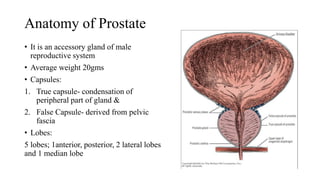
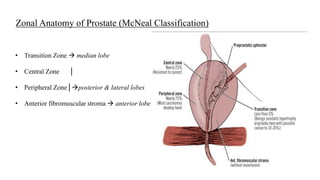
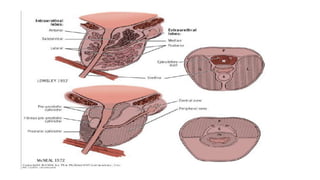
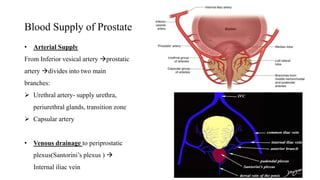
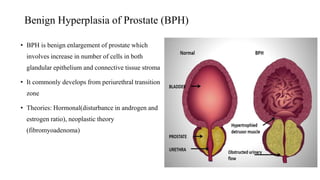
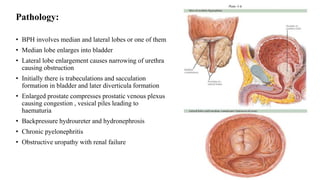
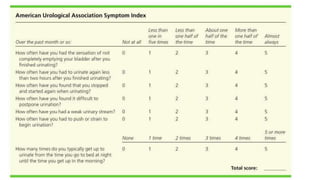
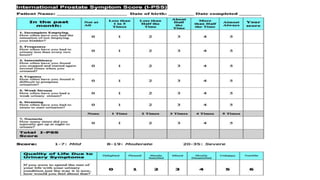
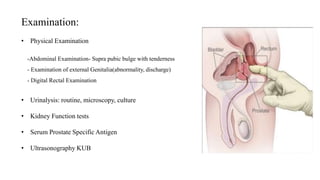
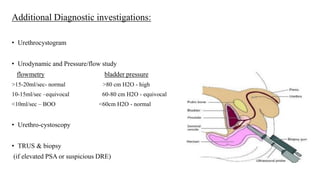
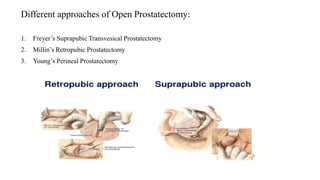
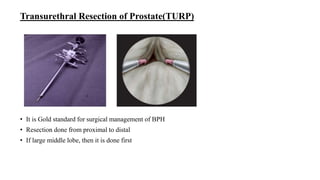
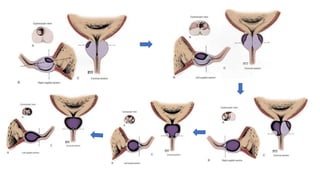
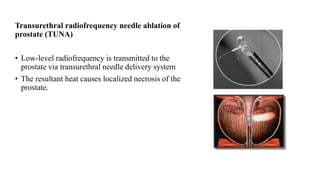
This document discusses the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It begins with the anatomy and blood supply of the prostate gland. It then describes BPH, including the pathology and common lower urinary tract symptoms. Diagnosis involves medical history, physical exam including digital rectal exam and tests like PSA, ultrasound and urodynamic studies. Treatment options discussed include watchful waiting, pharmacological treatments like alpha blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors, and surgical options ranging from minimally invasive procedures like transurethral resection of the prostate to more invasive open prostatectomy. Complications of treatments like TURP are also reviewed.