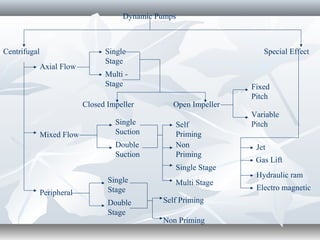
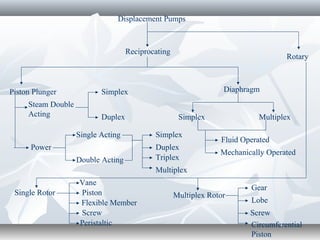
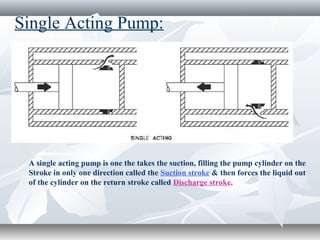
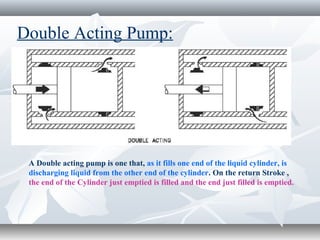
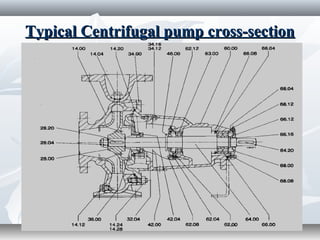
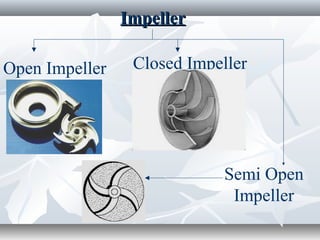
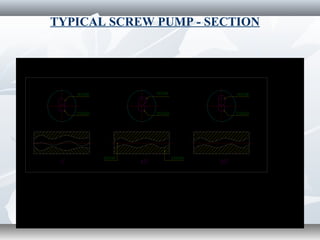
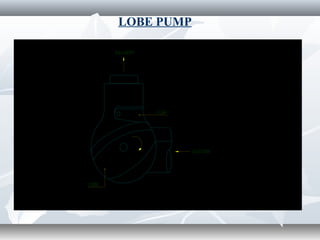
The document discusses the basics of pumps, including their classification into dynamic and displacement pumps. Dynamic pumps continuously add energy to increase fluid velocity, while displacement pumps periodically add energy by directly applying force to the fluid. Pumps are further classified based on their mechanism and components, such as centrifugal, reciprocating, and rotary pumps. The document also covers pump terminology like suction and discharge heads, priming, and cavitation, as well as factors to consider when specifying a pump like capacity, total head, and NPSH.