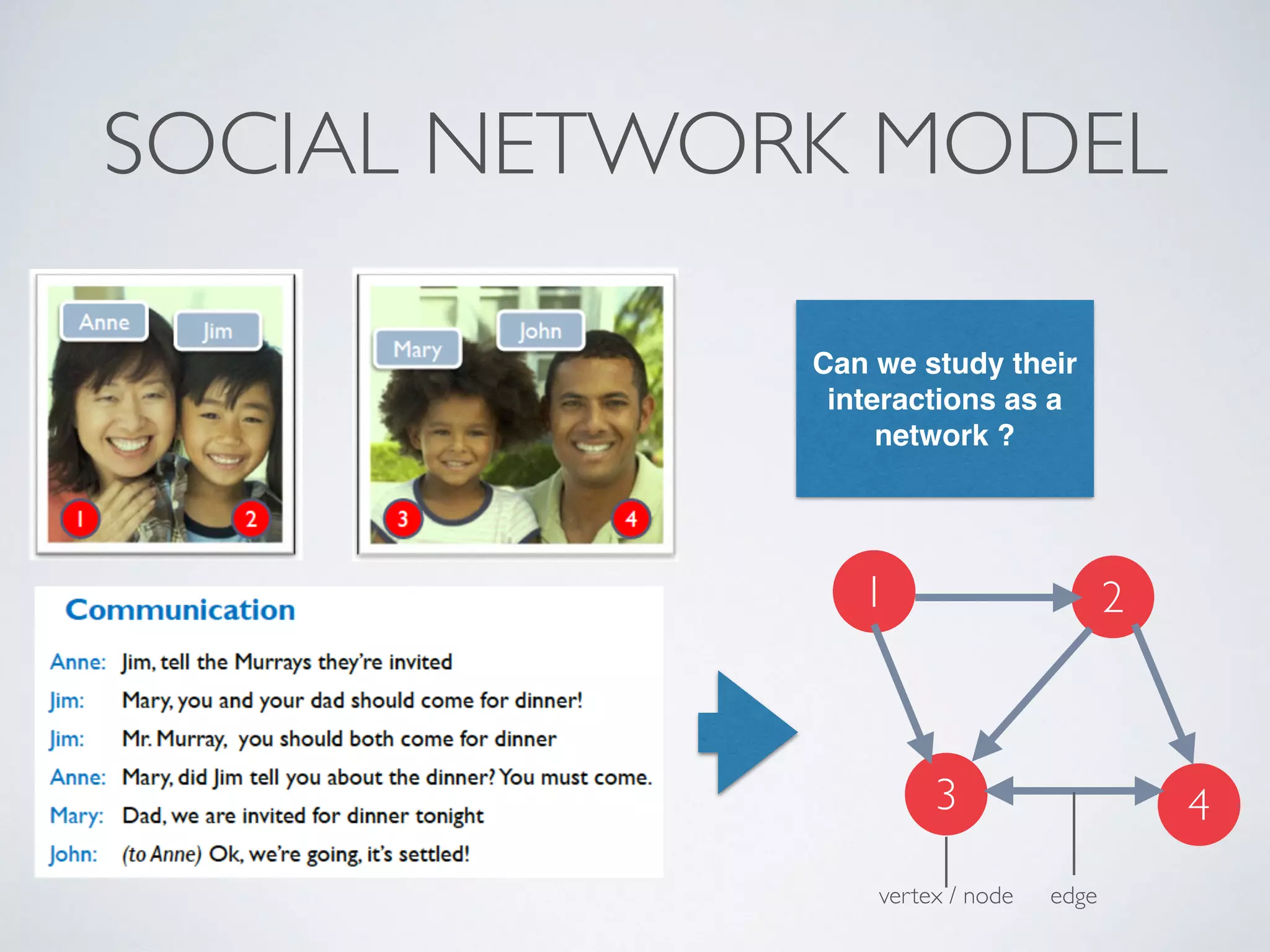
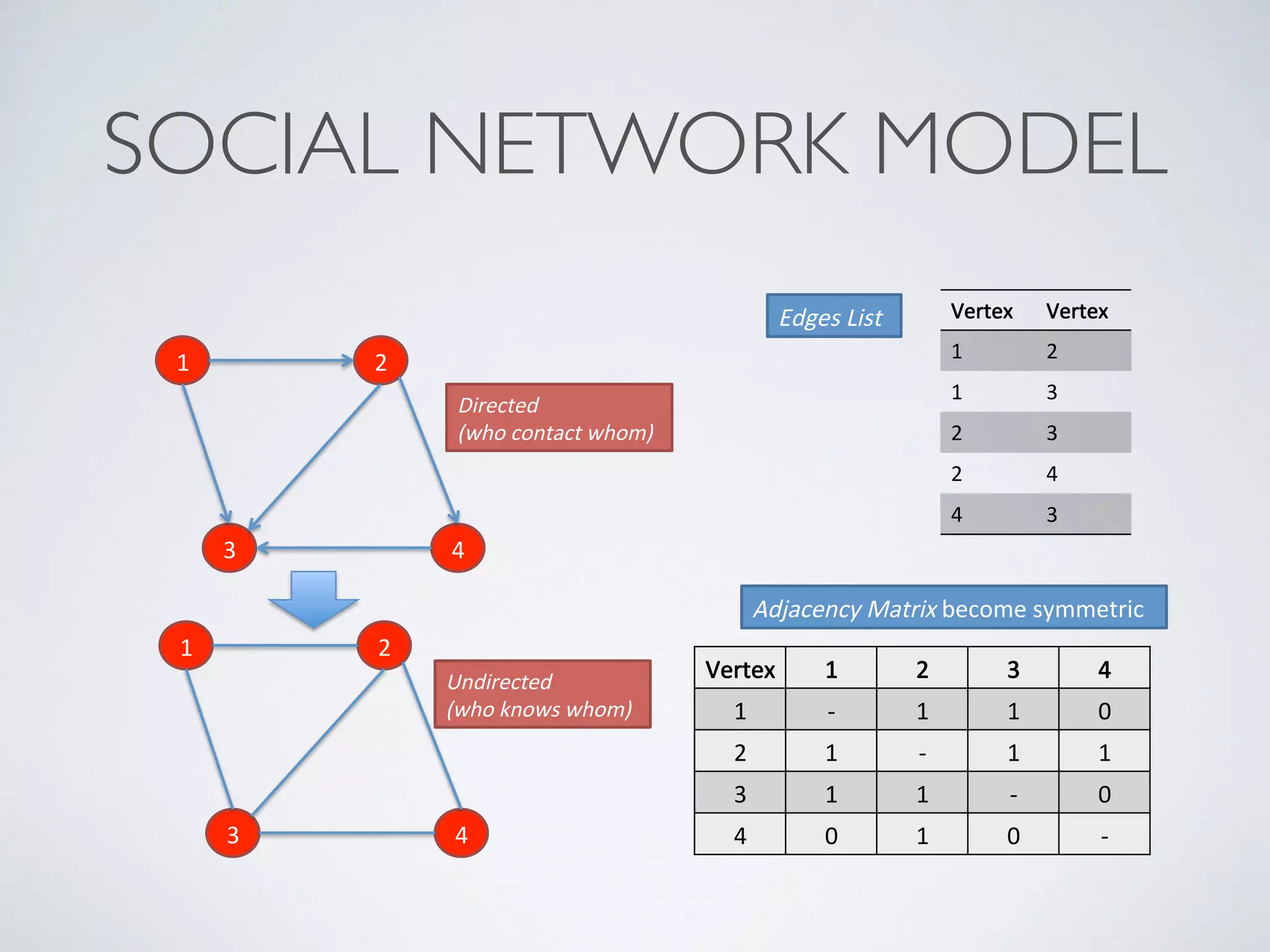
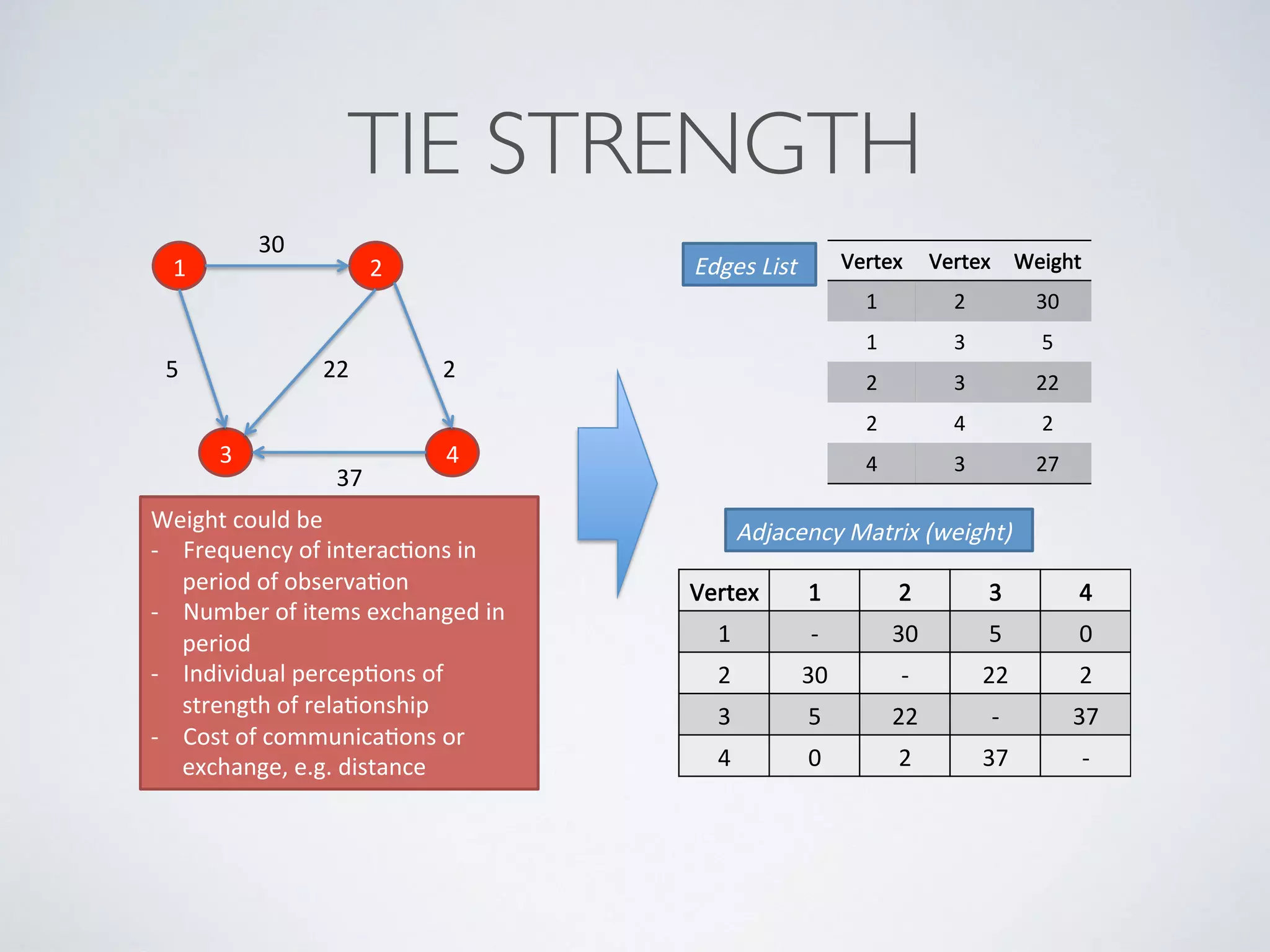
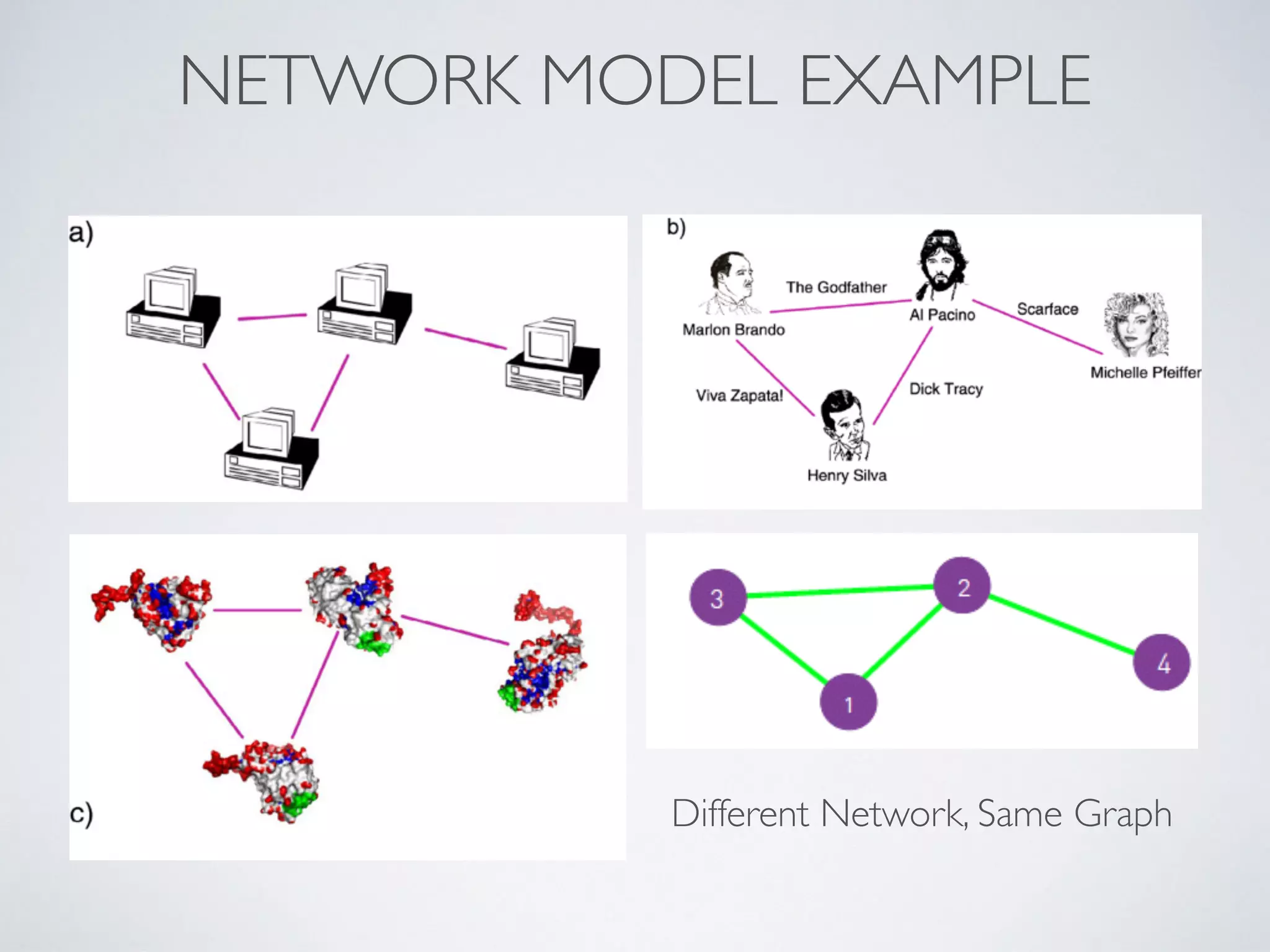
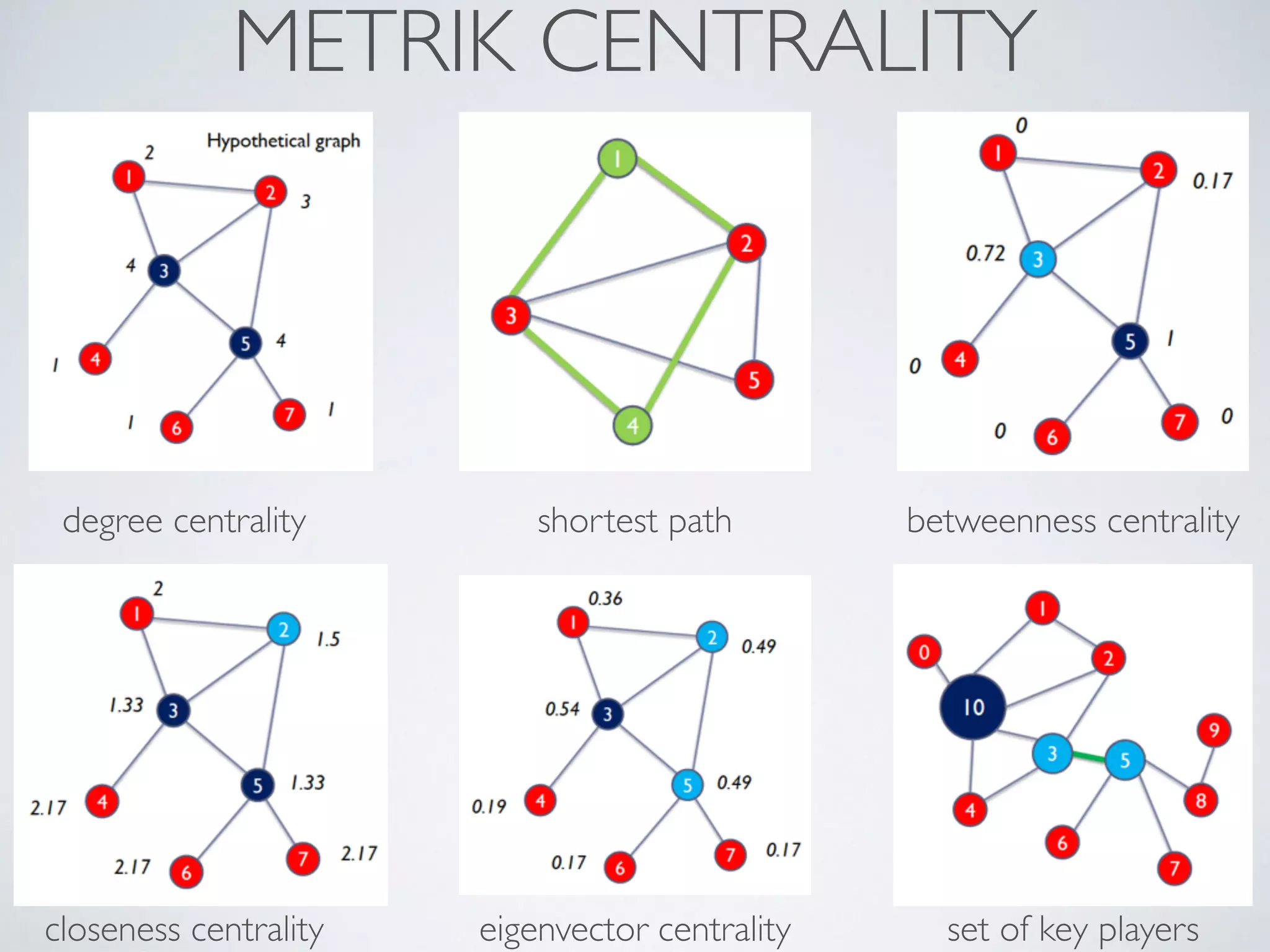
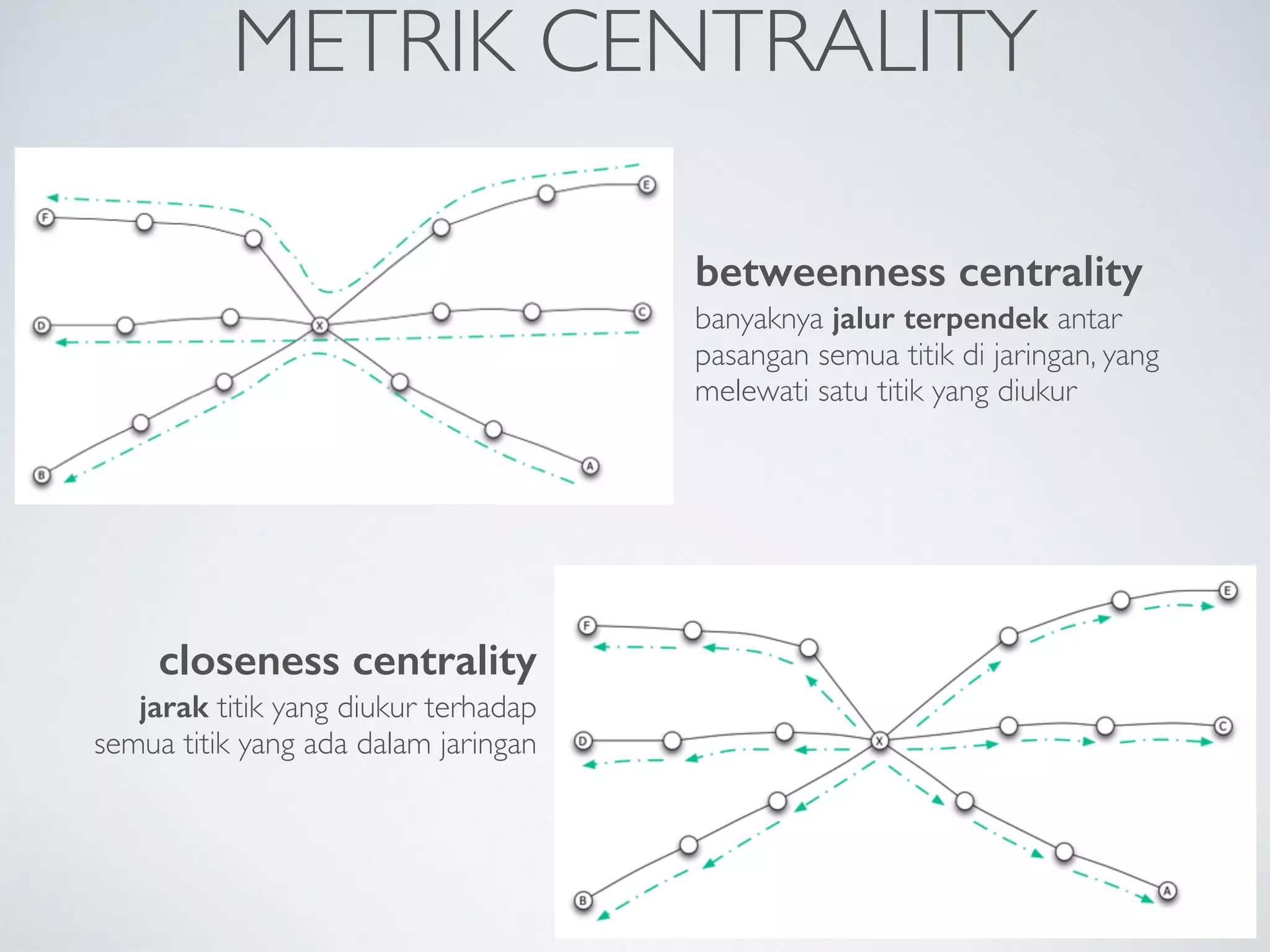
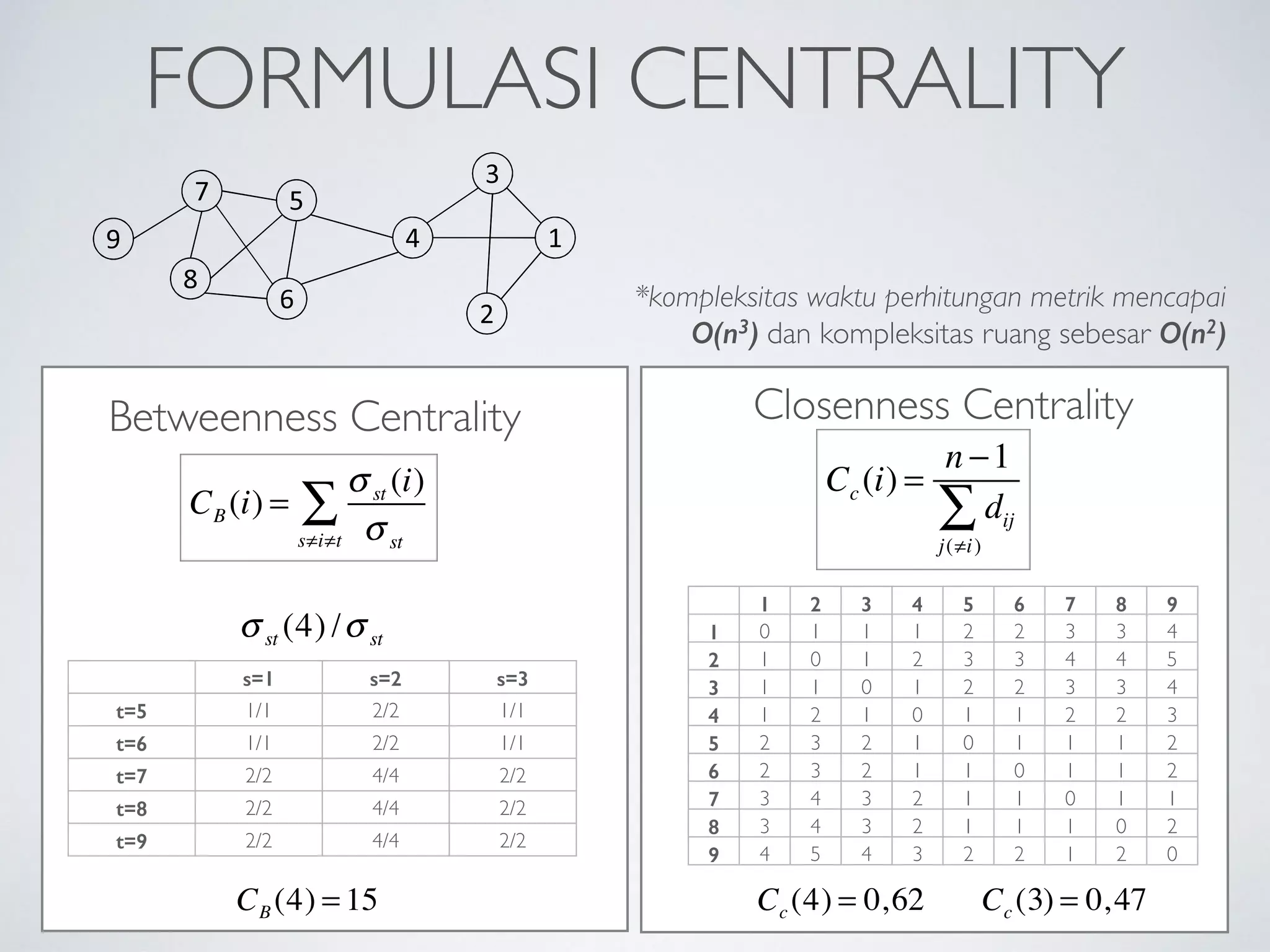
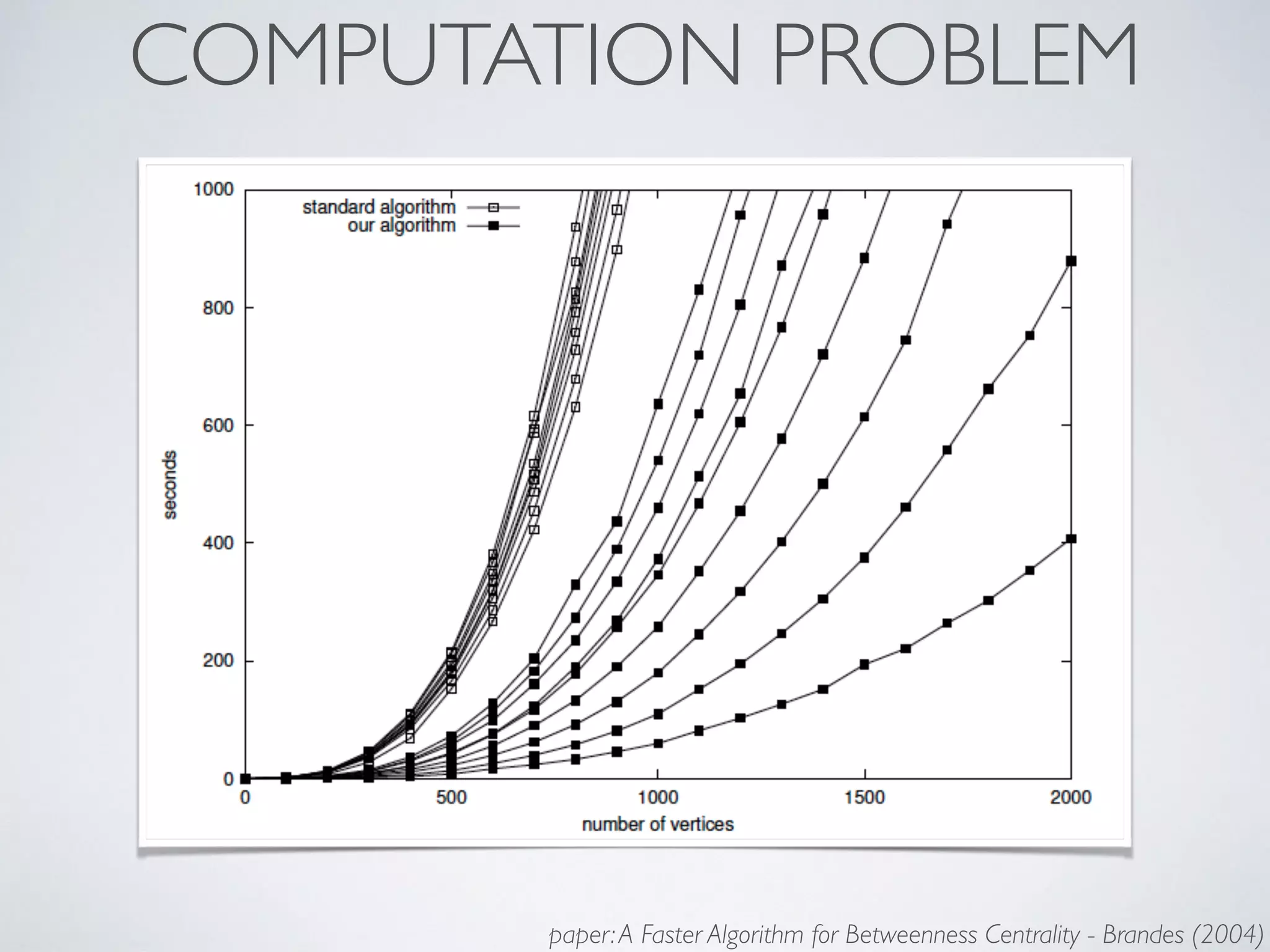
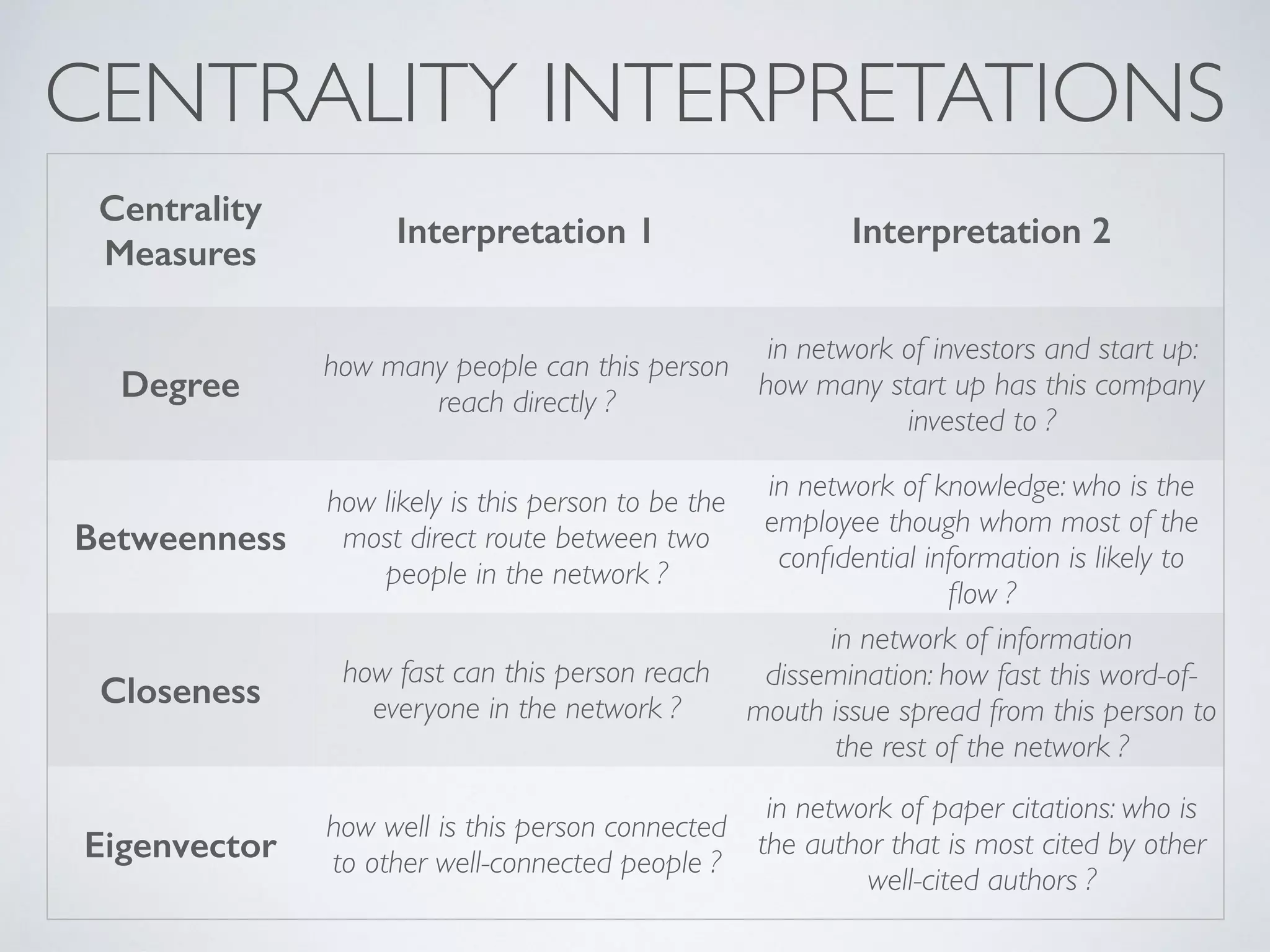
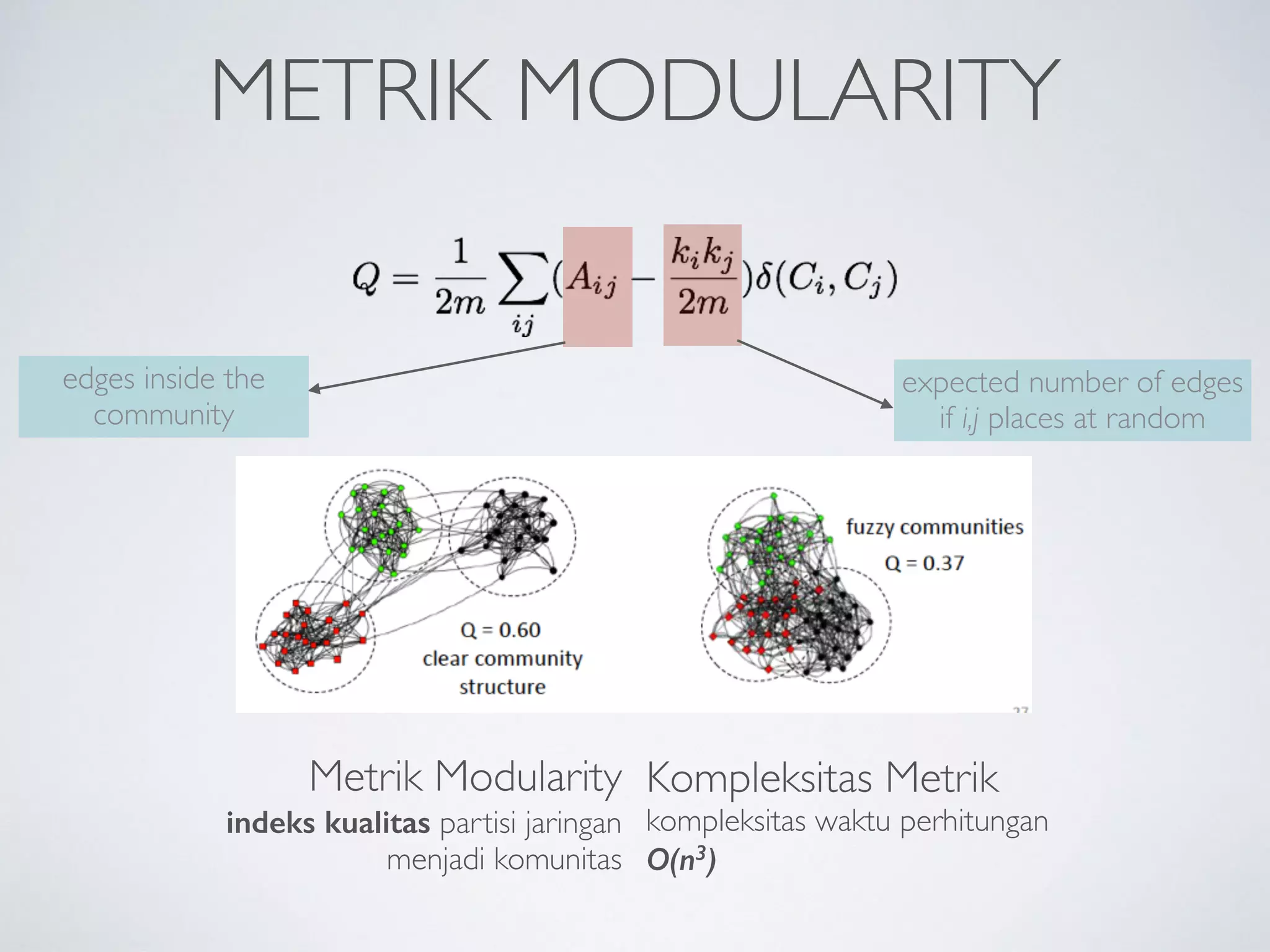
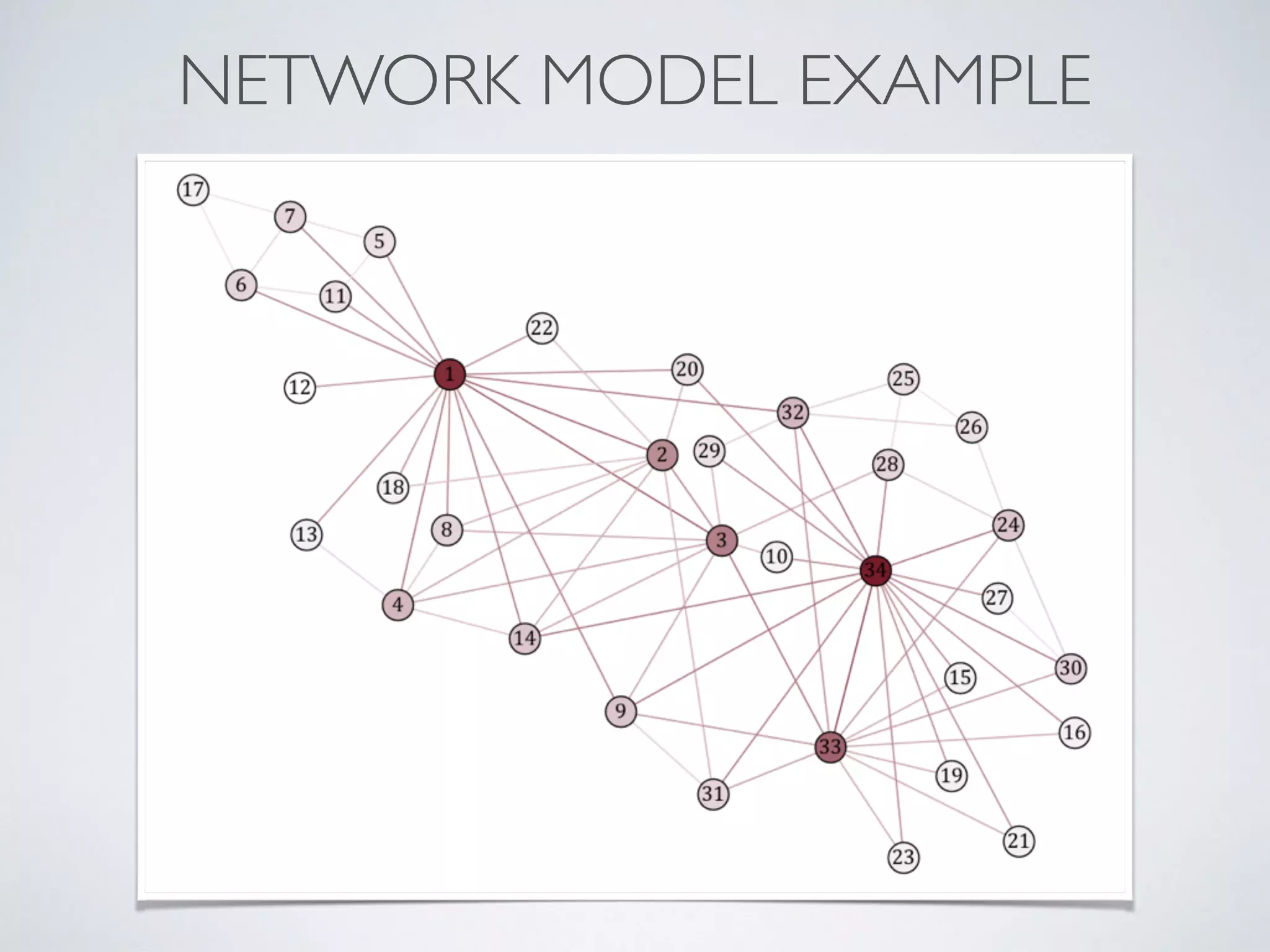
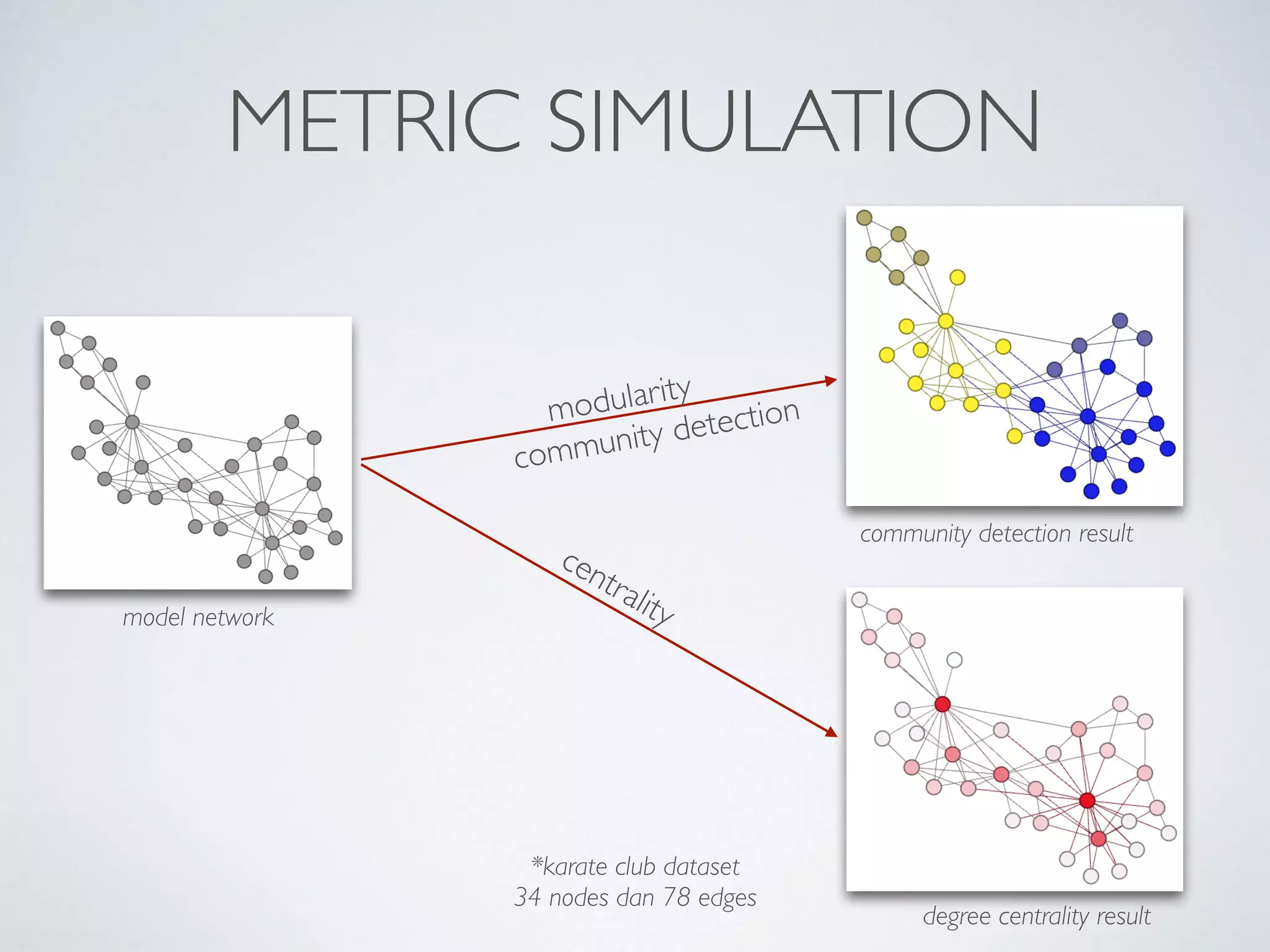
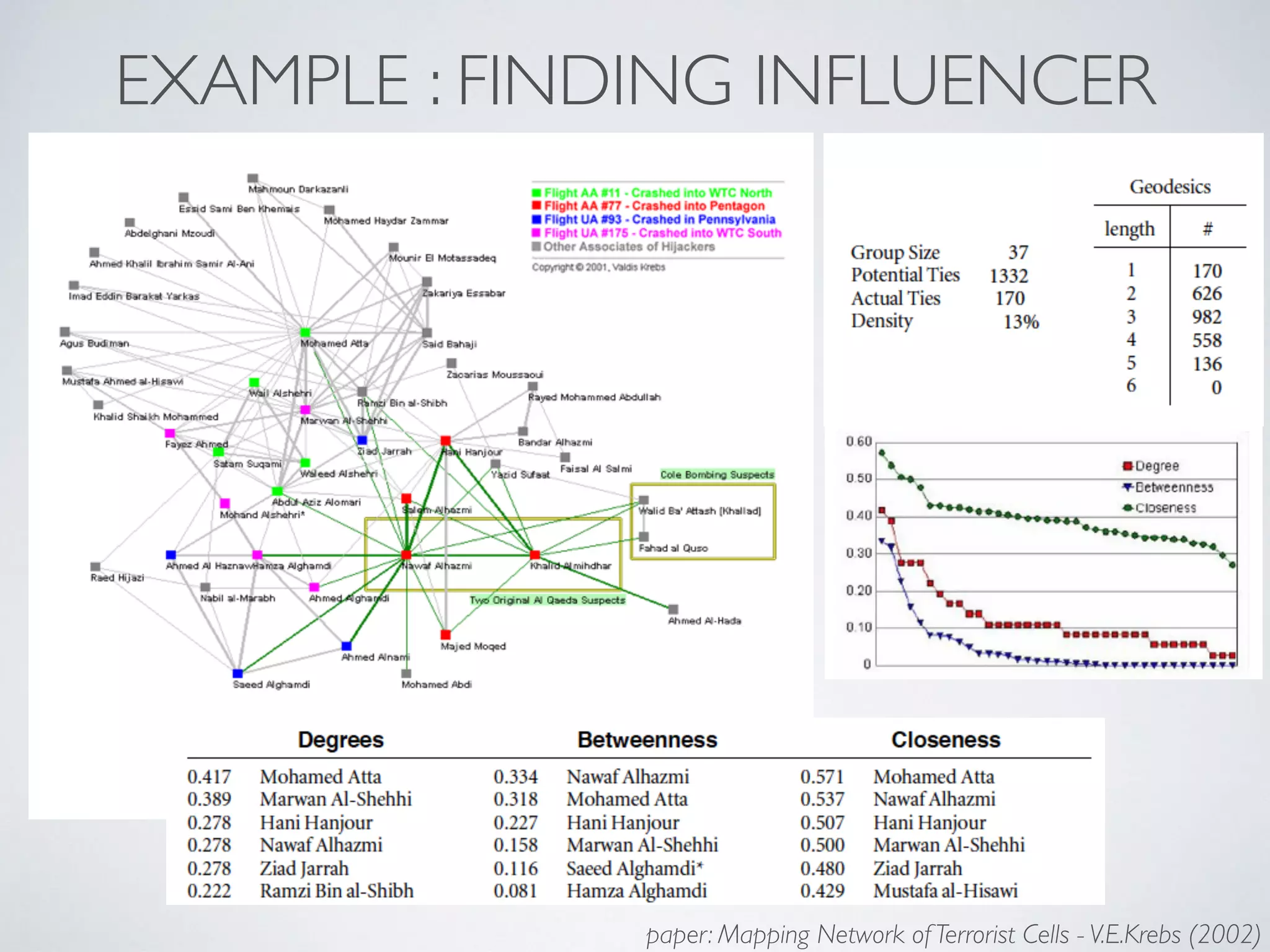
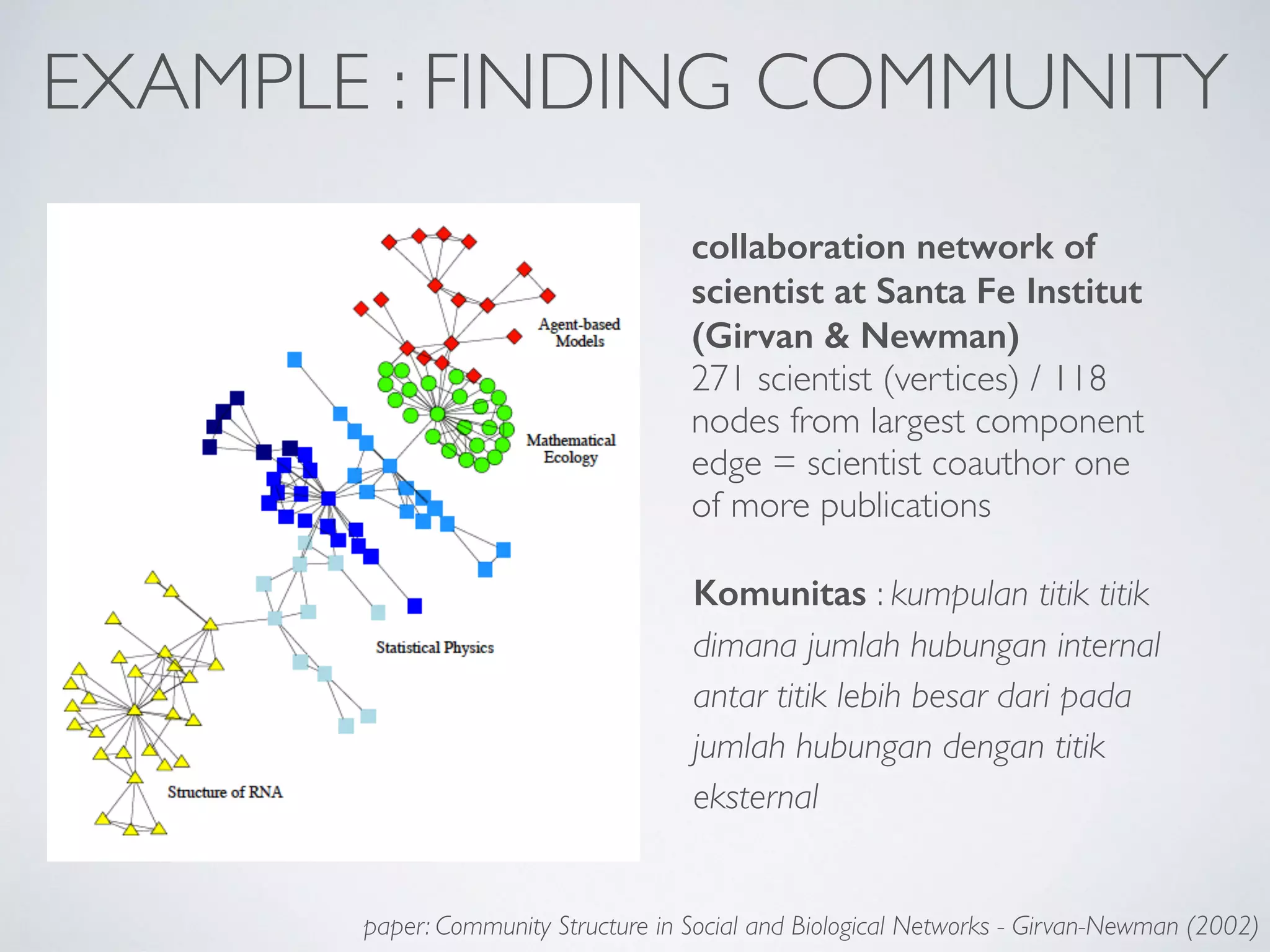
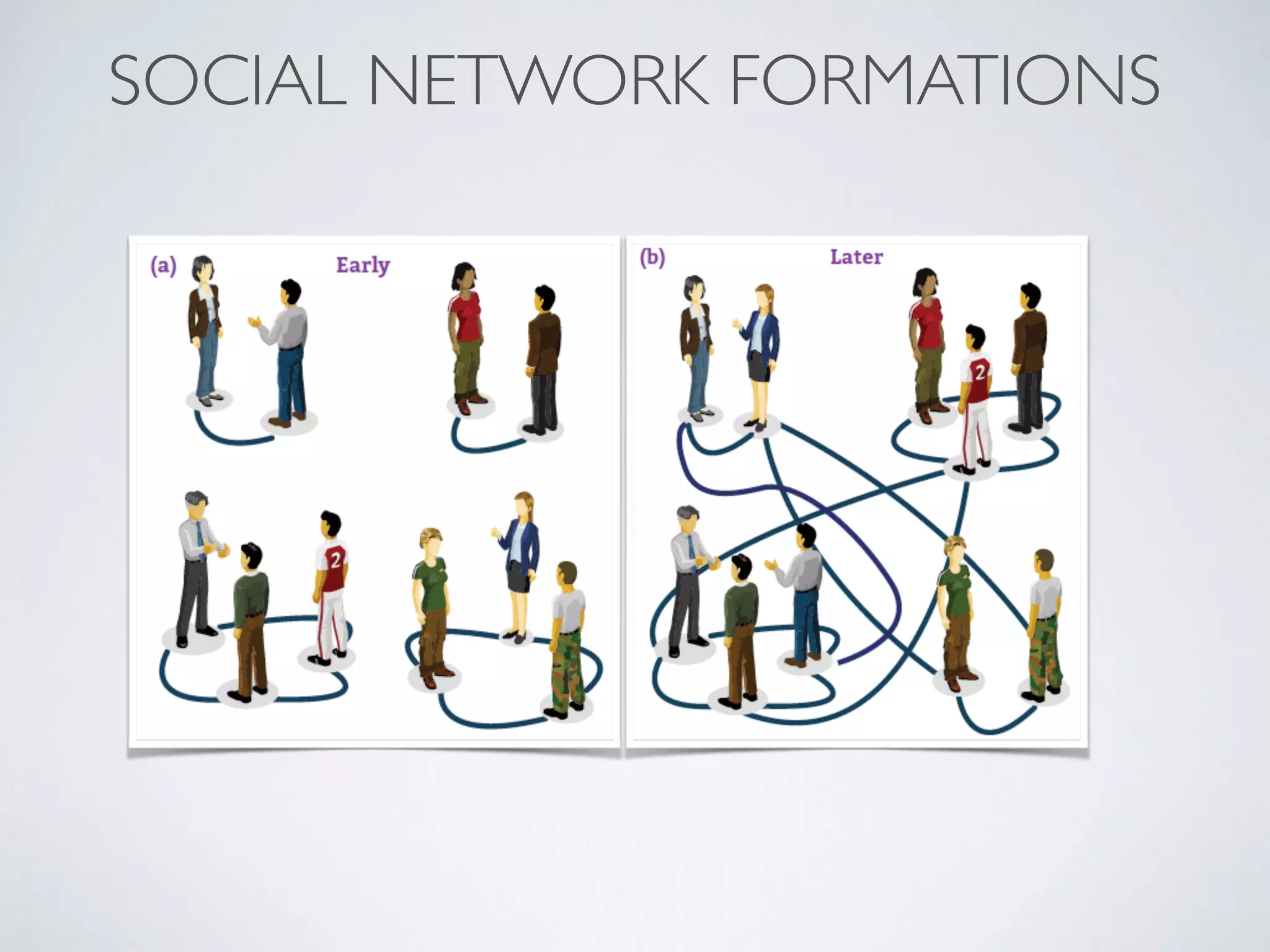
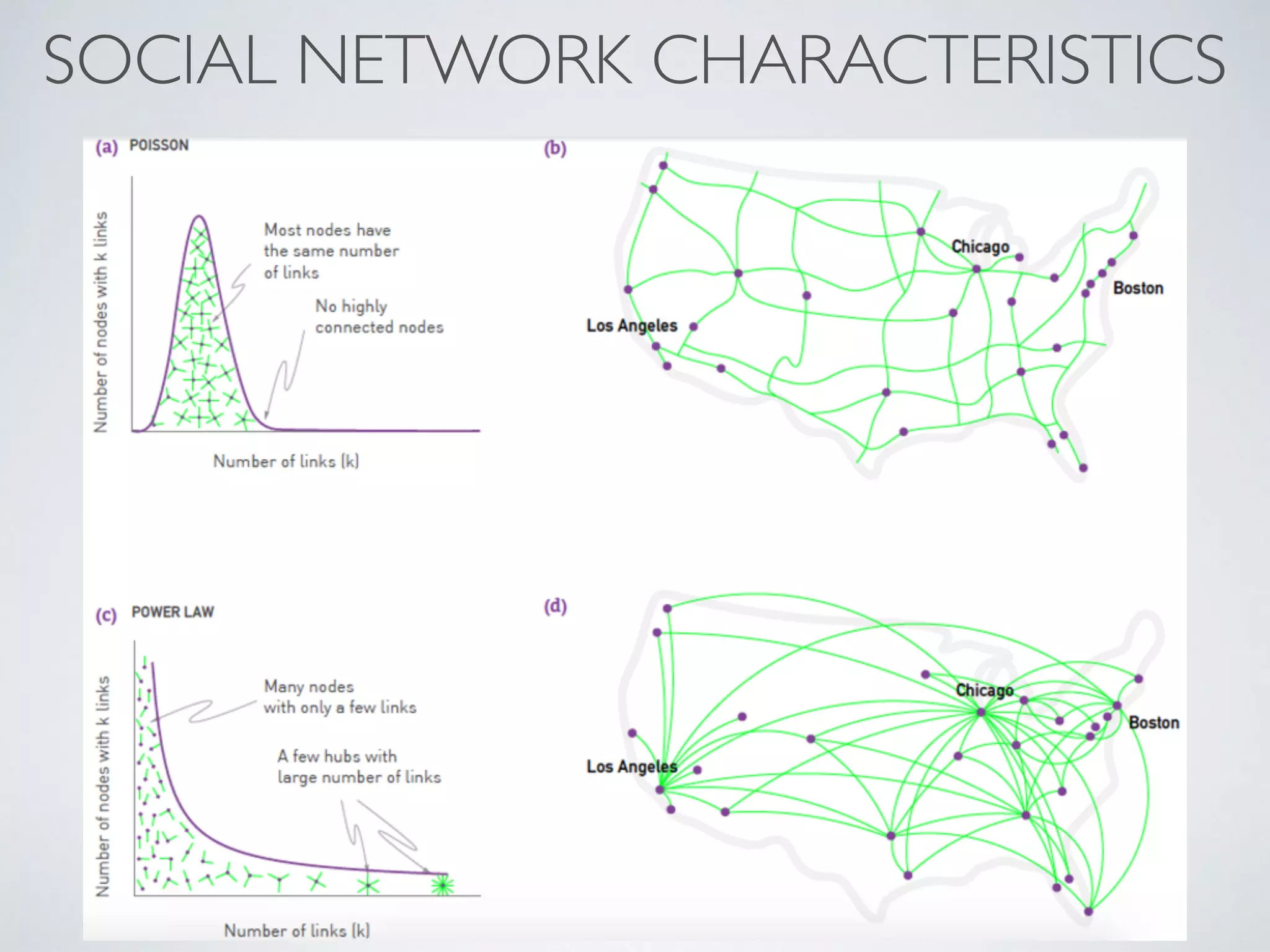
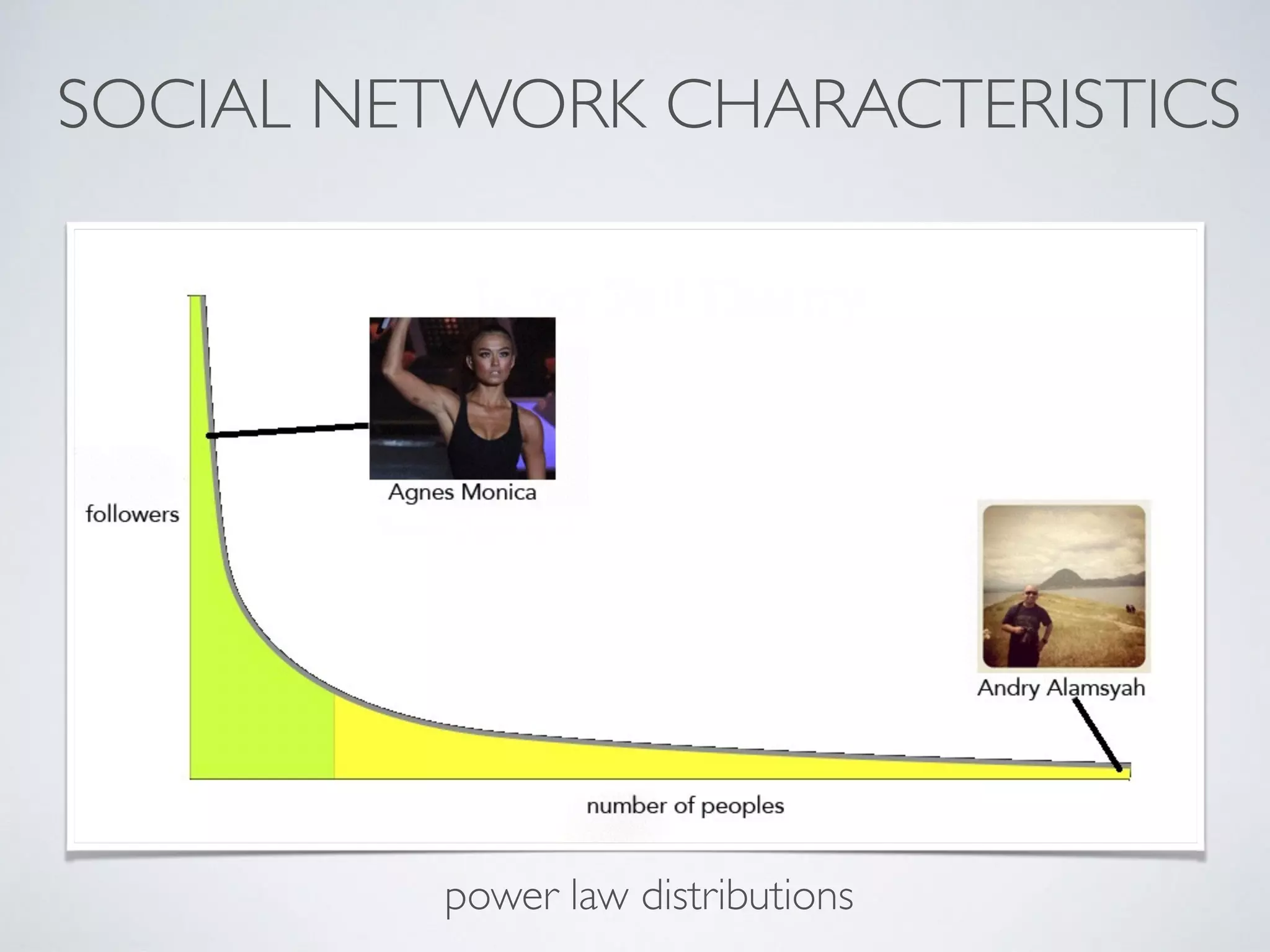
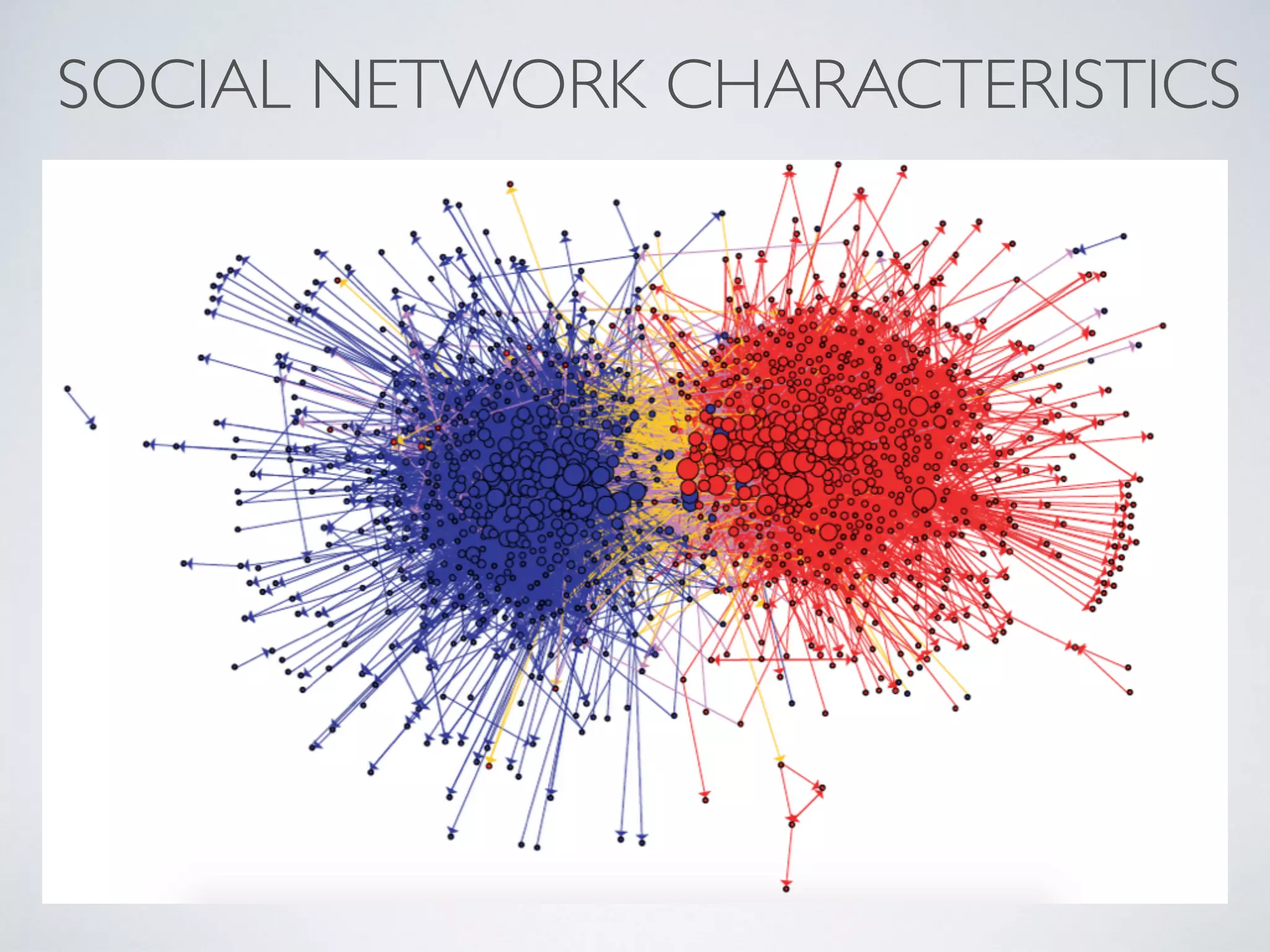
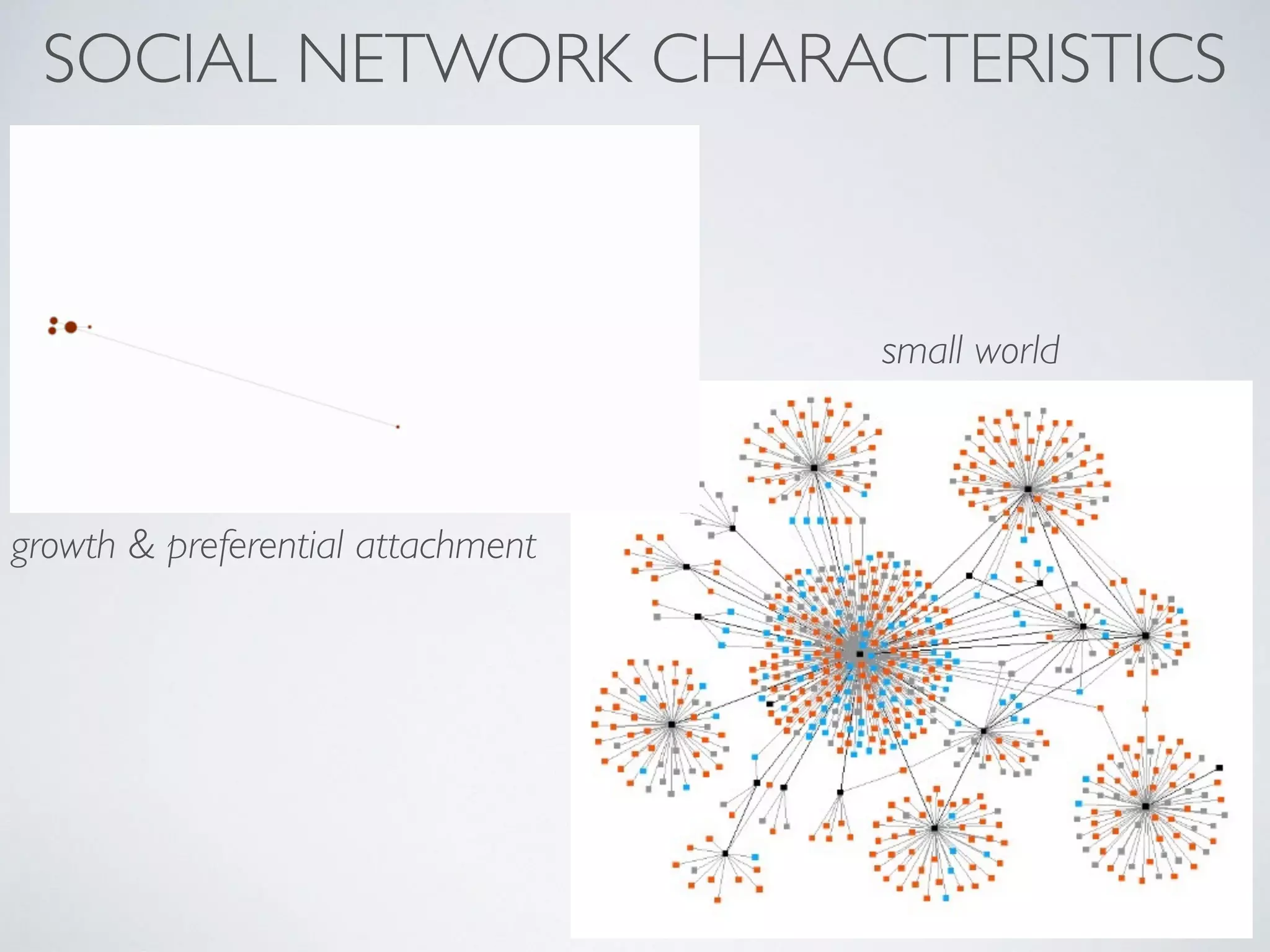
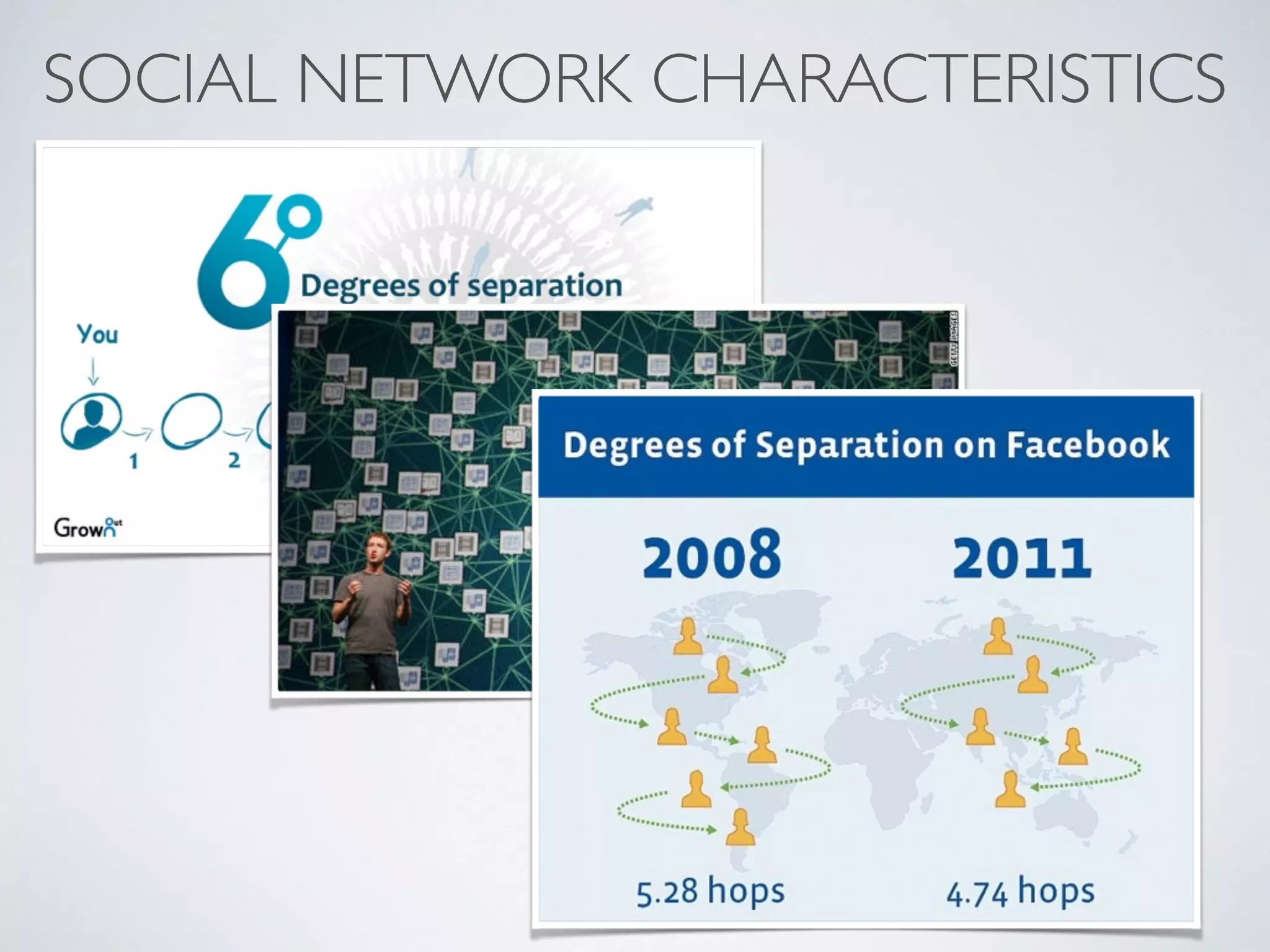
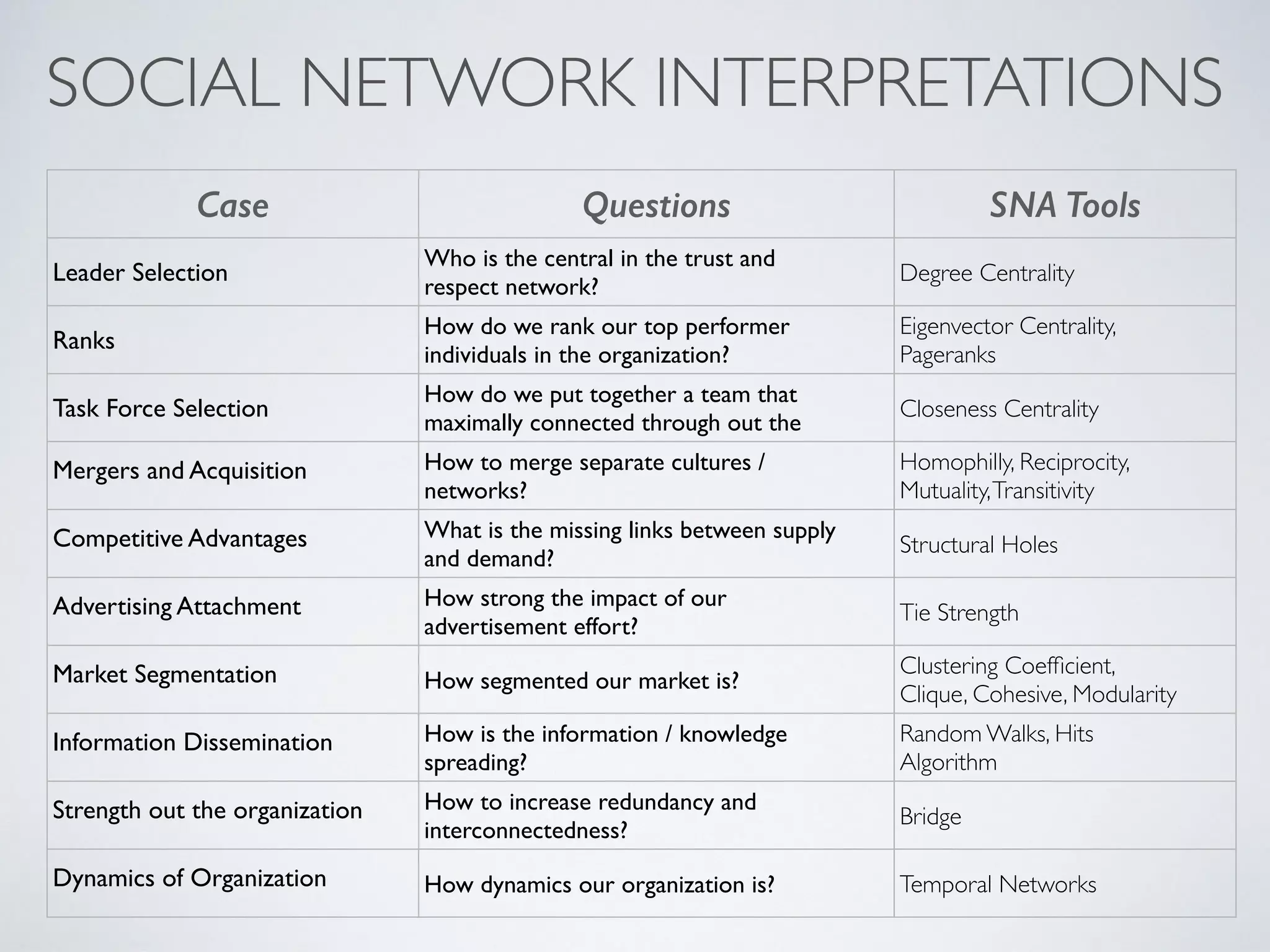
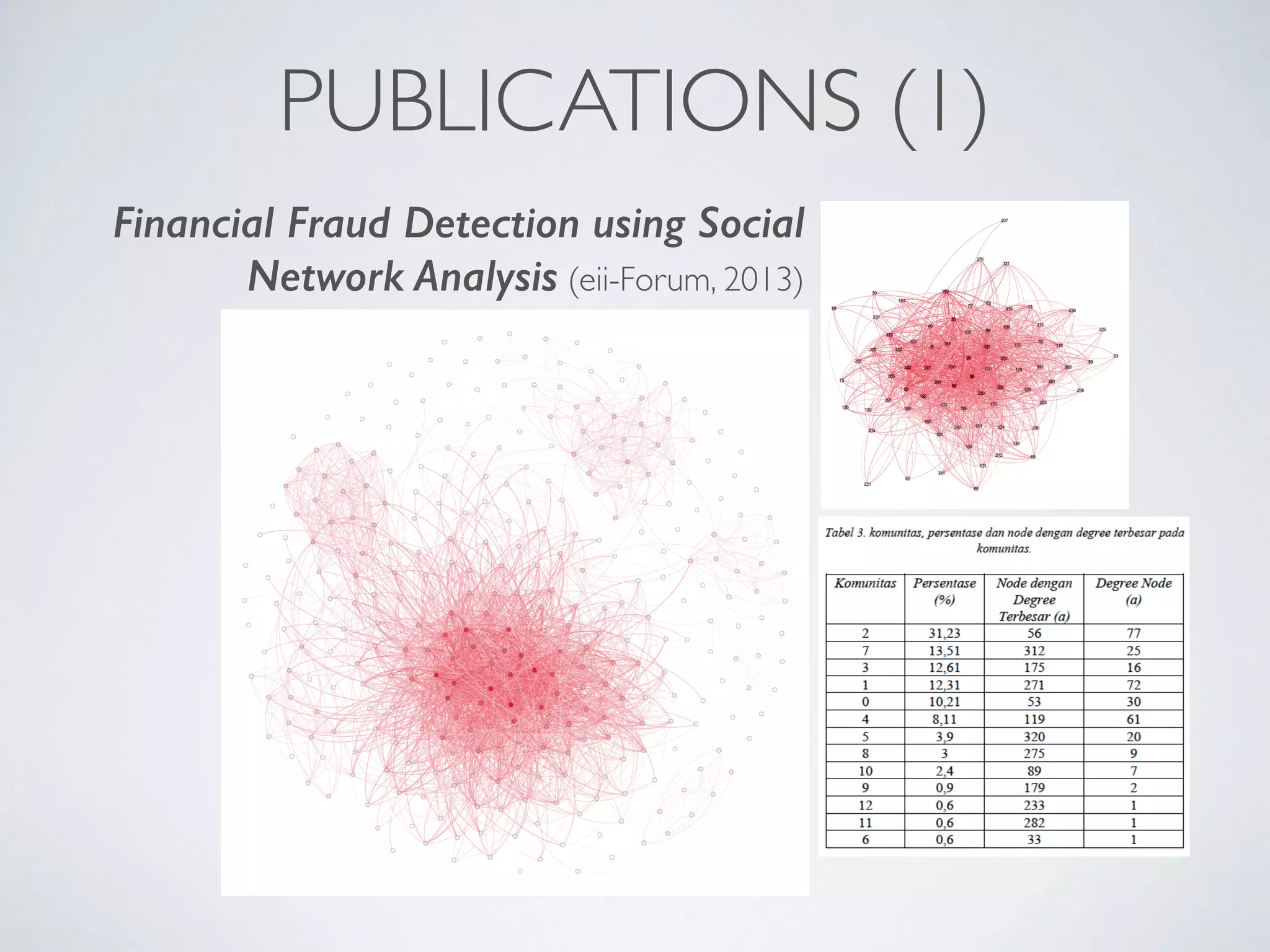
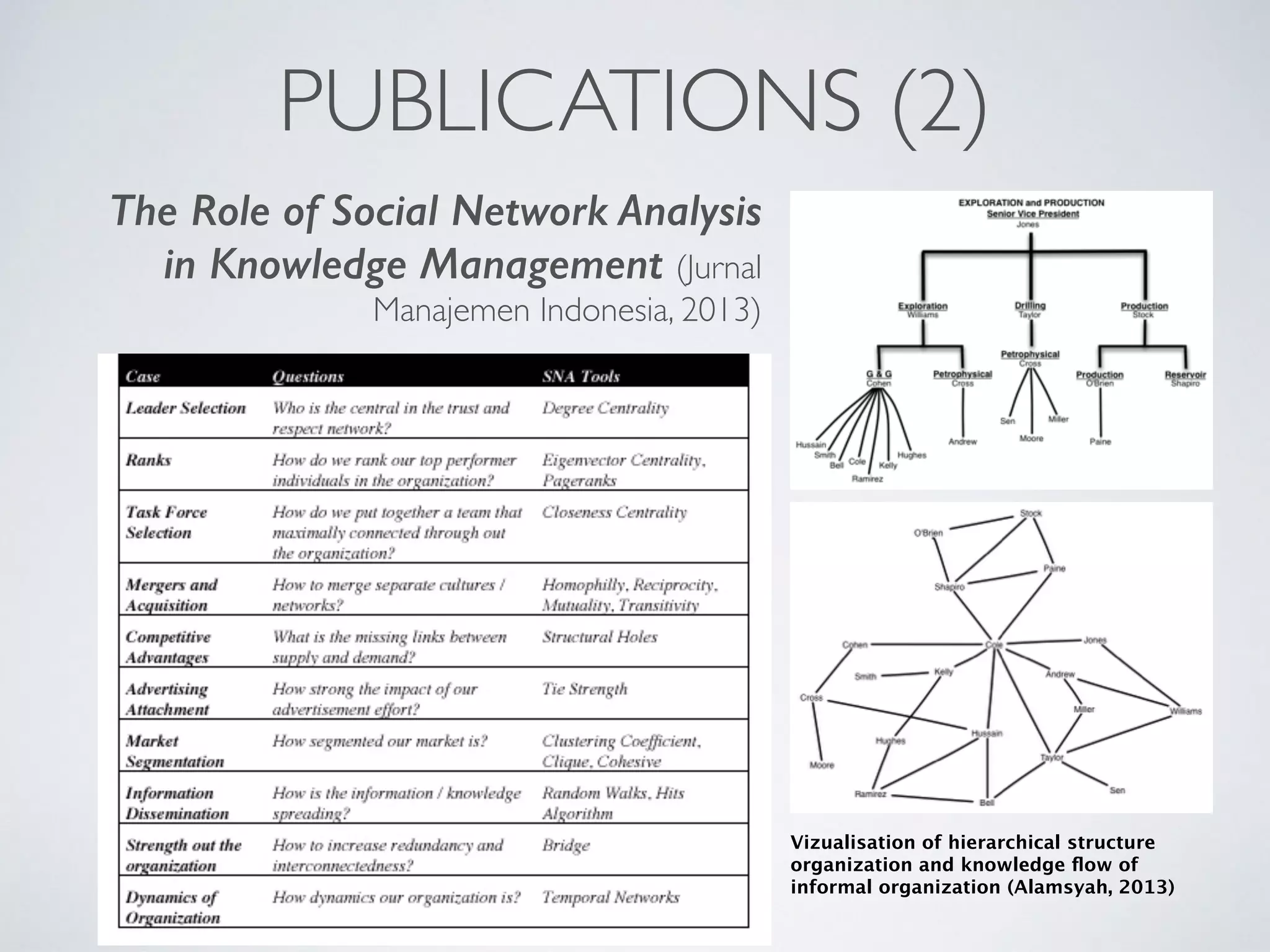
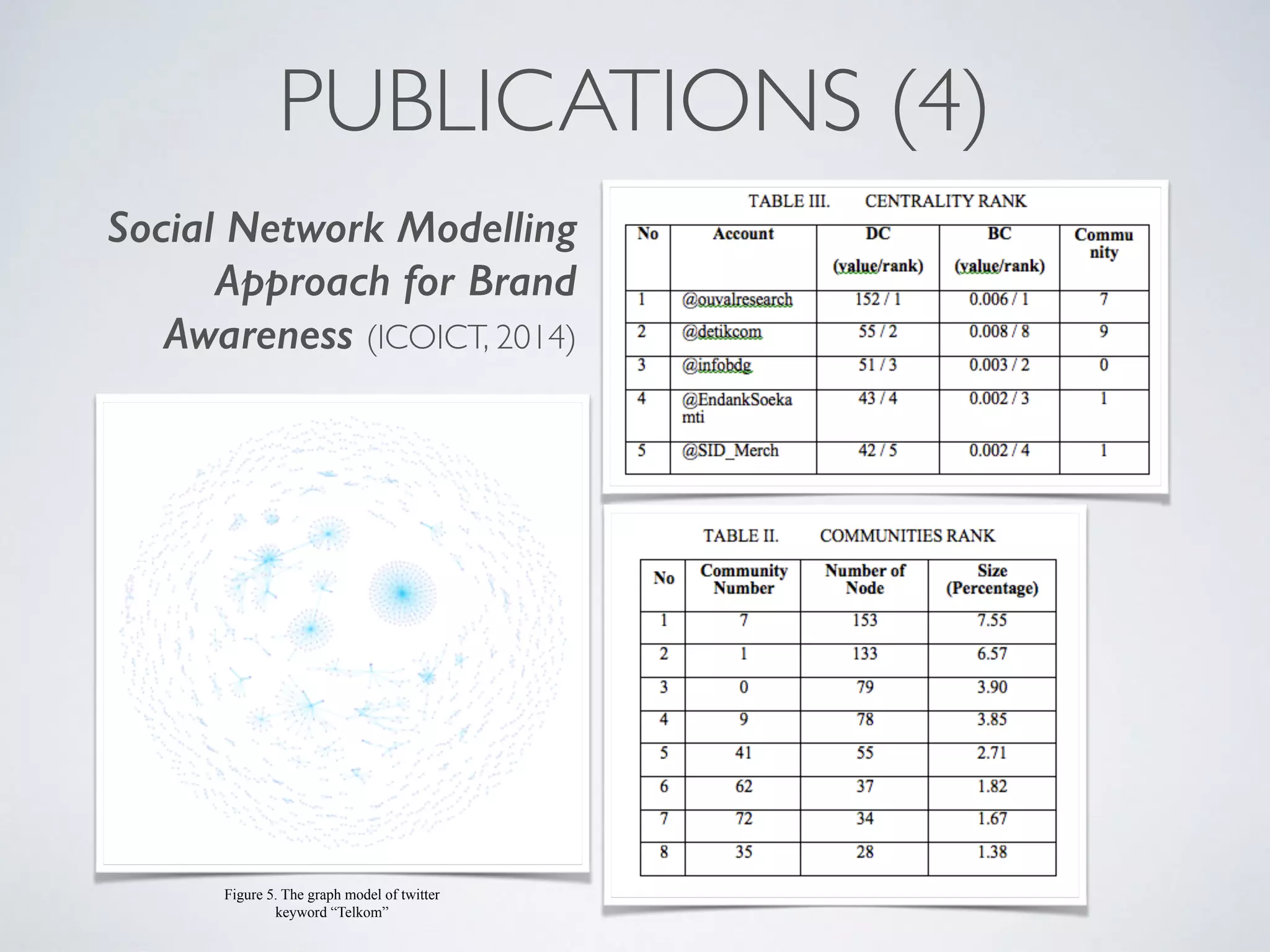
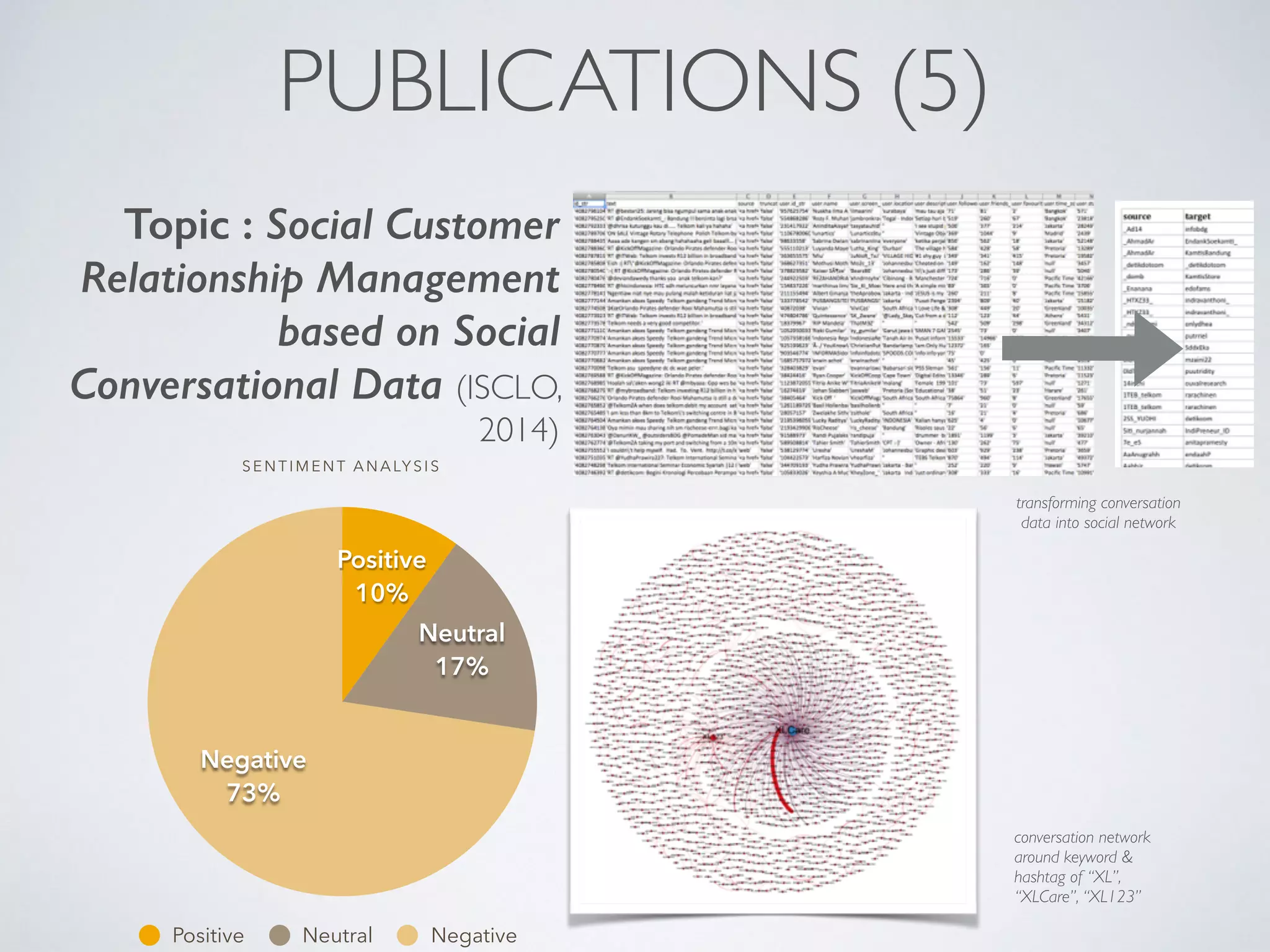
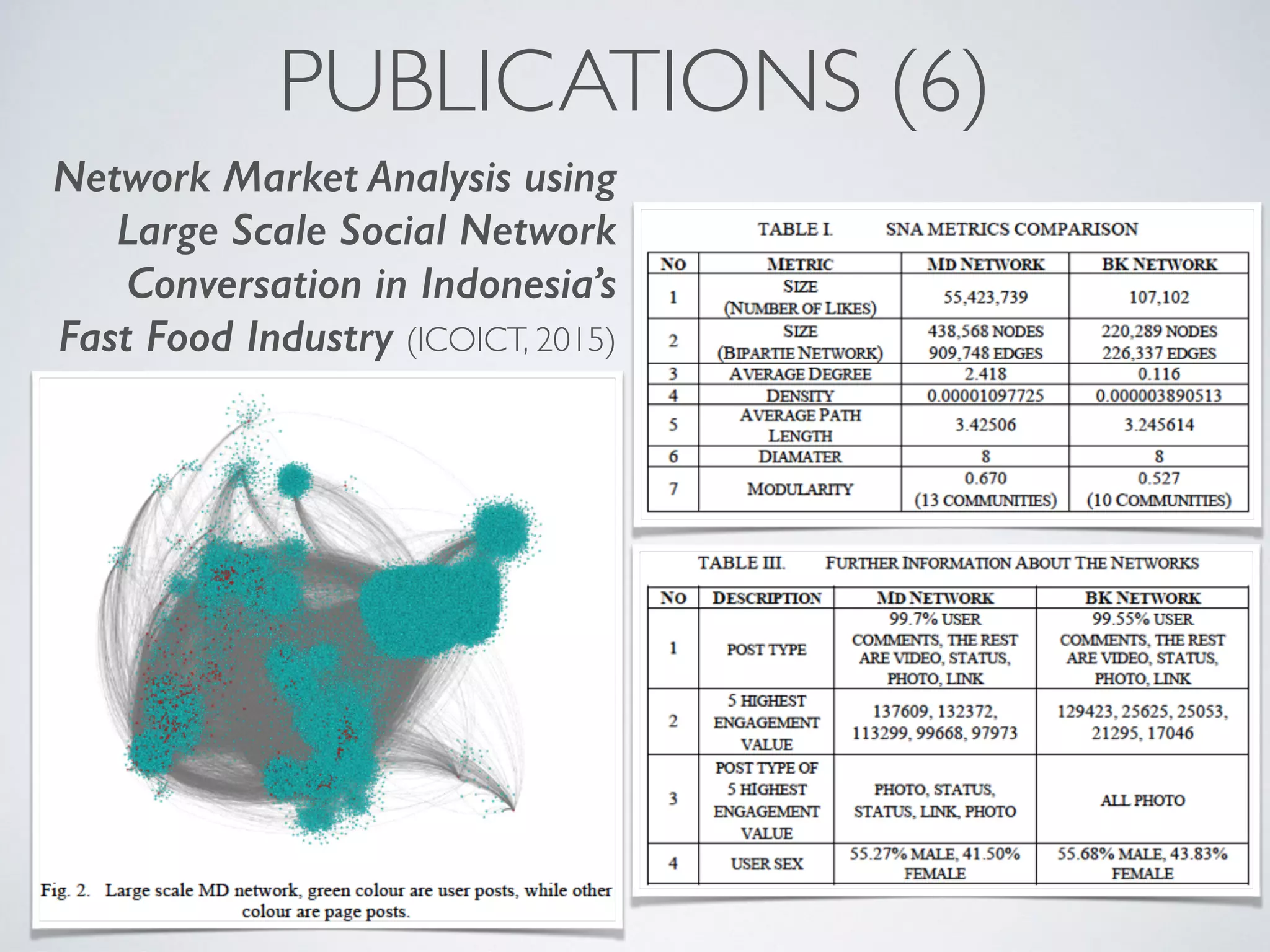
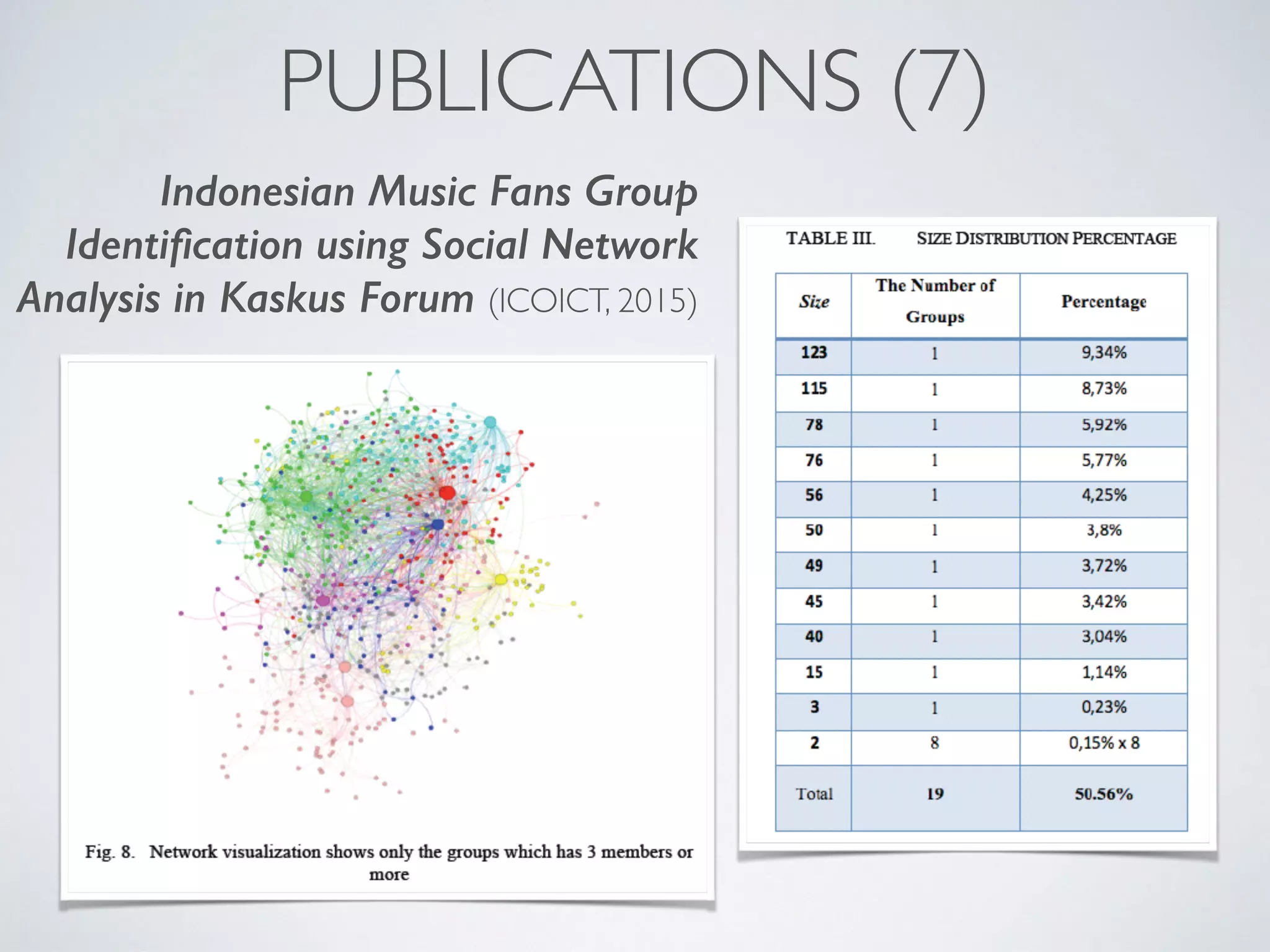
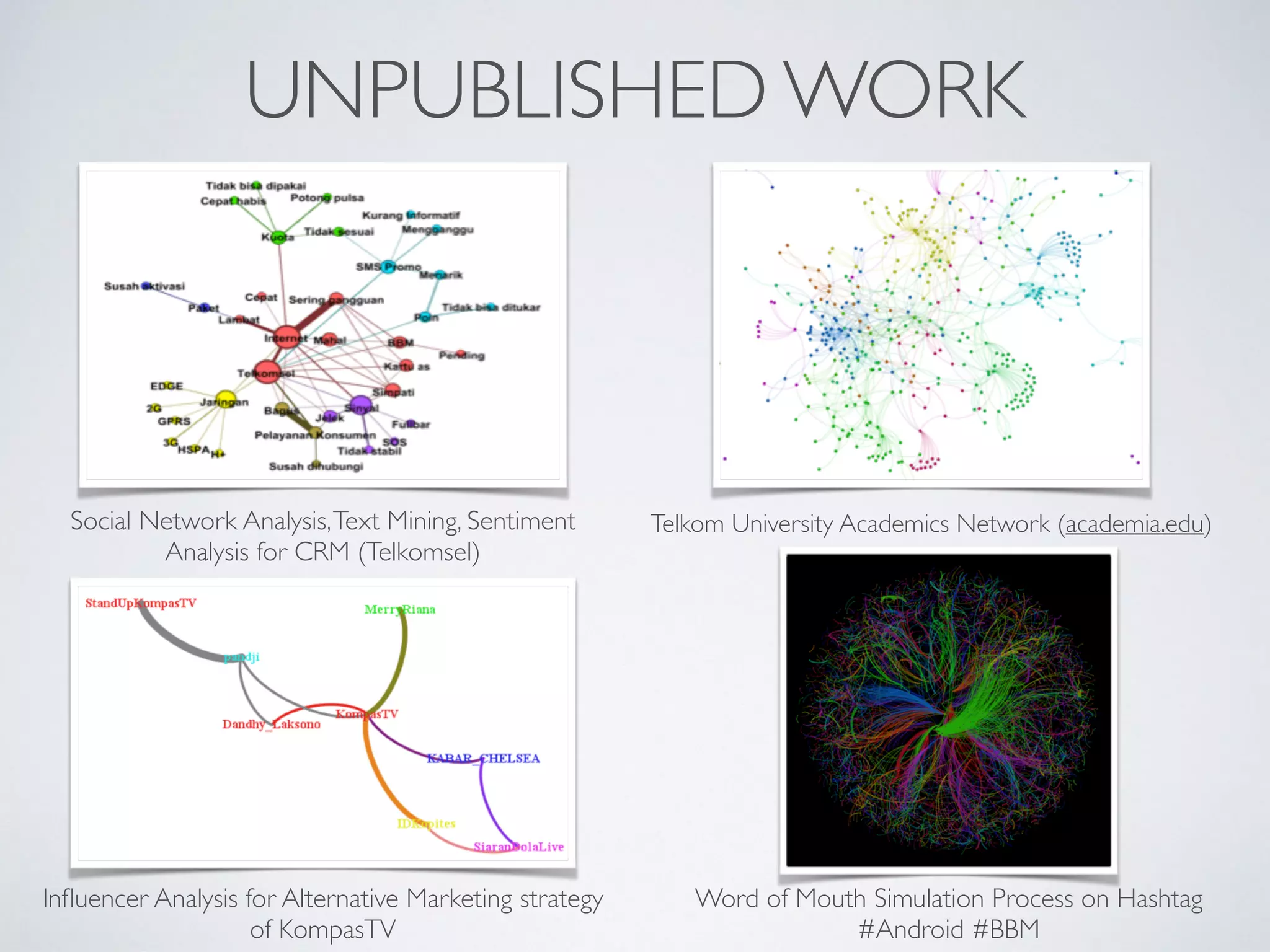
This document discusses using social network analysis approaches for big data analytics. It begins by introducing social network metrics like centrality and modularity that can be applied to large social network datasets. It then provides examples of how social network analysis has been used to detect terrorist cells and identify research communities. Finally, it outlines the author's research interests and publications in areas like sentiment analysis on social media and using social networks to analyze industries.