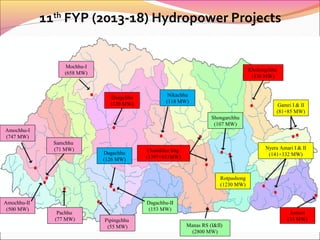
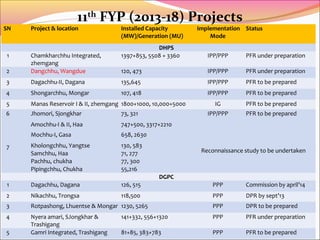
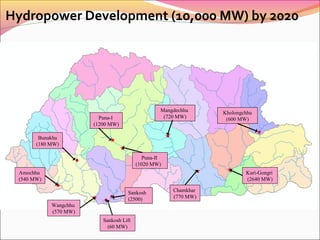
This document summarizes Bhutan's energy sector, including its goals and initiatives to achieve universal energy access, energy efficiency, and increased use of renewable energy as part of its commitments under SE4ALL. It outlines Bhutan's institutional arrangements and existing energy policies, then discusses the country's progress toward each of the three SE4ALL goals. Challenges are presented, such as a lack of legal frameworks and institutional capacity for renewable energy and energy efficiency. Investment opportunities are mentioned, primarily in ongoing studies and hydropower projects planned for implementation under public-private partnerships.