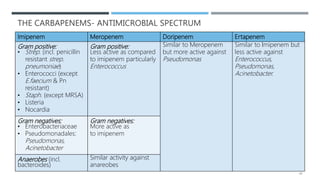
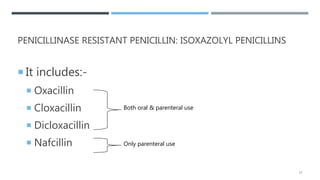
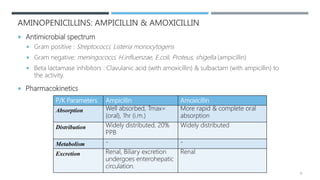
Beta lactam antibiotics include penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, and monobactams. They share a common beta lactam ring structure and inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis. Penicillins are classified based on their antimicrobial spectra. They are effective against gram-positive bacteria by inhibiting the last step of peptidoglycan synthesis. Bacteria develop resistance through beta-lactamases or modifying penicillin binding proteins. Common penicillins include benzylpenicillin, phenoxymethylpenicillin, aminopenicillins, antipseudomonal penicillins, and isoxazolyl penicillins. They are used to treat various bacterial infections.



![BACTERIAL CELL WALL SYNTHESIS & MECHANISM OF ACTION OF
BETA LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS
Cytoplas
m
• Synthesis of Aminosugars: N-acetyl-glucosamine (NAG) & N-acetyl-muramic
(NAM)
• Addition of pentapeptide to NAM
• Formation peptidoglycan precursor [NAG-NAM(pentapeptide)]
Periplasm
• Elongation of peptidoglycan chain (transglycosylation)
•
• Cross linking of peptide chain (transpeptidation)
Beta Lactams
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/betalactamantibiotics-200805043144/85/Beta-lactam-antibiotics-4-320.jpg)



















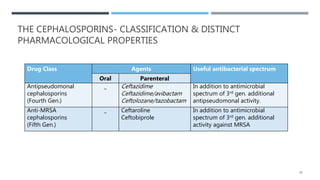





![THE CEPHALOSPORIN- THIRD GENERATION
Specific Agents
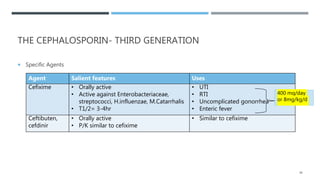
Agent Salient features Uses
Cefotaxime • Good activity against
gr+ve & gr-ve aerobic
organisms
• T1/2= 1hr
• Concentration in CSF if
good
• Community acquired pneumonia (serious infection)
[2 g IV q4-8hr]
• Bacterial meningitis [50 to 180 mg/kg IM or IV q4-
6h]
• Gonococcal urethritis, cervicitis, rectal gonorrhoea
[0.5/1.0 g IM once]
Ceftriaxone • Antibacterial activity
similar to cefotaxime
• Long T1/2= 8hr
• Both renal & biliary
excretion
• Gonococcal urethritis, cervicitis, rectal gonorrhoea
[250 mg IM once]
• Bacterial meningitis [1-2 g IV q12hr]
• Community acquired pneumonia (serious infection)
[1-2 g IV q12hr]
• UTI [1-2 g IV q12hr]
• Enteric fever [2 g IV q12hr]
36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/betalactamantibiotics-200805043144/85/Beta-lactam-antibiotics-36-320.jpg)
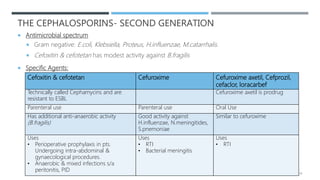
![THE CEPHALOSPORIN- THIRD GENERATION
Specific Agents
Agent Salient features Uses
Ceftizoxime • Antibacterial activity similar to
cefotaxime
• Less active against S.pneumoniae
• More active against B.fragilis
• T1/2= 1.8hr
• Similar to cefotaxime
Cefpodoxime
proxetil,
cefditoren
pivoxil
• Prodrug
• Orally active
• Activity against streptococci,
H.influenzae & M.catarrhalis similar to
cefotaxime
• Respiratory tract infection [100-
200 mg or 5mg/kg/dose PO q12h]
• Uncomplicated skin & soft tissue
infection
37](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/betalactamantibiotics-200805043144/85/Beta-lactam-antibiotics-37-320.jpg)