This document outlines topics in social network analysis presented by Suman Banerjee of IIT Kharagpur. It introduces basics of modeling social networks as graphs and outlines several research issues including community detection, link prediction, opinion dynamics, influence propagation, and stability analysis. It also lists some tools, journals, conferences, and top researchers in the field of social network analysis.









![Introduction
1 Study of Social Entities and Their Relationships.
2 Can be Modeled as a graph.
3 A graph G(V,E) where V= Set of Vertices,E= Set of Edges/
Links.
4 Several E-business application.[1]
Suman Banerjee, Social Network Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sna-160330062350/85/Social-Network-Analysis-10-320.jpg)
![Introduction
1 Study of Social Entities and Their Relationships.
2 Can be Modeled as a graph.
3 A graph G(V,E) where V= Set of Vertices,E= Set of Edges/
Links.
4 Several E-business application.[1]
5 In Social Network [2]V represents Social Entities and there
will be an edge between two Social Entities if they have some
relation which is under consideration.
Suman Banerjee, Social Network Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sna-160330062350/85/Social-Network-Analysis-11-320.jpg)


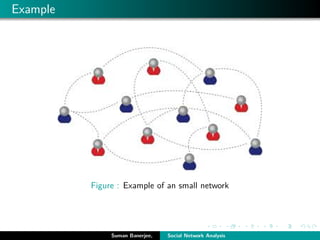

![Community
1 Community[3] is formed by individuals such that those within
a group interact with each other more frequently than with
those outside the group.
a.k.a. group, cluster, cohesive subgroup, module in different
contexts.
2 Community detection means discovering groups in a network
where individuals group membership are not explicitly given.
3 Why communities in social media?
Human beings are social.
Easy-to-use social media allows people to extend their social
life in unprecedented ways.
Difficult to meet friends in the physical world, but much easier
to find friend online with similar interests.
Interactions between nodes can help determine communities.
Suman Banerjee, Social Network Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sna-160330062350/85/Social-Network-Analysis-17-320.jpg)
![Community Detection
1 An old research problem for SNA research.
2 Different algorithms exist.
Sprectal Bisection Method.
Graph Partitioning Method.
3 A Modularity function is maximized. [4]
Q = 1/2m n
i,j(Aij − ki.kj/2.m)δ(i, j)
n= no. of nodes of the network.
m= no. of edges of the network.
A= Adjacency matrix of the network.
δ(i, j) = (i, j) th entry of the matrix A.
Suman Banerjee, Social Network Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sna-160330062350/85/Social-Network-Analysis-18-320.jpg)
![Contd . . . .
1 Maximum modularity value means better community
structure. [5]
2 Degree matrix of a graph is a diagonal matrix.
D = (deg1, deg2, deg3, ....., degn)
3 Graph Laplacian can be defined as
L = D − A
4 Graph Laplacian can also be considered.
Suman Banerjee, Social Network Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sna-160330062350/85/Social-Network-Analysis-19-320.jpg)
![Contd . . . .
1 Different meaning in different networks.
2 In friendship network community means friends with strong
communication.
3 In a collaboration network a community means researchers
working almost similar topics.
4 In a citation network a community signifies papers of almost
similar topics.
5 Product- Customer Network.[6, 7]
Suman Banerjee, Social Network Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sna-160330062350/85/Social-Network-Analysis-20-320.jpg)
![Link prediction
1 Given a social network at time ti predict the social link
[8]between actors at time ti+1.
2 Given a social network with an incomplete set of social links
between a complete set of actors, predict the unobserved
social links.
3 Given information about actors, predict the social link between
them (this is quite similar to social network extraction).
4 Links are Dynamic in nature.[9]
5 Considers a score function Score(u , v).
Suman Banerjee, Social Network Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sna-160330062350/85/Social-Network-Analysis-21-320.jpg)
![Opinion Formation
1 How users update opinions based on their neighbors opinions.
2 Well studied problem in SNA research.
3 Use an Opinion matrix.[10]
4 Opinion is iteratively updated by
Xi(t + 1) = Wi1X1(t) + Wi2X2(t) + ..... + WikXk(t)
Suman Banerjee, Social Network Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sna-160330062350/85/Social-Network-Analysis-22-320.jpg)
![Influence Propagation
1 Sub work of the previous one. [11]
2 Topical Affinity Propagation (TAP) is used for modeling.[10]
3 Characterization of dynamicity of a networks.
4 Vector based modeling is used.
5 Considers weighted network. Influence from node s to node t
is µst.
6 Considers three following function:
Node feature function.
Edge feature function.
Global feature function.
Suman Banerjee, Social Network Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sna-160330062350/85/Social-Network-Analysis-23-320.jpg)
![Stability Analysis
1 Real world networks are unstable in nature. [13]
2 Analyzing group stability is an important job.
3 Communities may evolve or shrink by influence propagation.
4 Threshold model techniques are used.
5 Some probabilistic models are required like markov chain etc.
Suman Banerjee, Social Network Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sna-160330062350/85/Social-Network-Analysis-24-320.jpg)
![Application of SC in SNA Research
1 Several algorithms exist for different problems .
2 Most of them run in Polynomial time.
3 Still, for large networks computational time is high.
4 Apply SC techniques to get approximate solution.
5 GDPSO, DE for community detection is already exist.[14]
6 ACO was used for link prediction problem. [15]
Suman Banerjee, Social Network Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sna-160330062350/85/Social-Network-Analysis-25-320.jpg)



![10 Conferences of SNA Research
1 European Conference on Social Media.
2 IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence.
3 International Conference on Social Network Analysis and
Mining.
4 ACM Conference on Online Social Networks.
5 International Conference on Web and Social Media.
6 International Conference on Social Computing and Social
Media.
7 International Conference on Computational Aspects of Social
Networks.
8 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence. [AAAI]
9 International Conference on Computational and Social
Sciences.
10 International Conference on Social Informatics.
Suman Banerjee, Social Network Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sna-160330062350/85/Social-Network-Analysis-29-320.jpg)


![Top 10 Cited Papers
1 L Page, S. Brin, R Motwani and T Winogard, ”The Page
Rank citation ranking: bringing order to the Web”, Stanford
InfoLab Technical report, 1999. [Cited by 8504]
2 N. B. Ellison, C. Steinfield, C. Lampe,” The Benefits of Face
book Friends: Social Capital and College Students Use of
Online Social Network Sites”, Vol. 12, Issue 4, 2007. [Cited
by 5319]
3 J. E. Hirsch, ”An index to quantify an individual’s scientific
research output.”, Proceedings of the National Academy of
Sciences, Vol. 102, No. 46, 2010. [Cited by 5081]
4 M. E. J Newman, ”The structure of scientific collaboration
networks”, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,
Vol. 98, No. 2, 2006. [Cited by 3455]
Suman Banerjee, Social Network Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sna-160330062350/85/Social-Network-Analysis-32-320.jpg)
![Top 10 Cited Papers
1 N. M. Tichy, M. L. Tushman and C. Fombrun, ”Social
Network Analysis For Organizations”,Academy of
management review, Vol. 4, No. 4, 1979. [Cited by 1136]
2 M. E. J. Newman,”Coauthorship networks and patterns of
scientific collaboration”, Proceedings of the National Academy
of Sciences, Vol. 101, No. 1, 2004.[Cited by 1106]
3 Eszter Hargittai,”Whose Space? Differences Among Users and
Non-Users of Social Network Sites” Journal of Computer-
Mediated Communication, Vol 13, pp 276-297, 2008.[Cited by
992]
4 M. E. J. Newman, D. J. Watts, and S. H. Strogatz,”Random
graph models of social networks”, Proceedings of the National
Academy of Sciences, Vol. 99, No. 1, 2002.[Cited 954]
Suman Banerjee, Social Network Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sna-160330062350/85/Social-Network-Analysis-33-320.jpg)
![Top 10 Cited Papers
1 H Small,”Visualizing science by citation mapping”, Journal of
the American society for Information Science, Vol. 50, No. 9,
pp 799 - 813,1999. [Cited by 692].
2 Hugo Liu,”Social Network Profiles as Taste Performances”,
Journal of Computer Mediated communication, Vol. 13, pp
252-275, 2008. [cited by 345]
Suman Banerjee, Social Network Analysis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sna-160330062350/85/Social-Network-Analysis-34-320.jpg)







