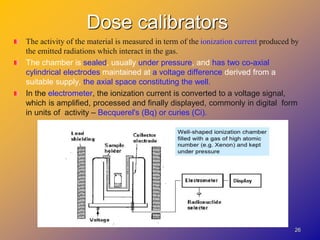
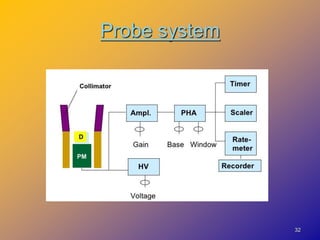
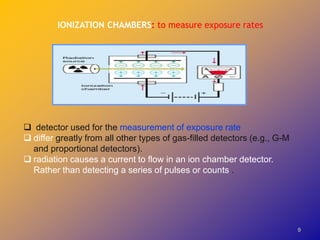
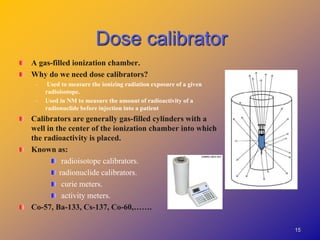
1) Dose calibrators are gas-filled ionization chambers used to measure the radioactivity of radionuclides by detecting the ionization current produced when radiation interacts with the gas.
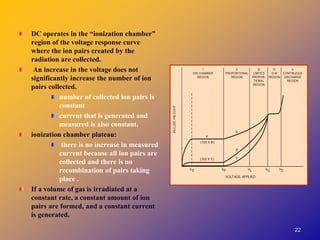
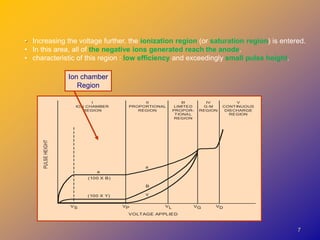
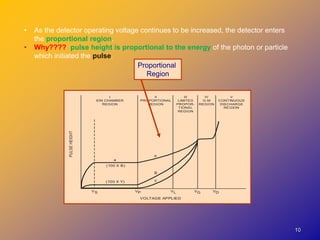
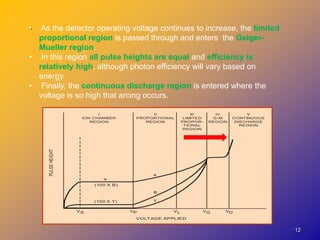
2) They operate in the ionization chamber region where a constant voltage collects all ion pairs produced, allowing measurement of high activity levels without dead time effects.
3) Dose calibrators measure the total ionization current rather than individual energy events, so they cannot distinguish between radionuclides in mixed samples like solid scintillation counters can.



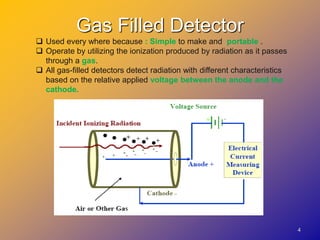




![Dose calibrator
These ionization chamber radiation
detectors are typically filled with highly
pressurized Argon [18-Ar] gas, compressed
to around 20 atmospheres.
able to measure activities anywhere from
1μCi-20Ci (3.7kBq – 740MBq).
The highly compressed gas creates an ionic
environment that favors the possibility of
ionizing events.
There is a direct relation between the
increased gas pressure and detector
efficiency.
16](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dosecalibrator-150415043426-conversion-gate01/85/Dose-calibrator-16-320.jpg)