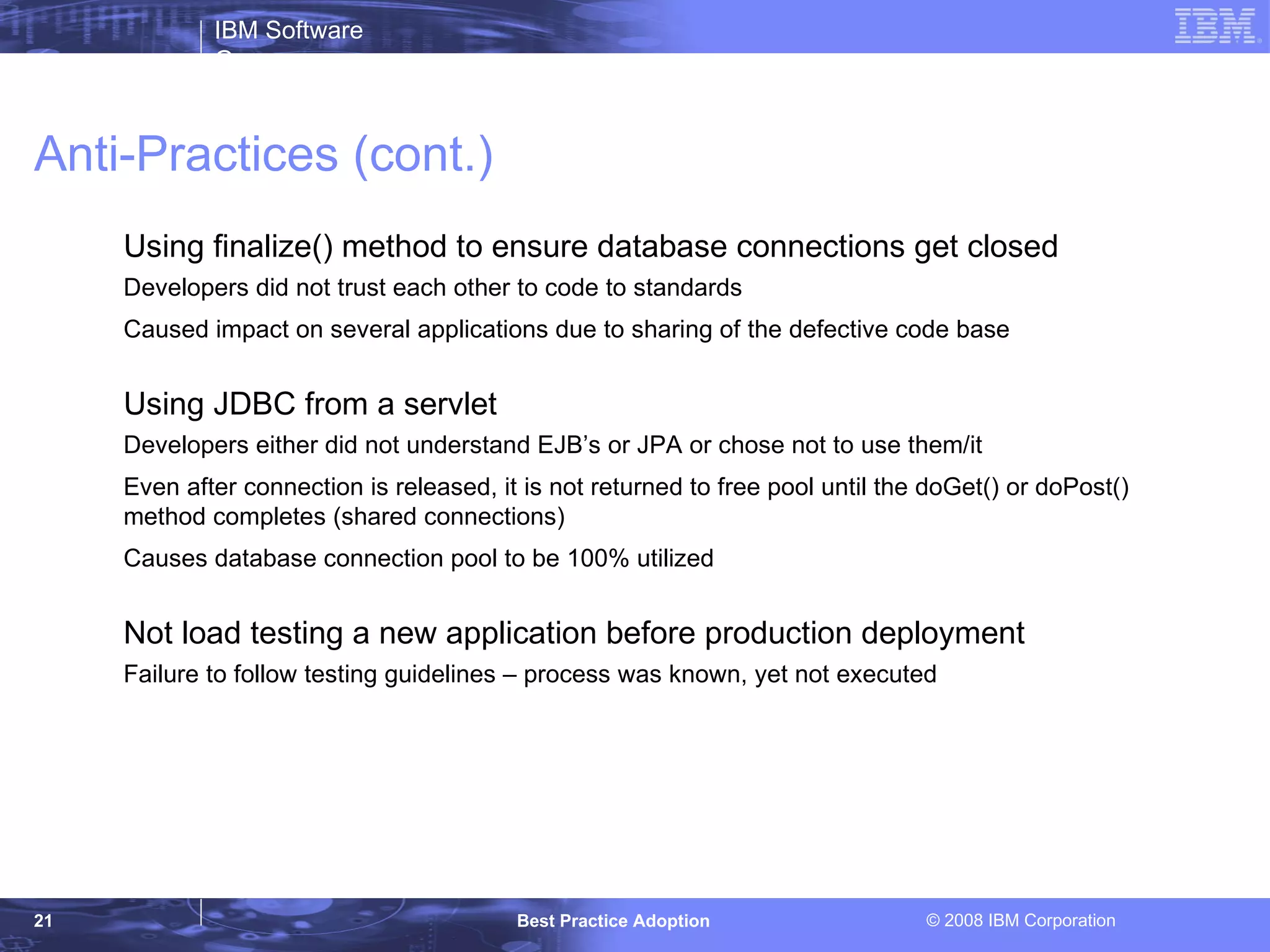
The document outlines best practices in application development and infrastructure management, emphasizing the importance of using effective techniques to improve efficiency and reduce rework. It covers various aspects including stateless application design, automation in infrastructure, and the importance of adhering to industry standards and proven design patterns. Additionally, it identifies common anti-practices and inefficiencies that can lead to significant operational issues.