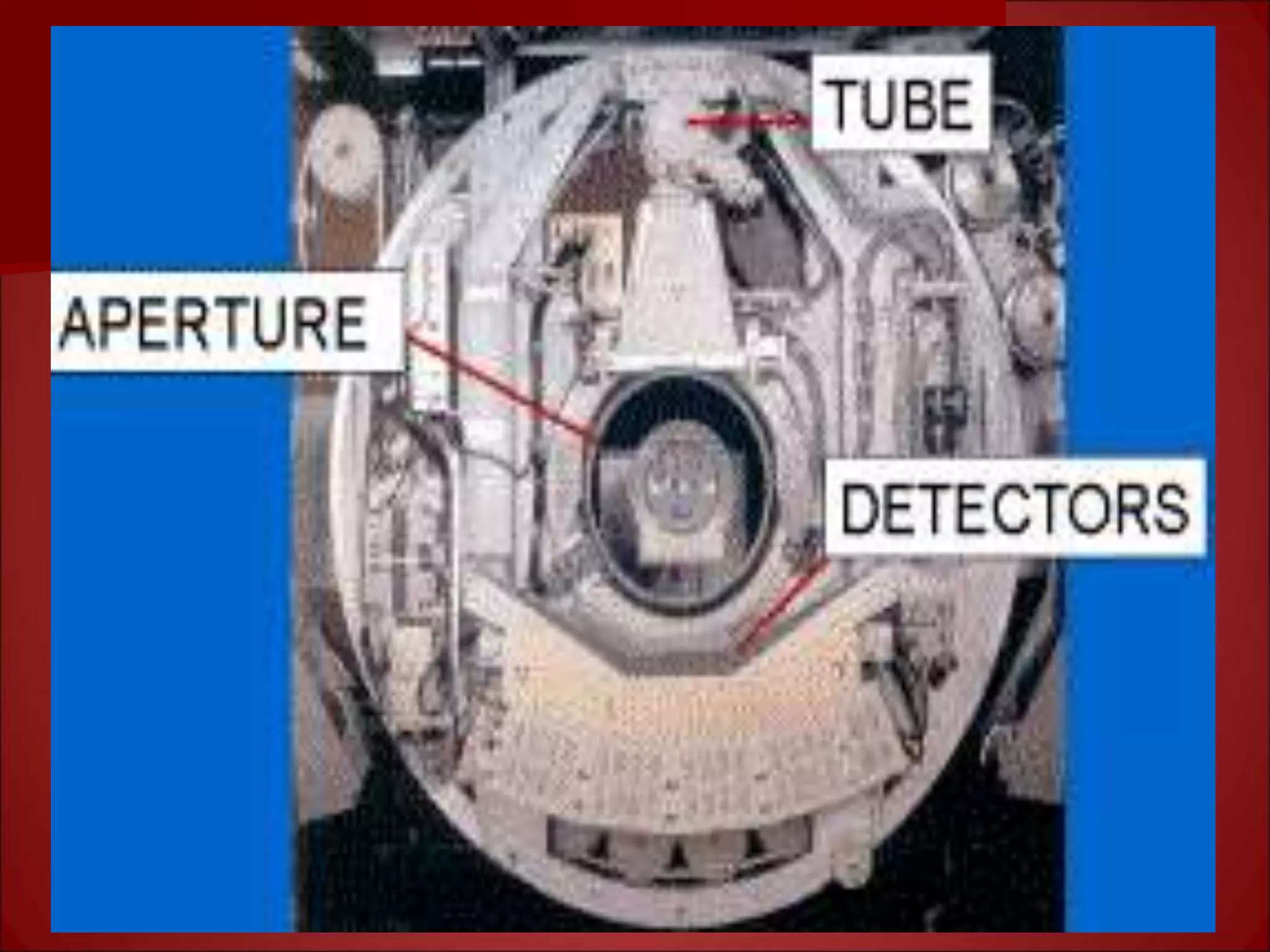
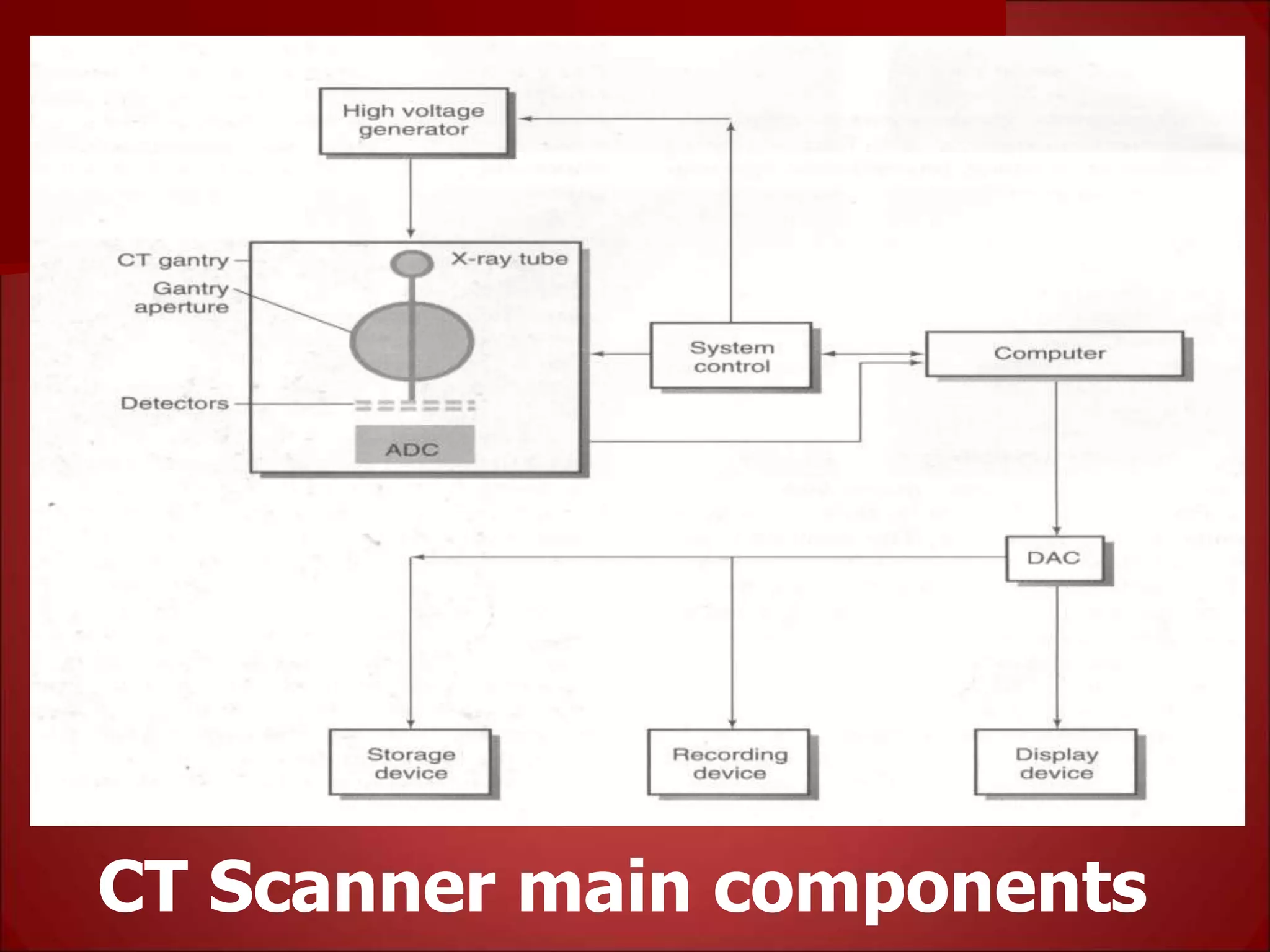
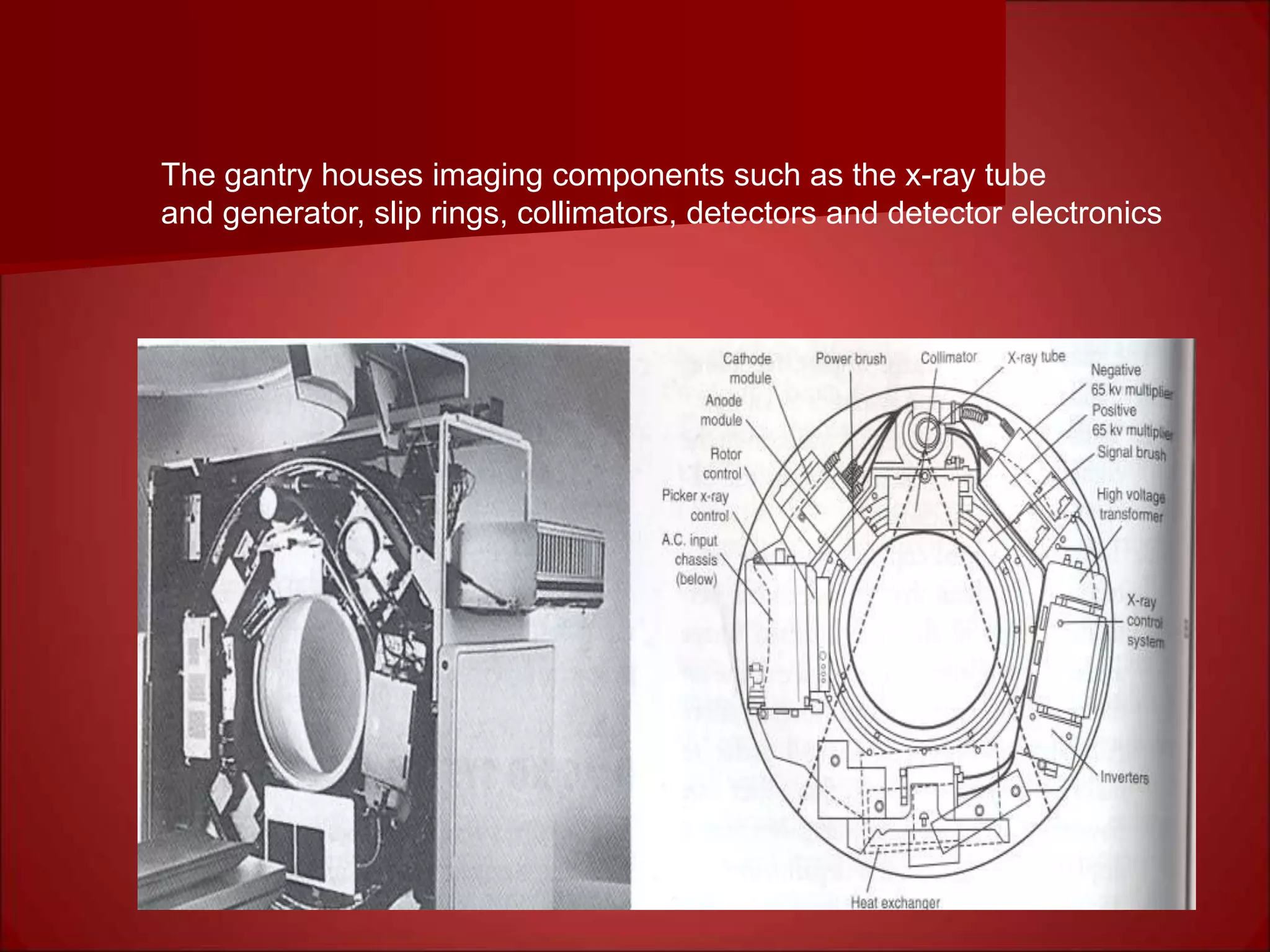
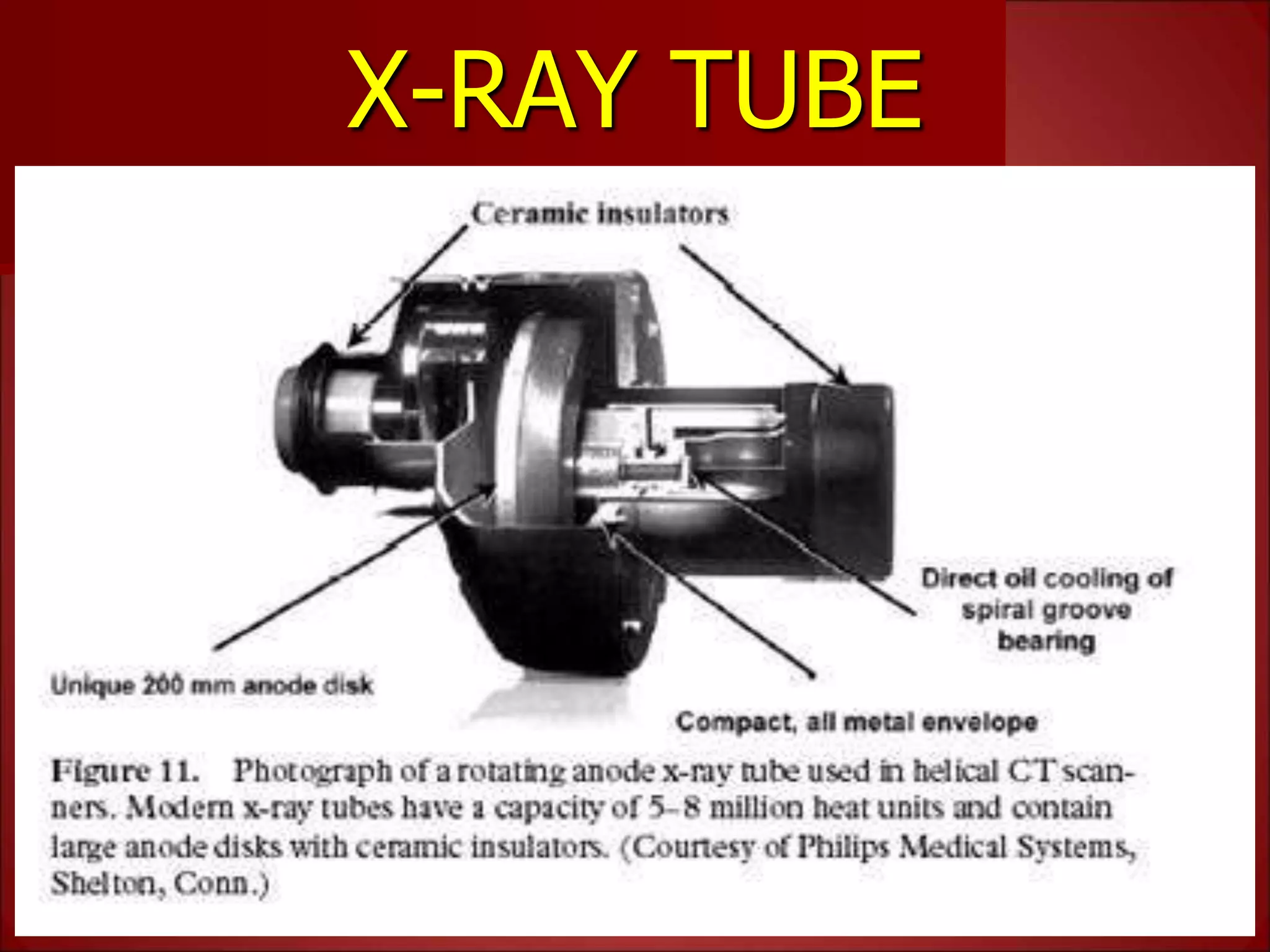
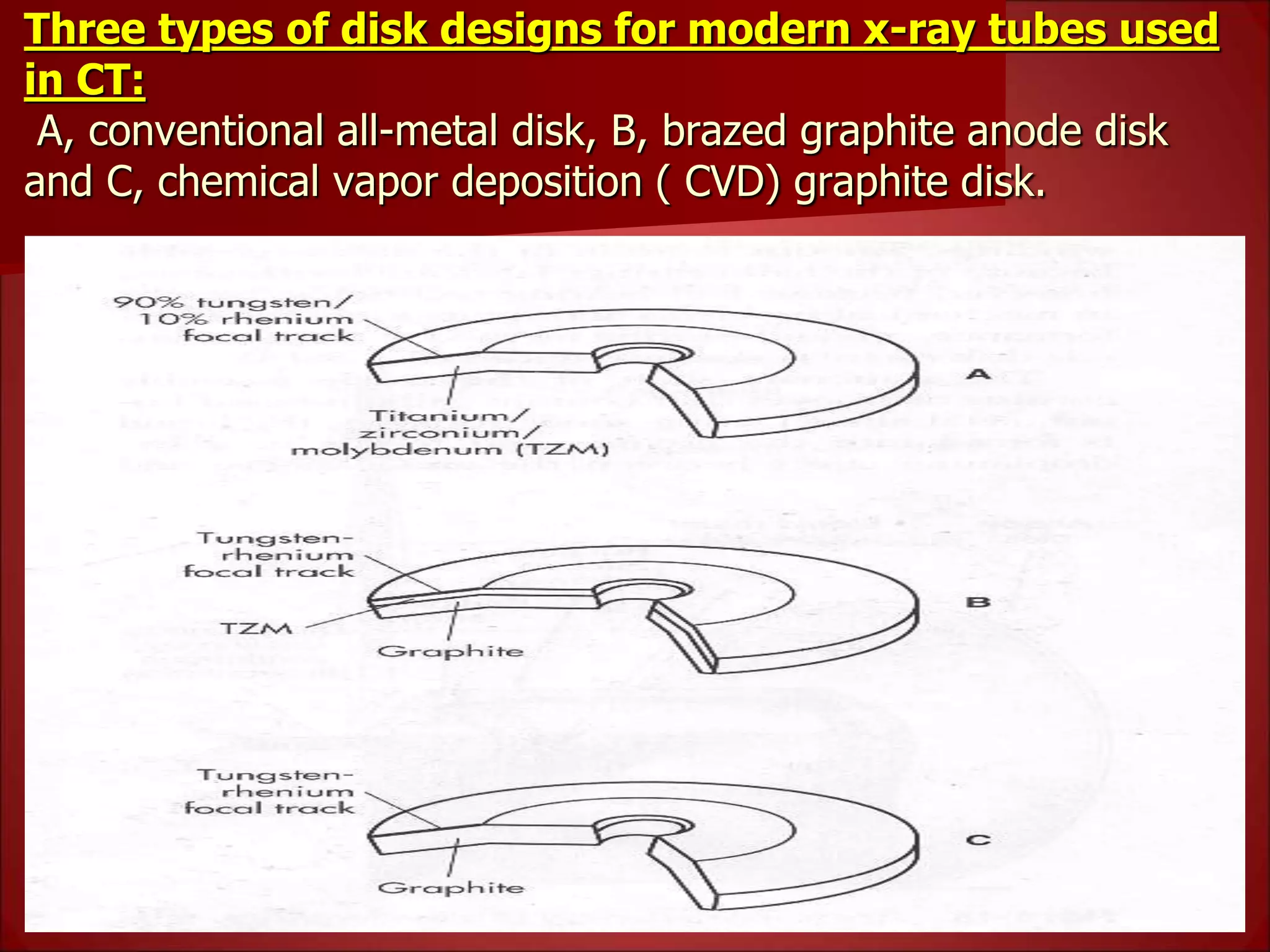
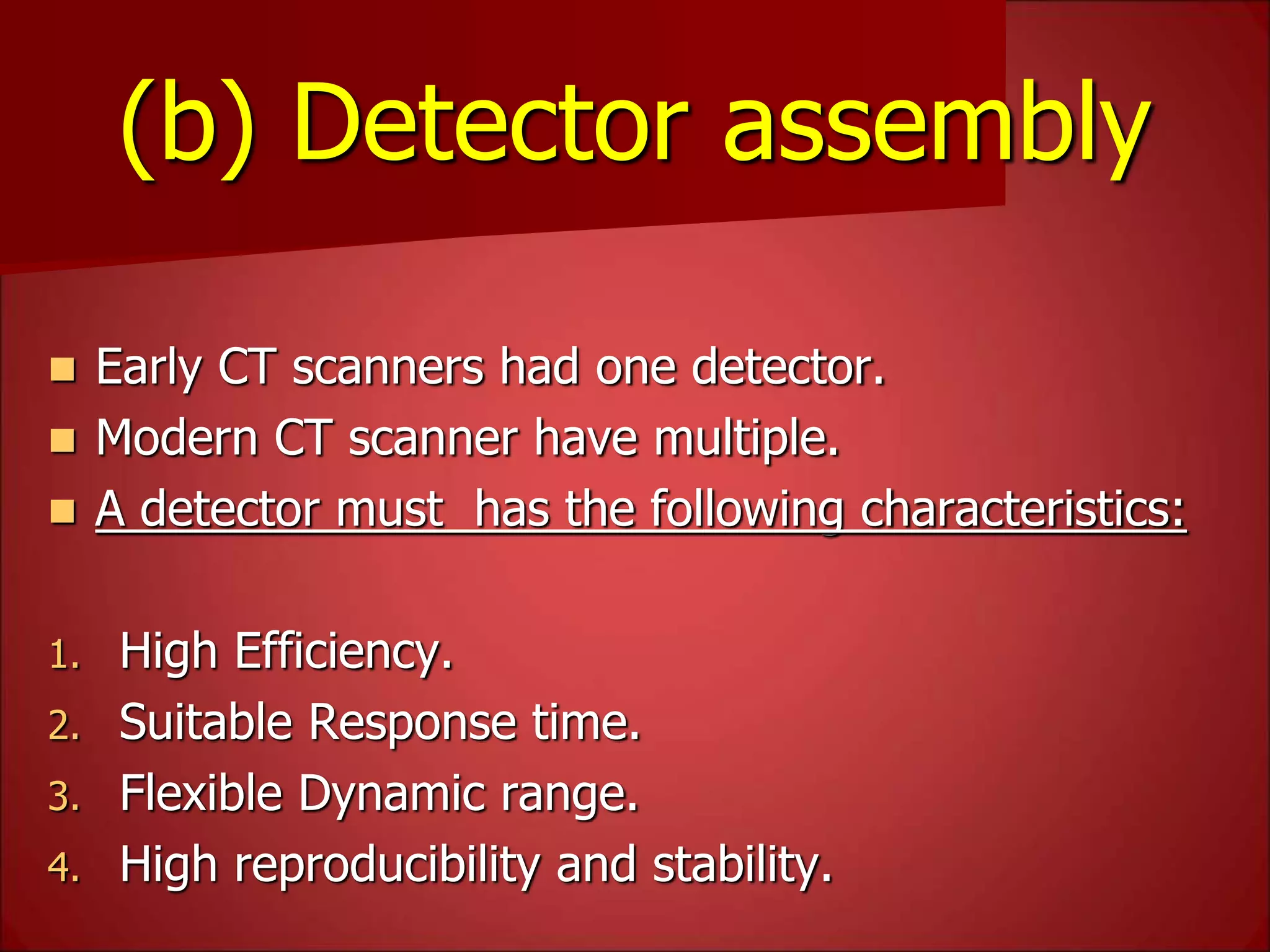
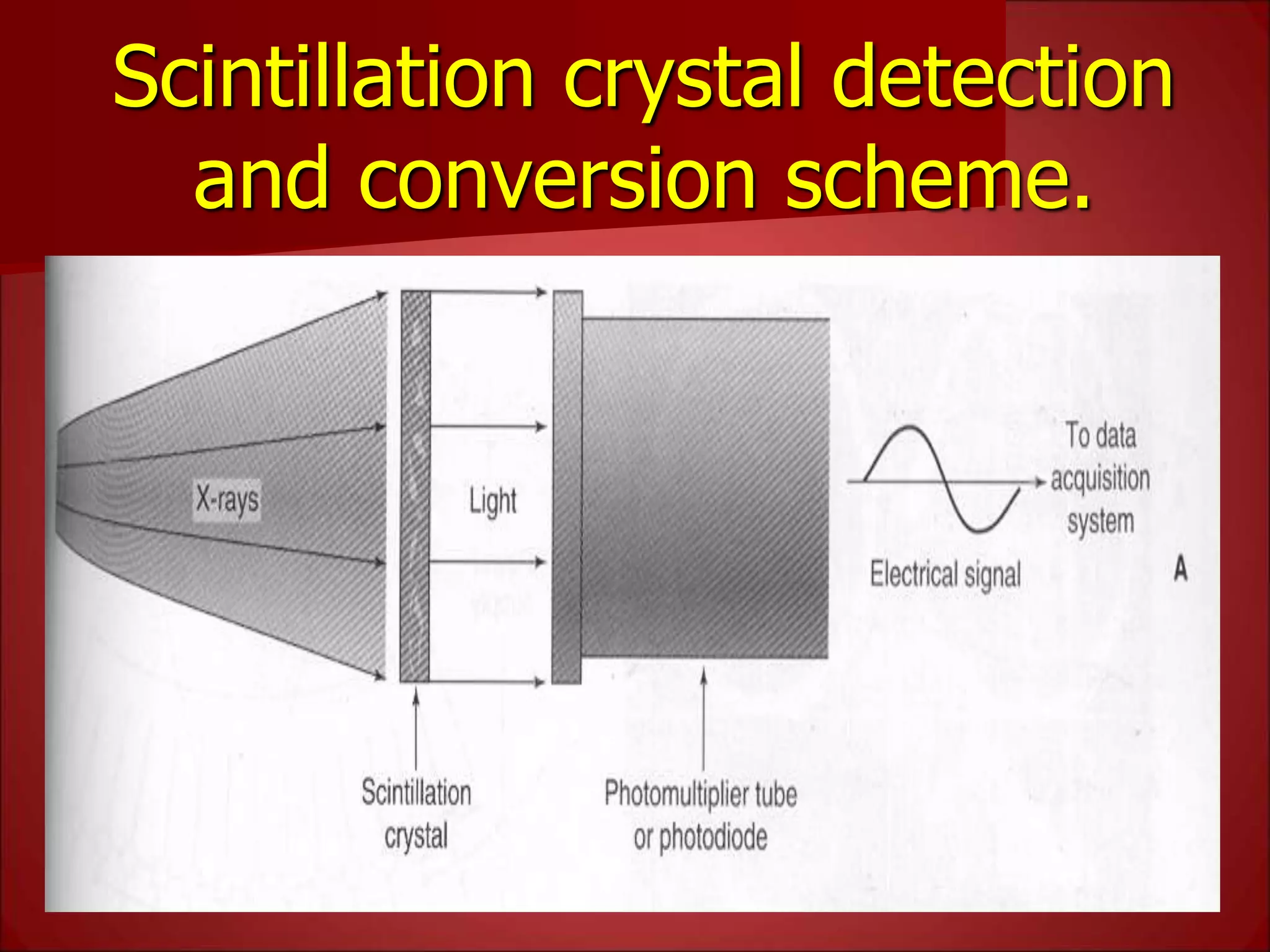
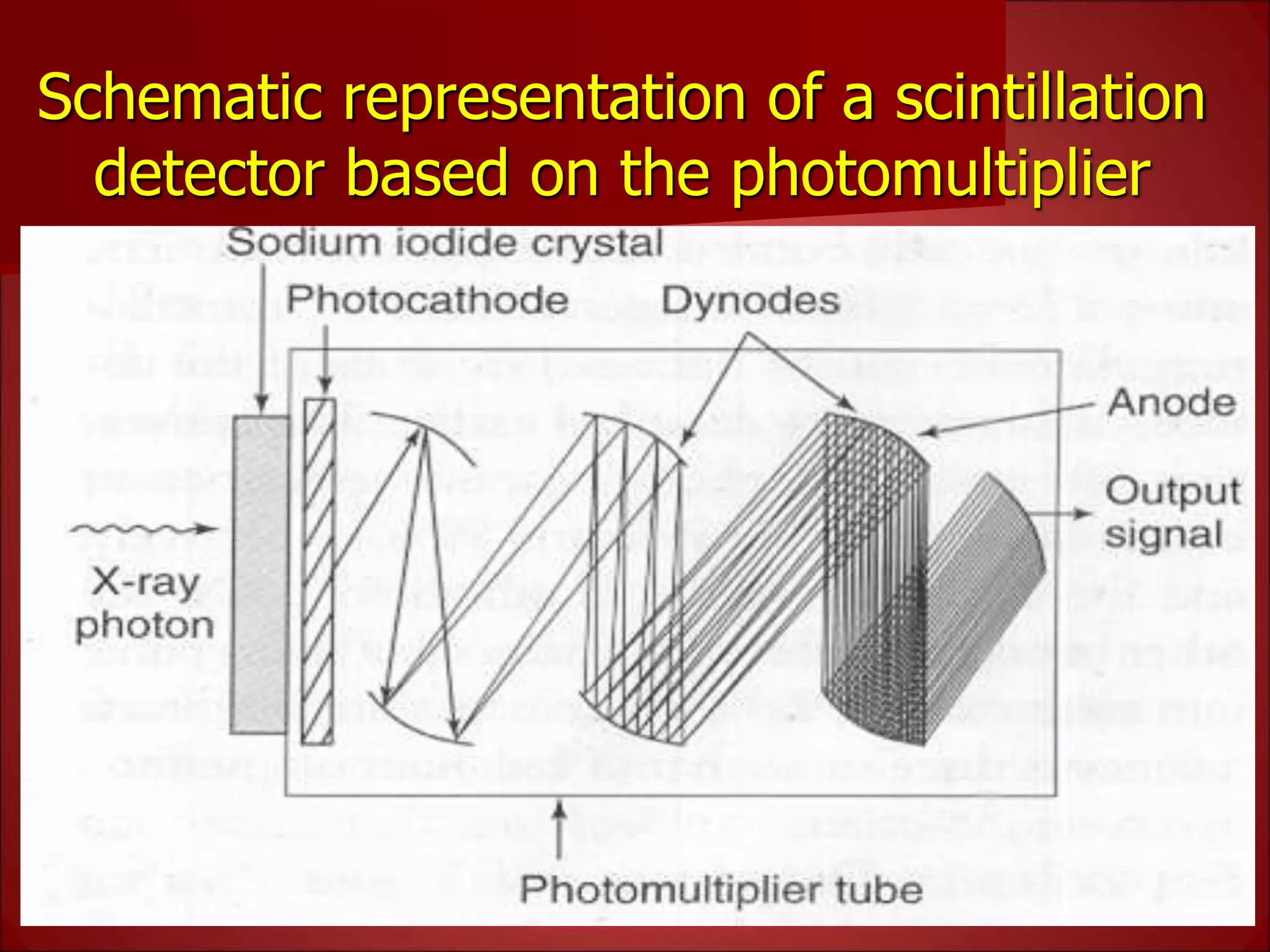
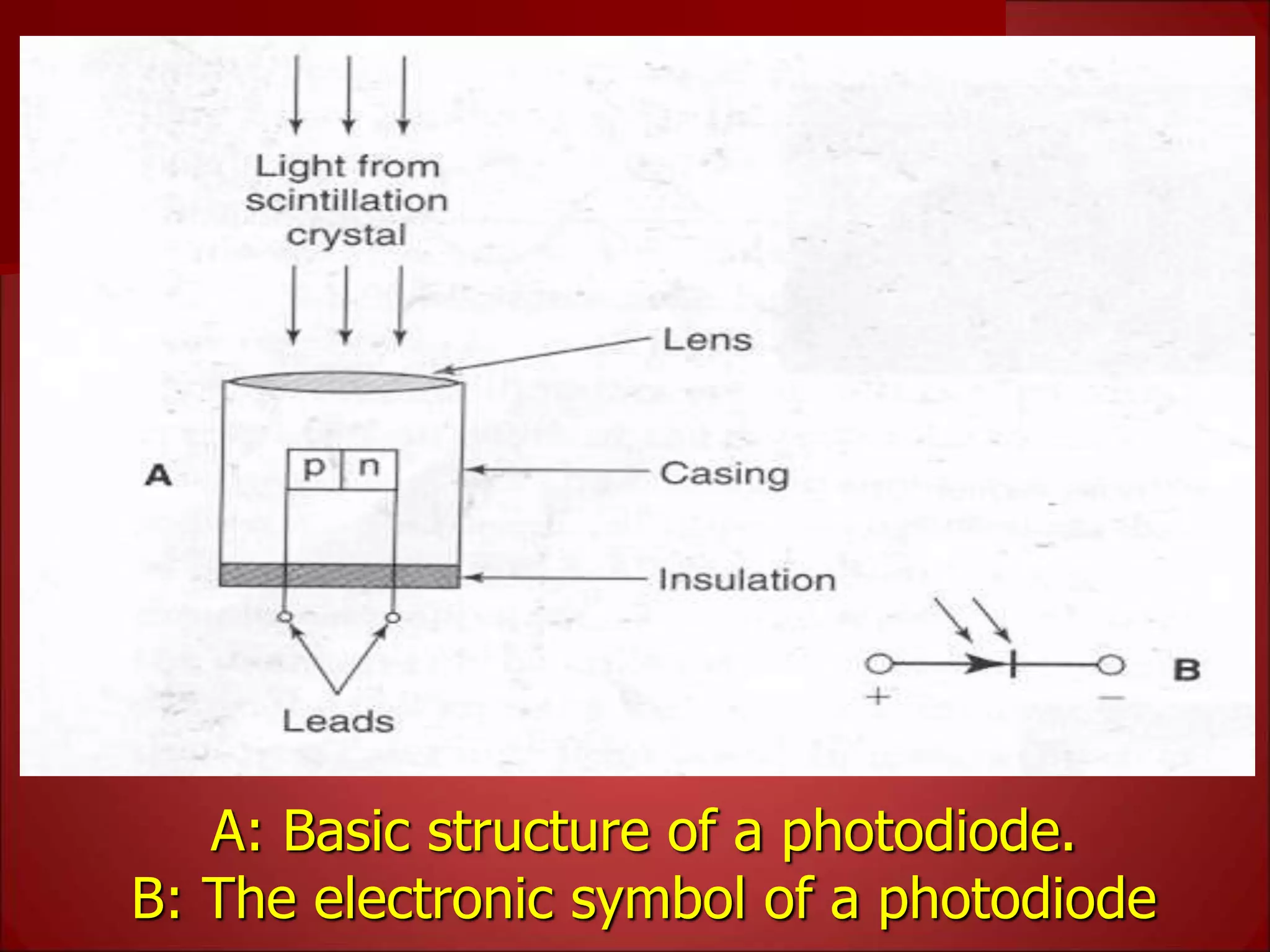
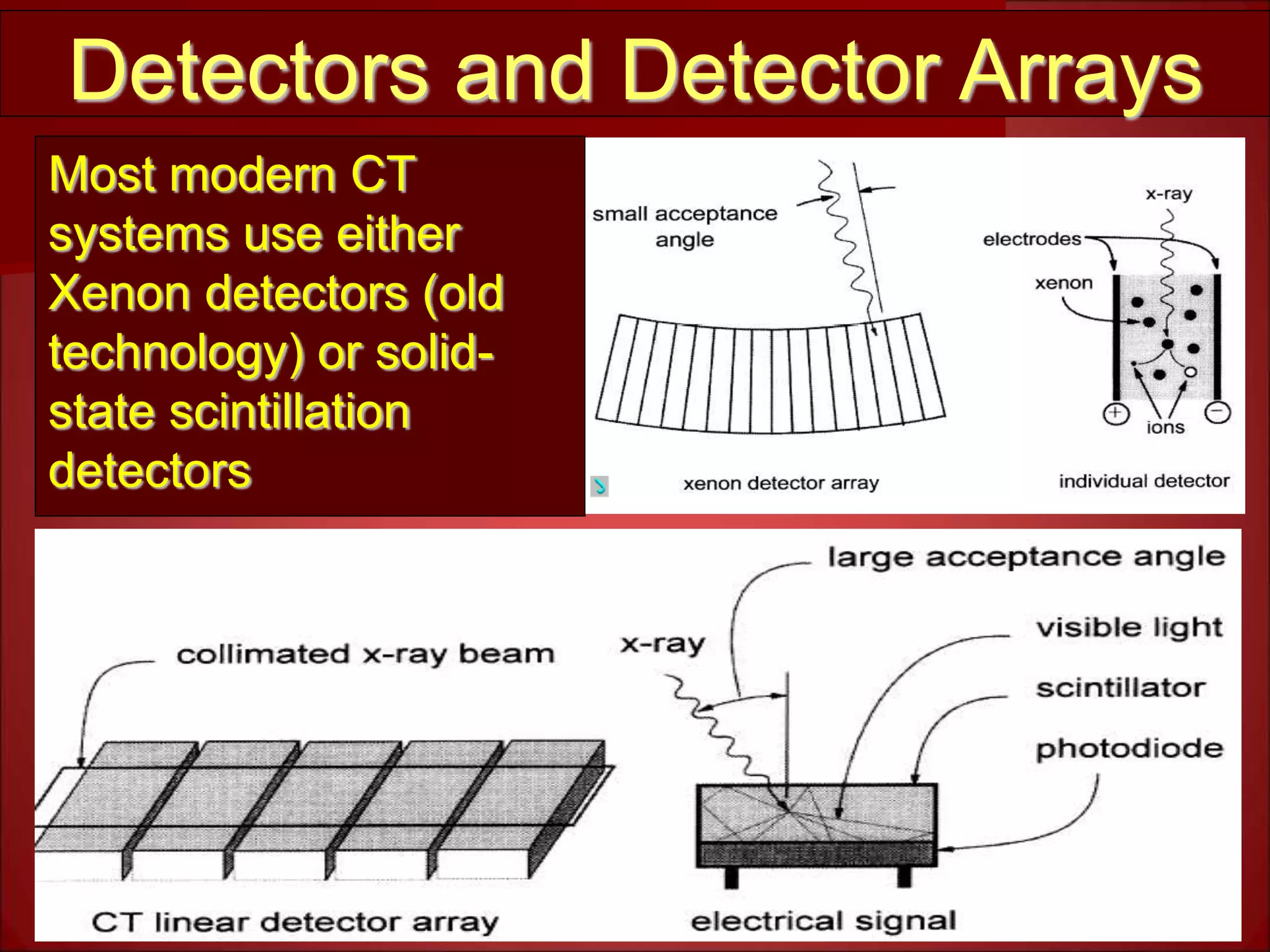
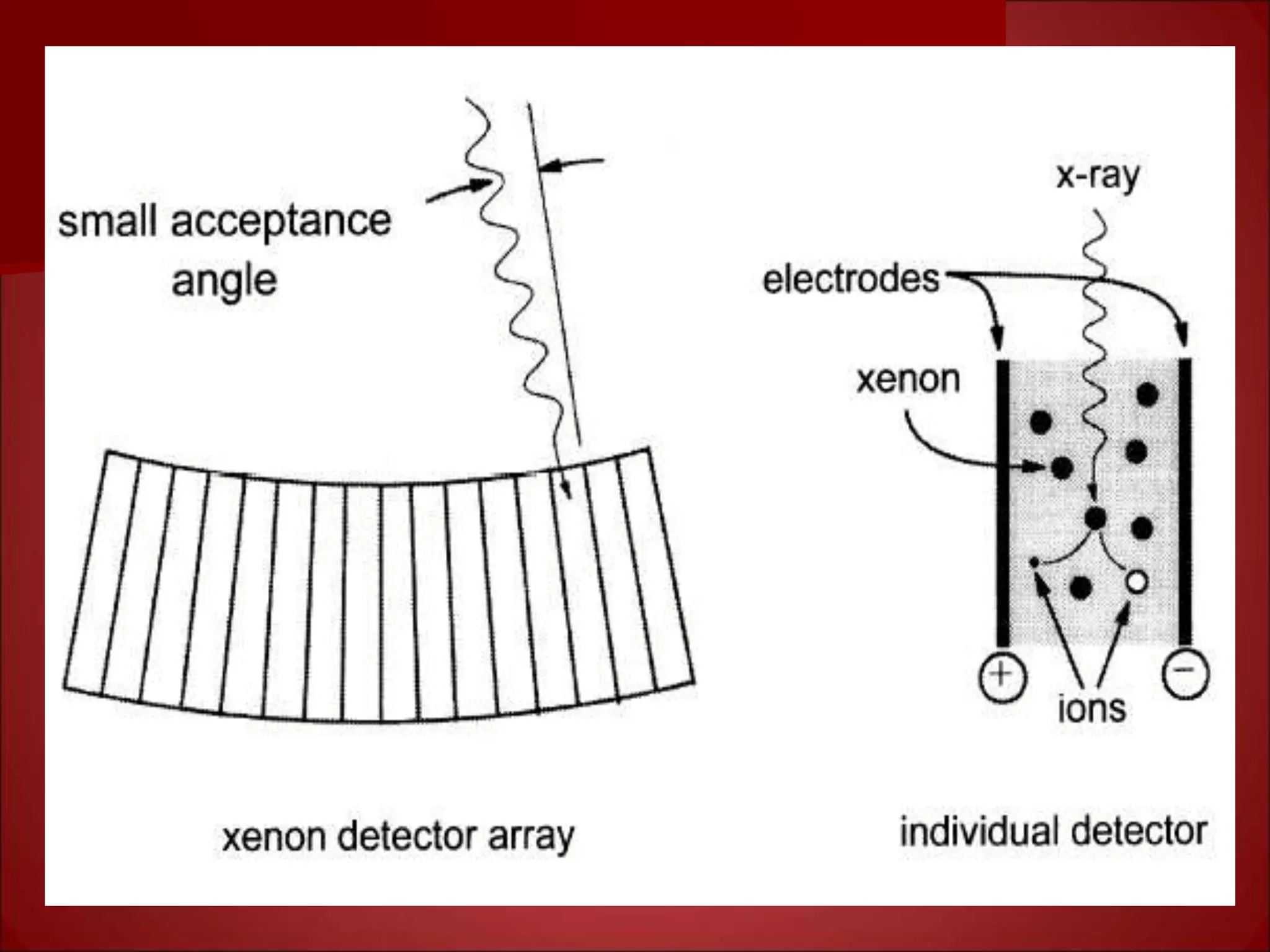
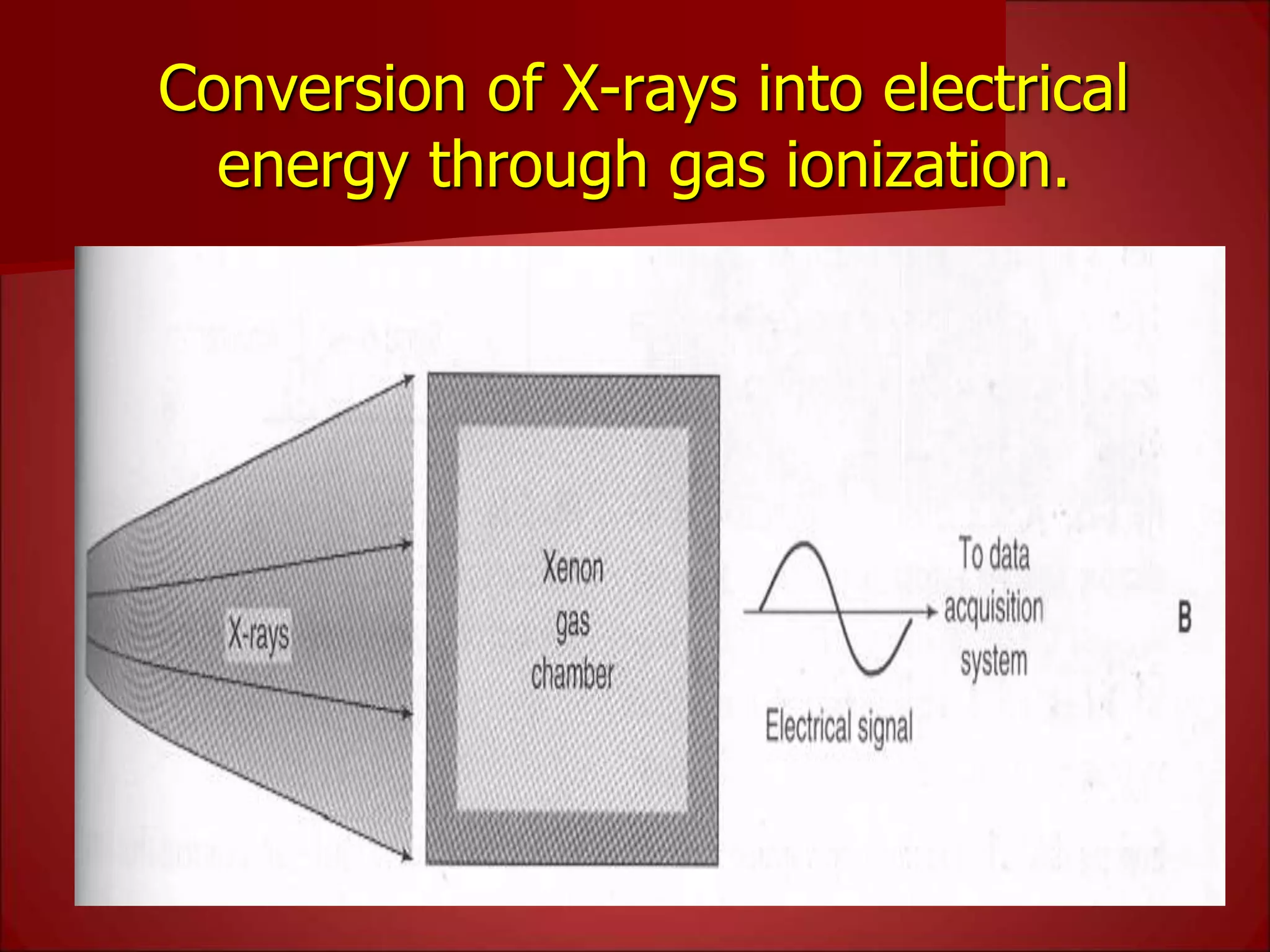
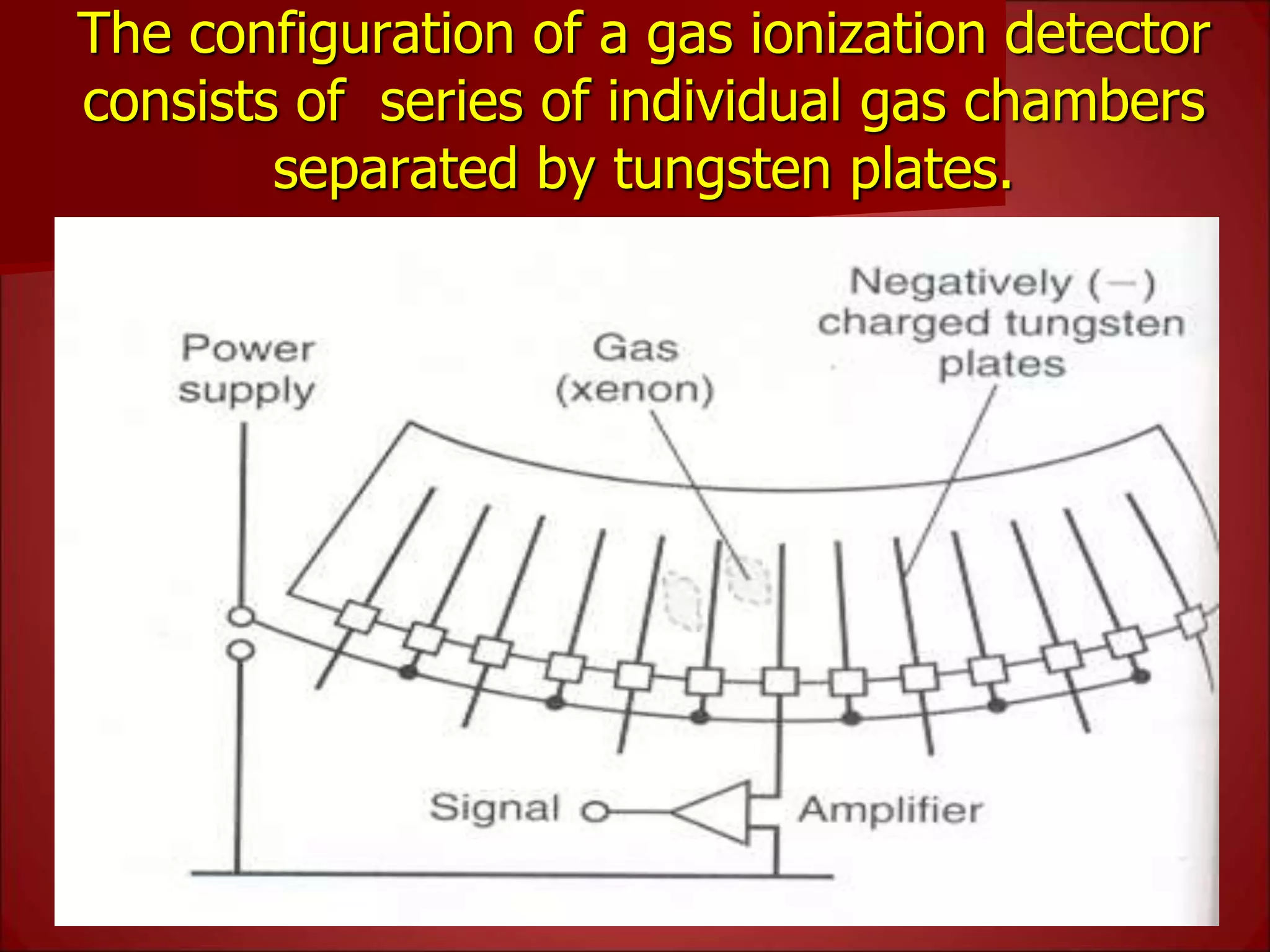
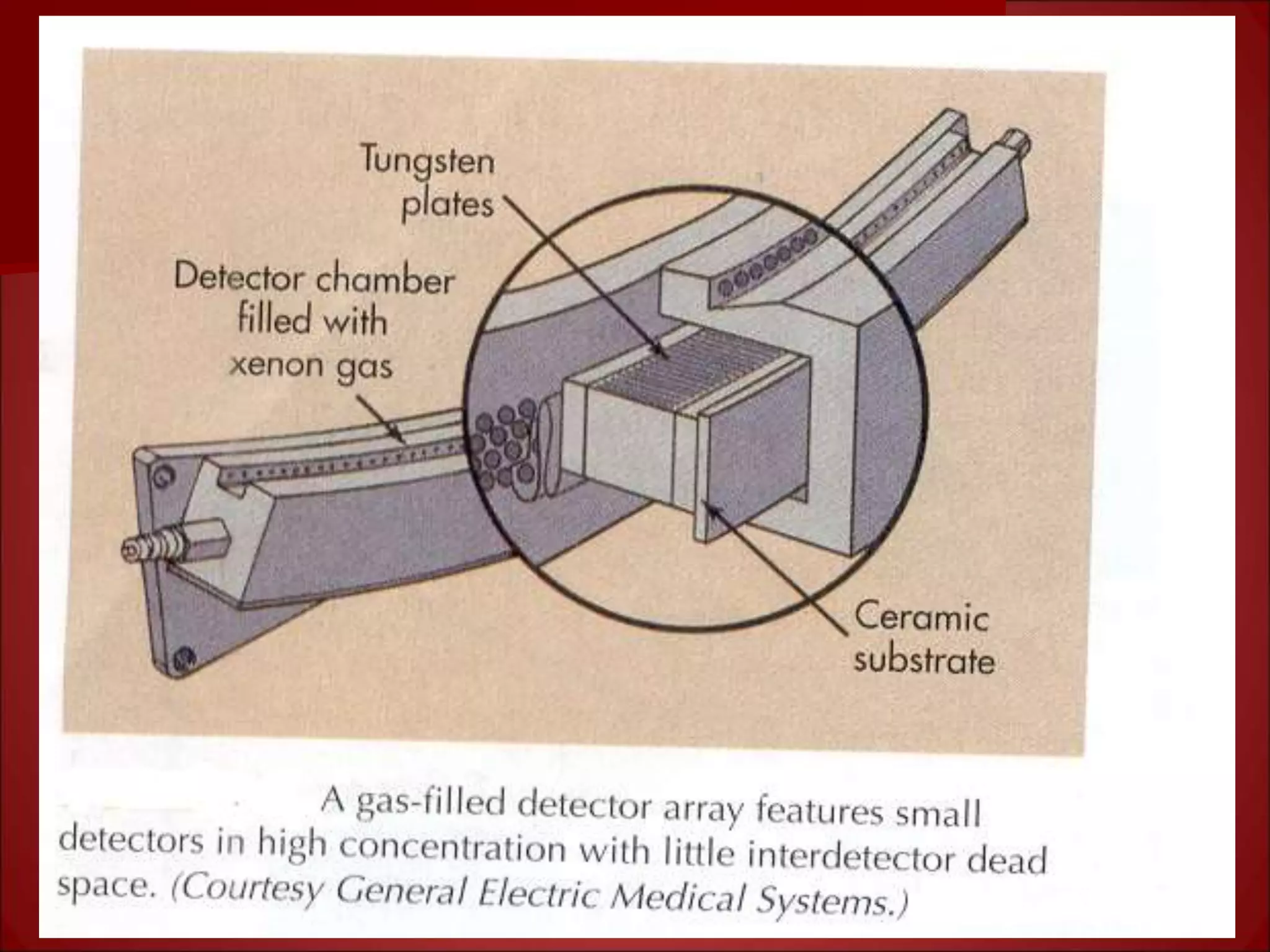
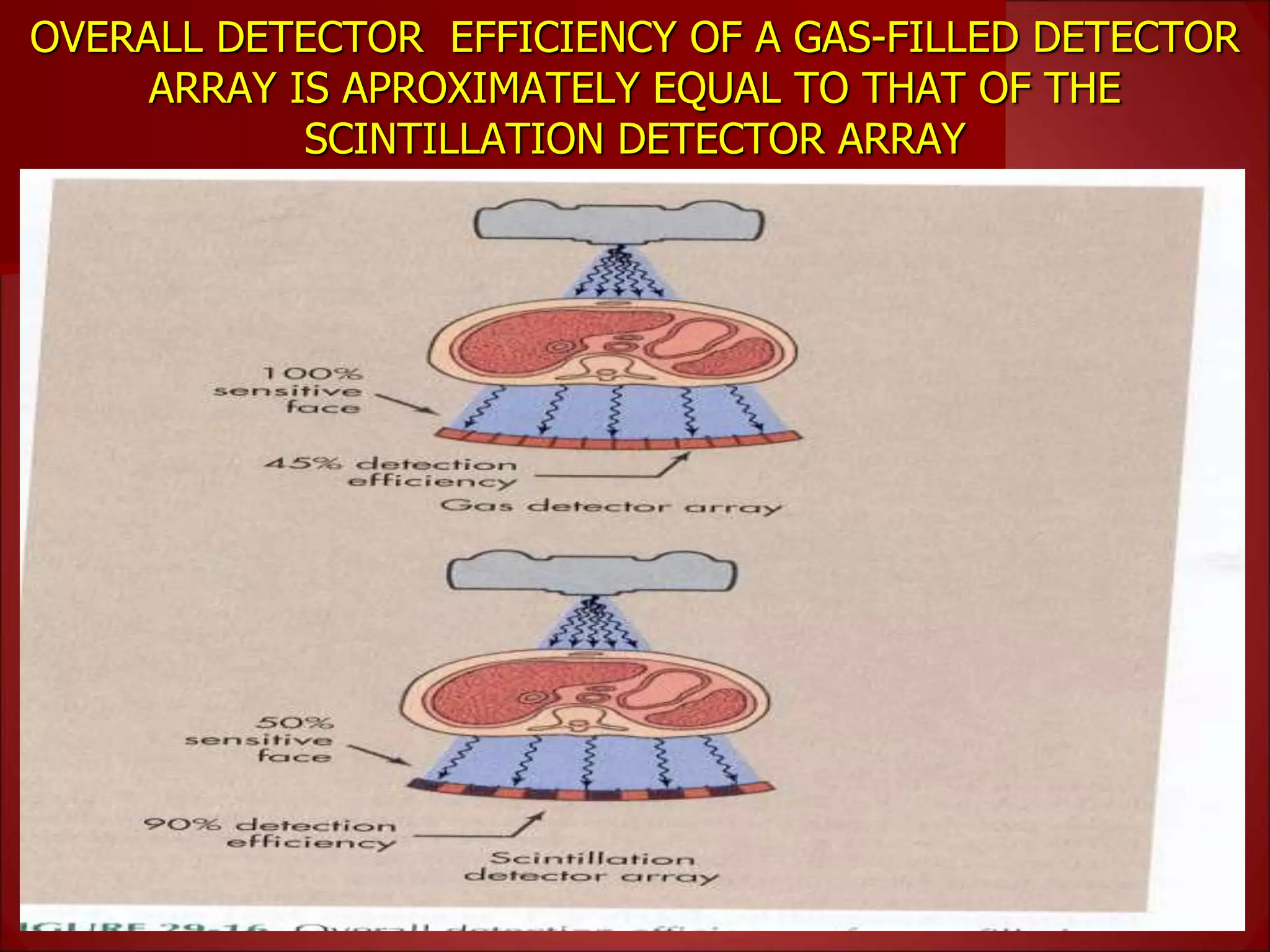
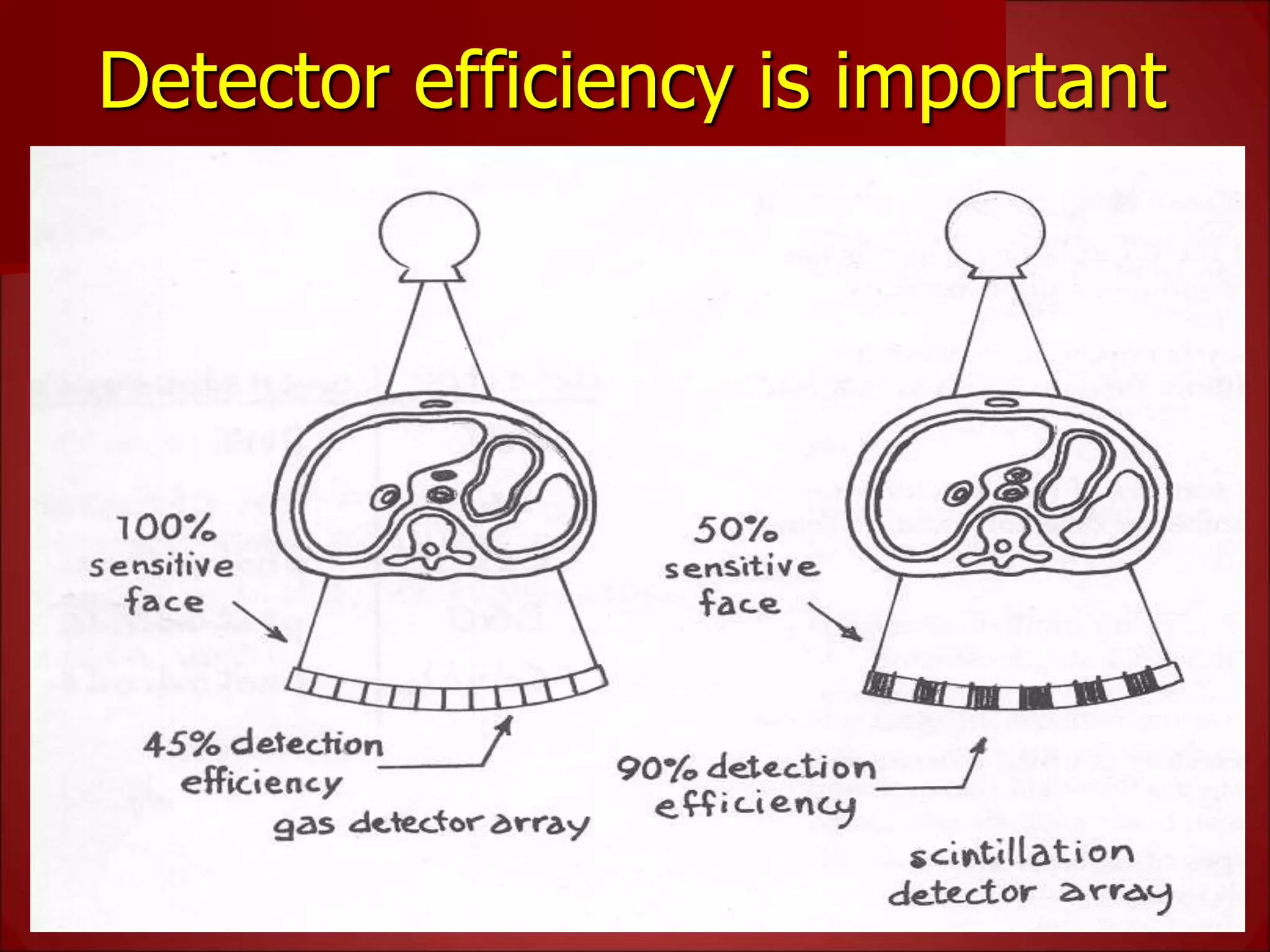
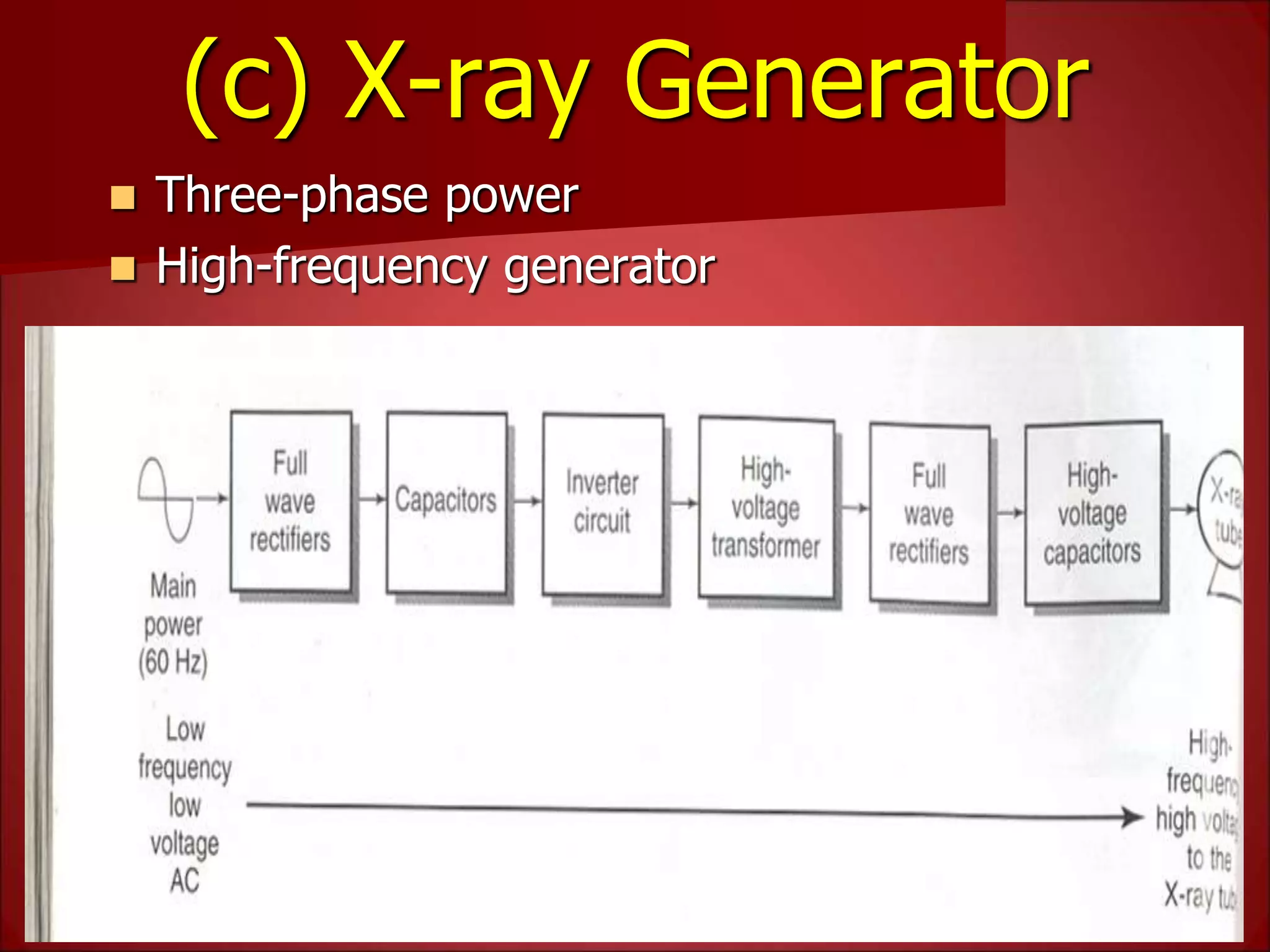
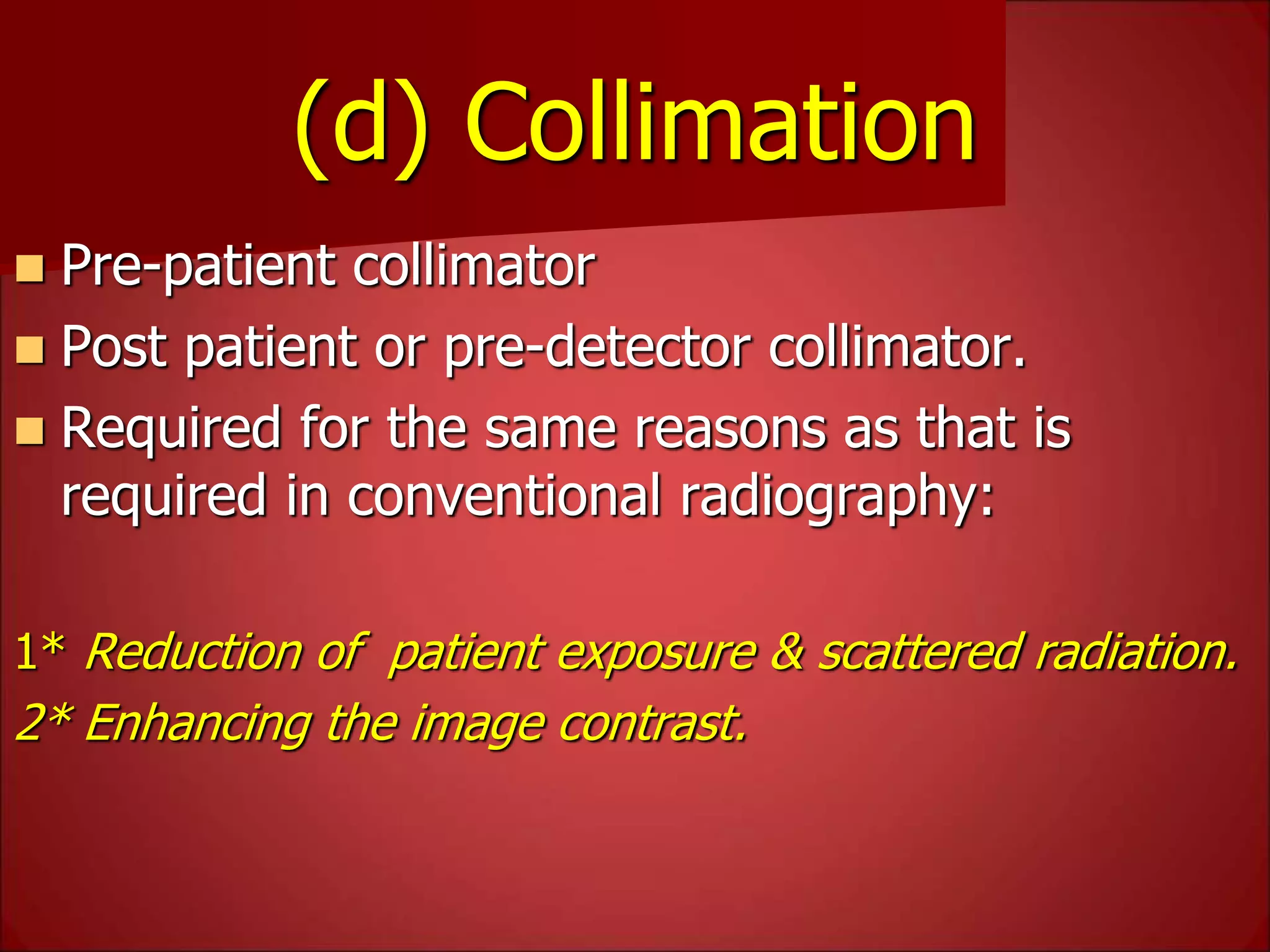
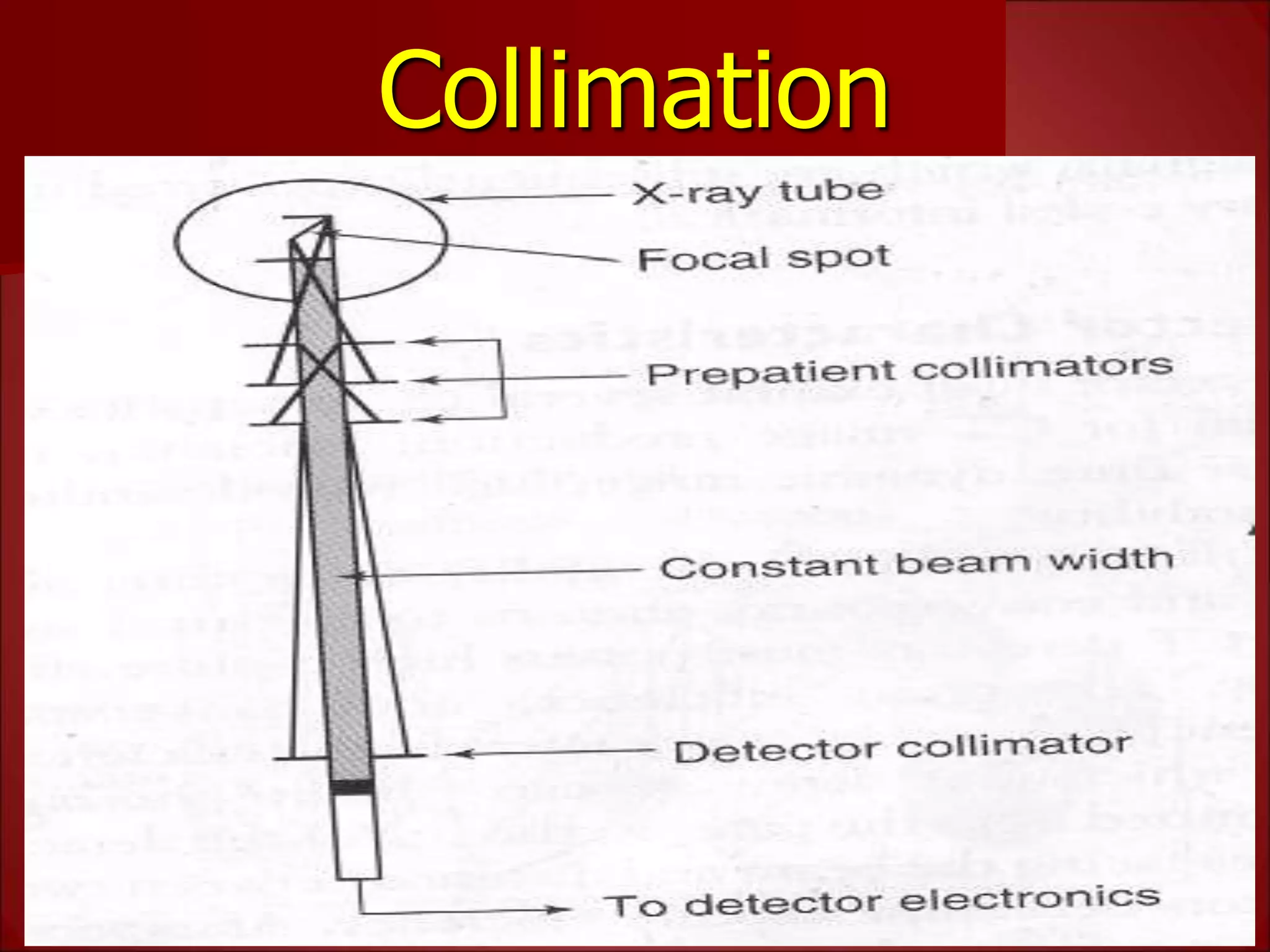
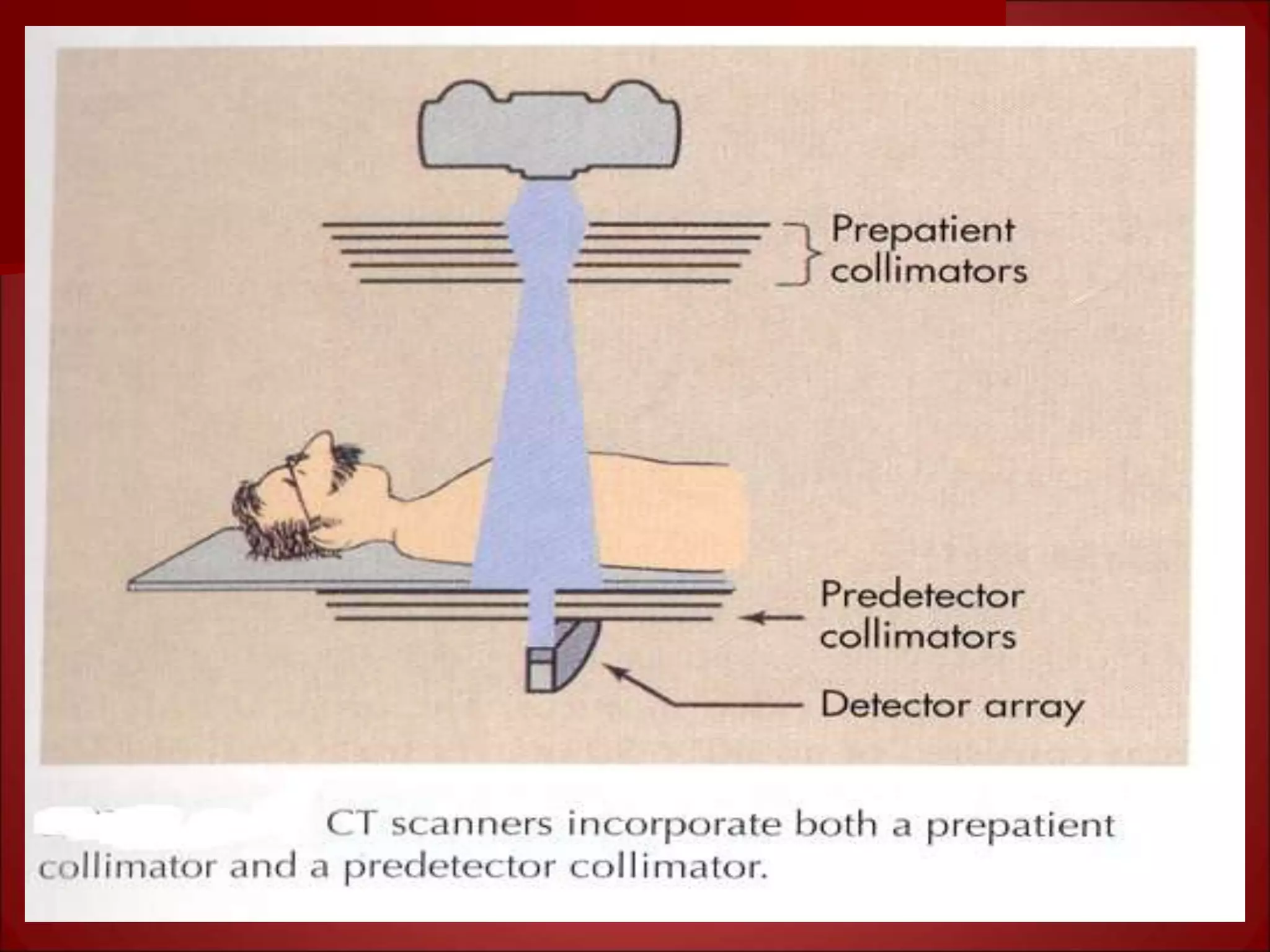
The document provides details on the key components of a computed tomography (CT) scanner. It discusses the gantry, which houses the x-ray tube, detector array, and high voltage generator. It describes different types of x-ray tubes, detectors, including scintillation and gas ionization detectors, and collimators. The computer is also highlighted as a crucial component, processing the data collected and representing the cross-sectional images.