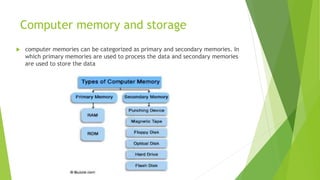
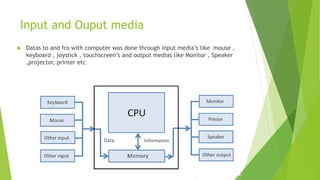
The document outlines the fundamentals of computer data representation, memory, and storage, explaining how data is processed and stored using logic 0 and 1. It categorizes computer memory into volatile primary memory and non-volatile secondary memory, detailing various input and output media used in computing. Current trends in computing highlighted include the rise of smart devices, multi-core processors, the Internet of Things, 3D printing developments, and advancements in security approaches.