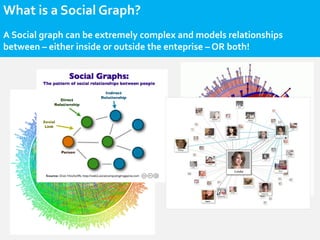
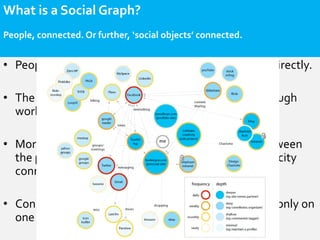
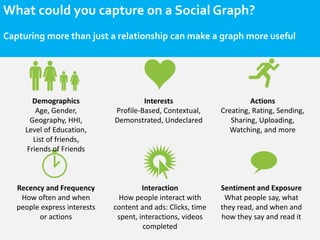
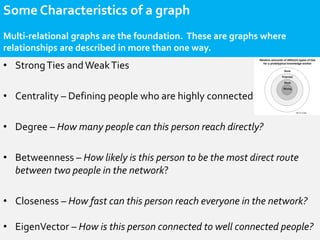
- Social network analysis uses social graph constructs to understand user behavior, recommendations, and influence. A social graph models relationships between connected social objects like people, interests, and actions. Characteristics of social graphs include strong and weak ties, centrality, degree, betweenness, and closeness. Social graphs can be used for recommendation engines, interest graphs, influence networks, sentiment analysis, and searching, scoring, and ranking. The use of social graphs in marketing is still nascent but will change how marketing is done in the future.