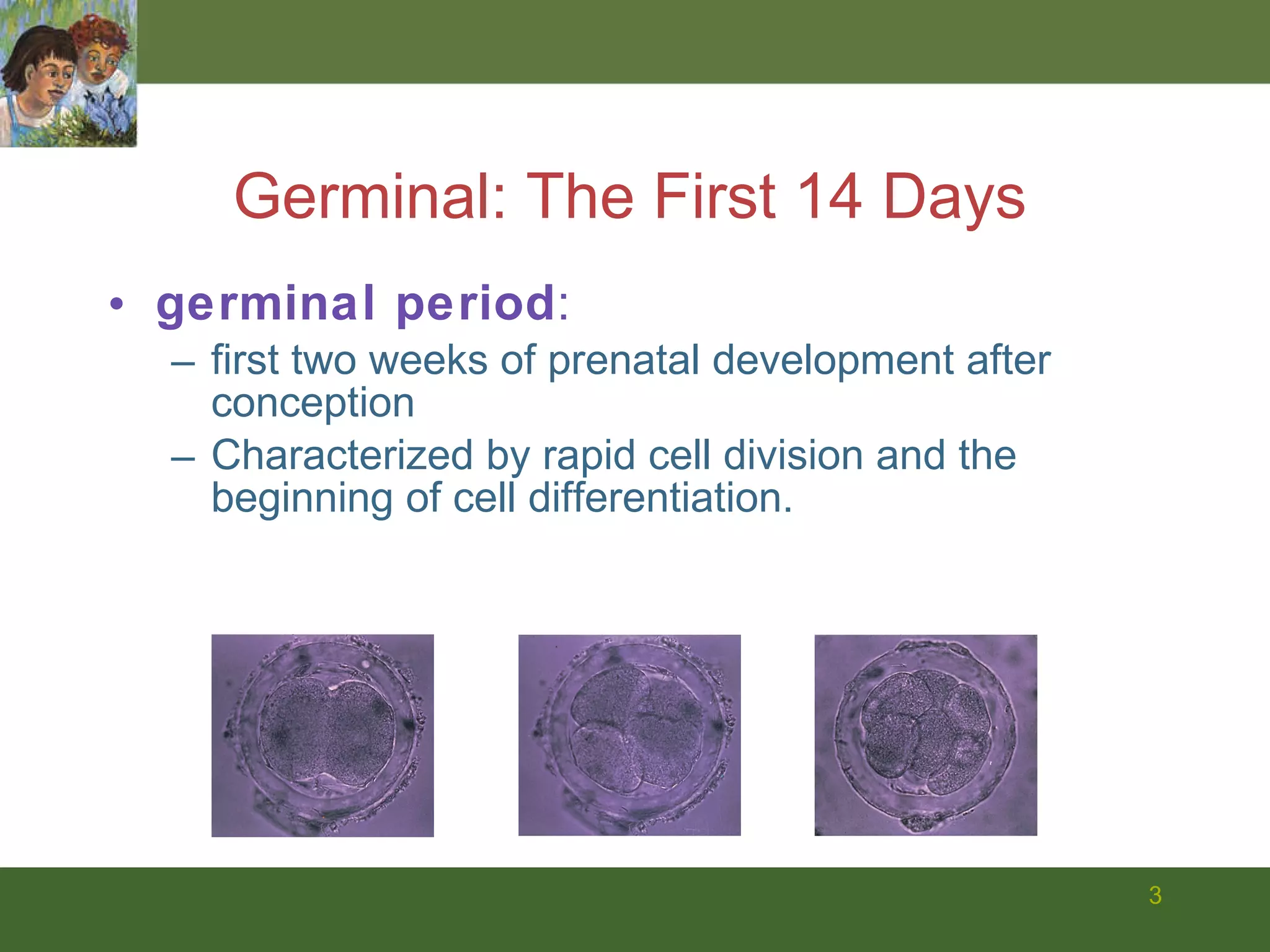
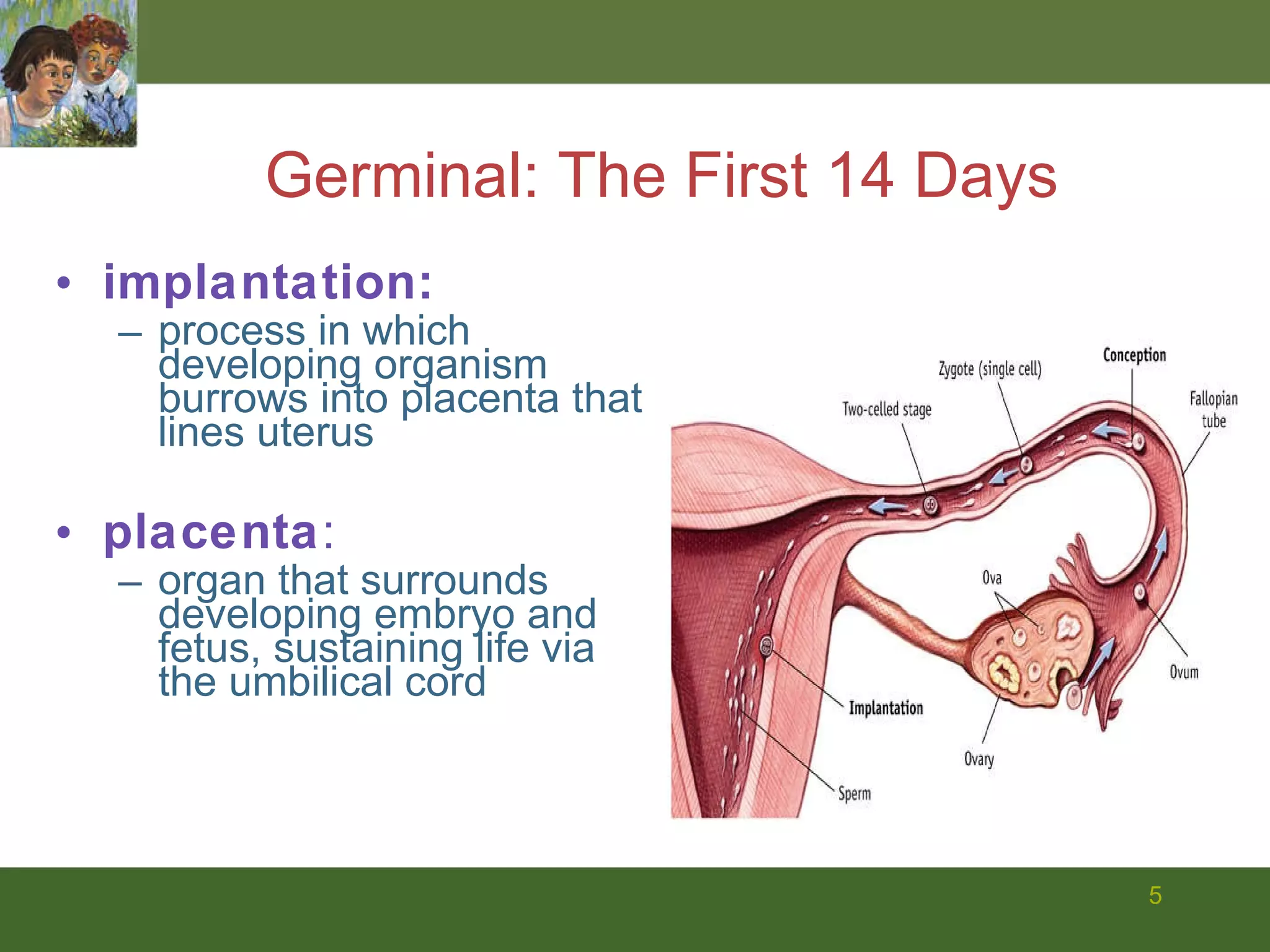
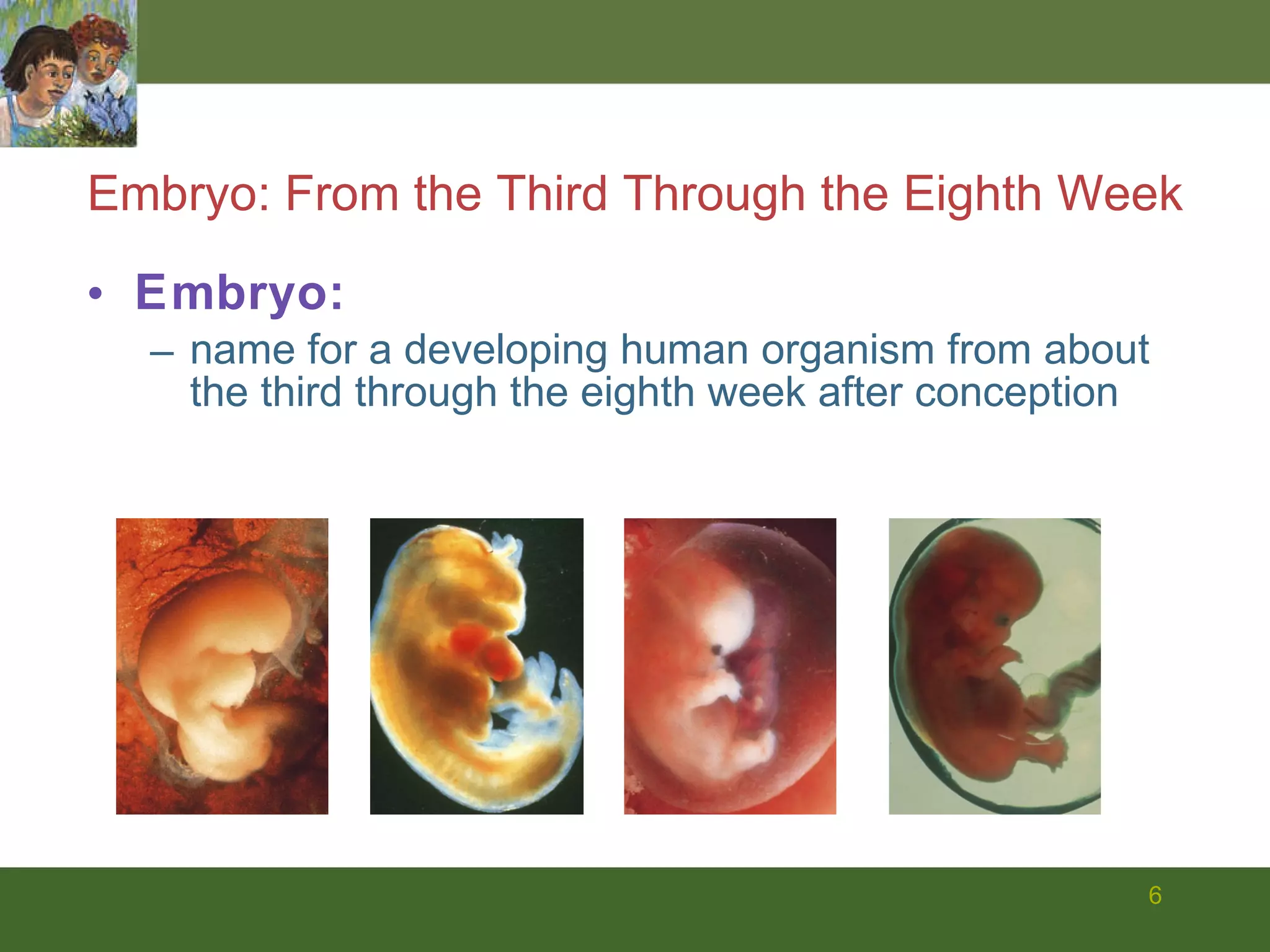
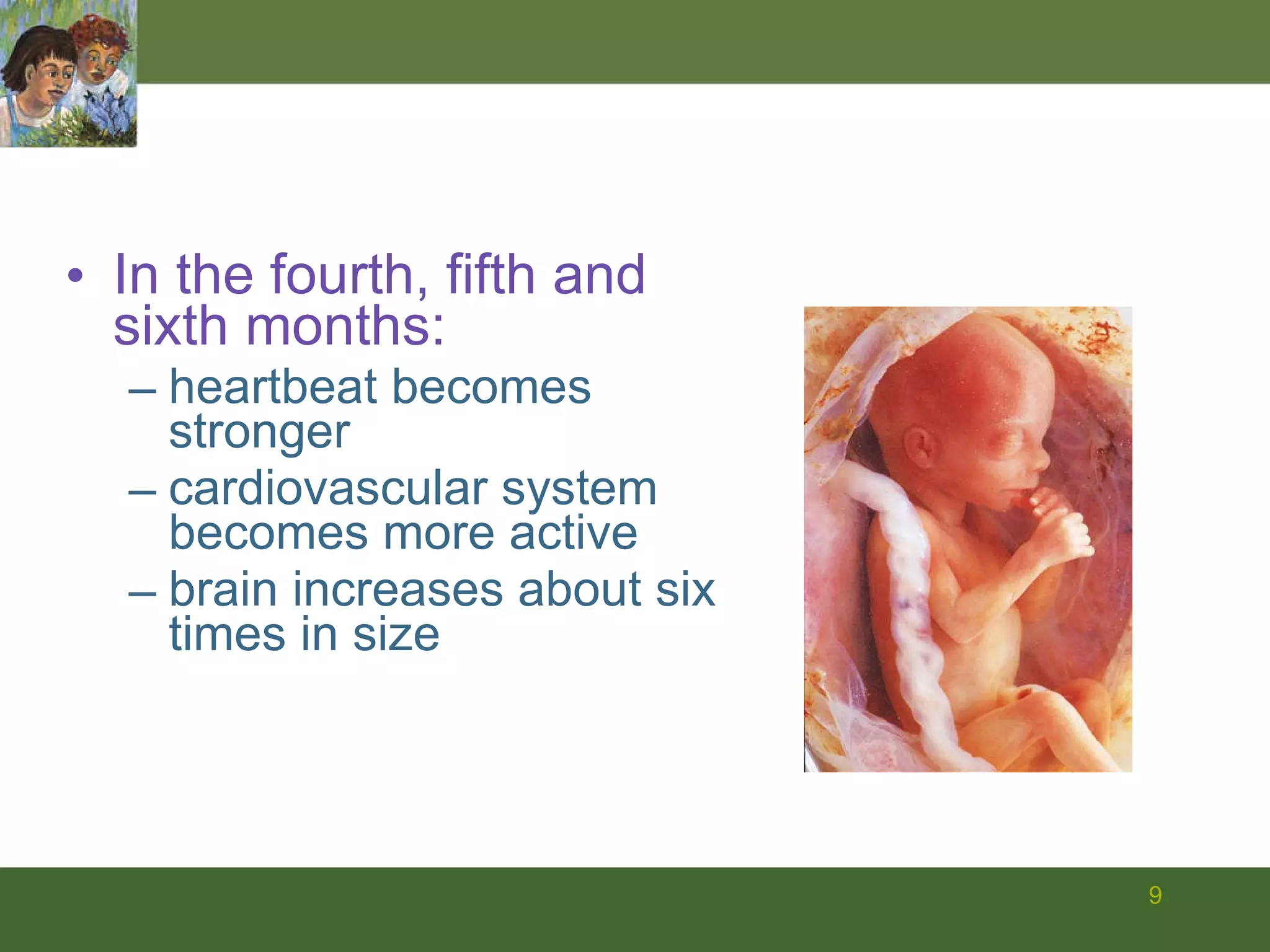
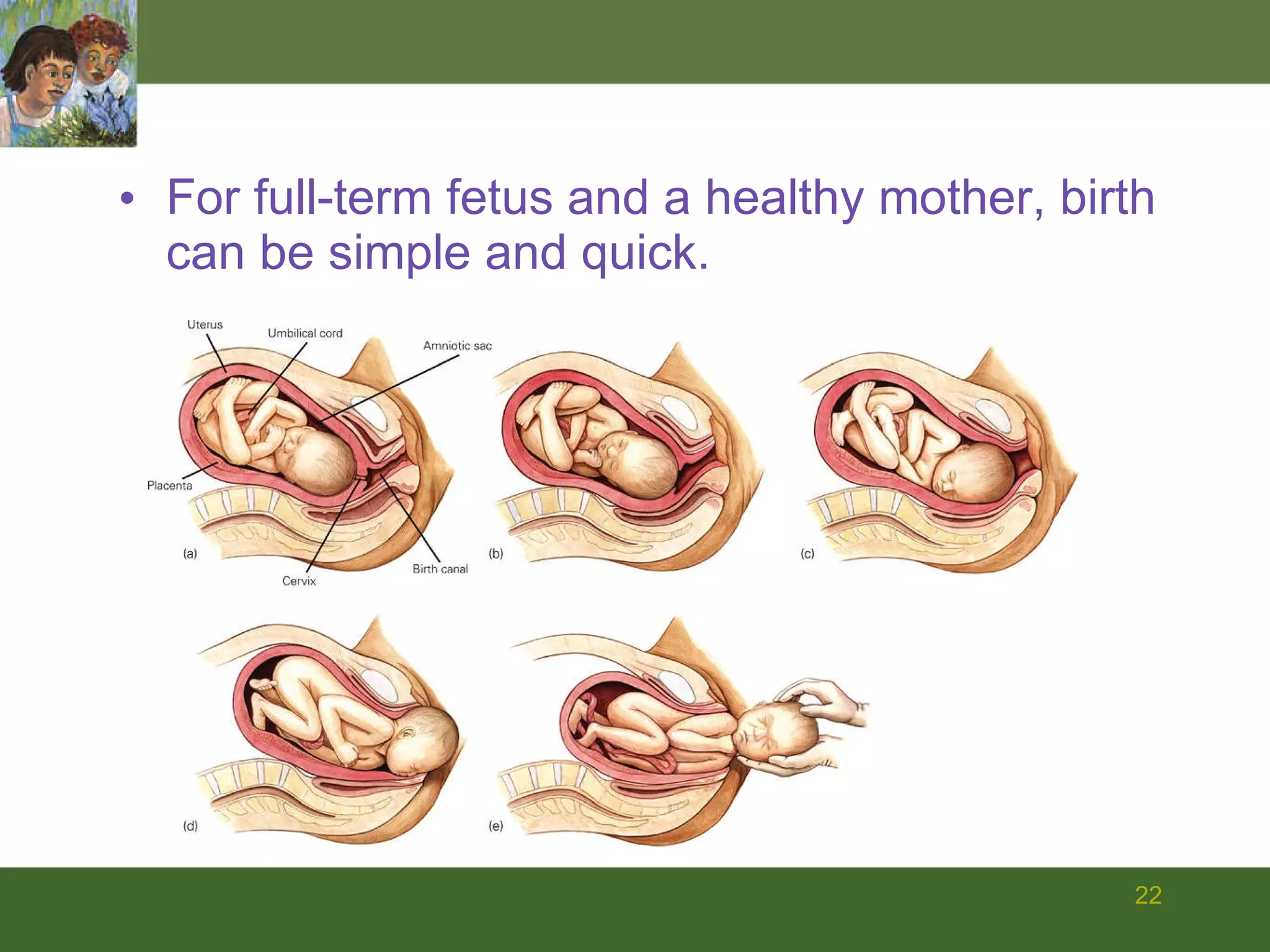
The document summarizes prenatal development from conception through birth. It describes the germinal, embryonic, and fetal periods and key developmental milestones. Risks to the developing fetus from genetic factors, environmental teratogens, and birth complications are discussed. The challenges of preterm birth and low birthweight are also covered.