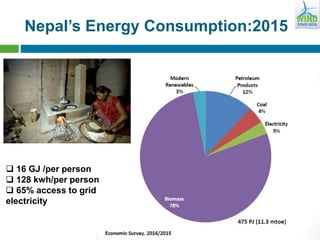
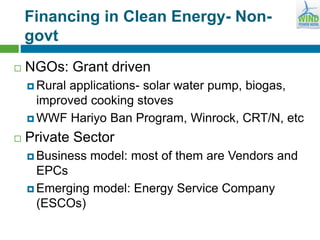
Nepal has significant potential for renewable energy, with 83,000 MW from hydro, 2,100 MW from solar, and 3,000 MW from wind. The government is pursuing various initiatives for clean energy financing, including subsidies and technical assistance, to support both on-grid and off-grid projects. Key challenges include unclear policies for renewables other than hydro, limited access to financing, and a growing demand for electricity amidst an annual growth rate of 10%.