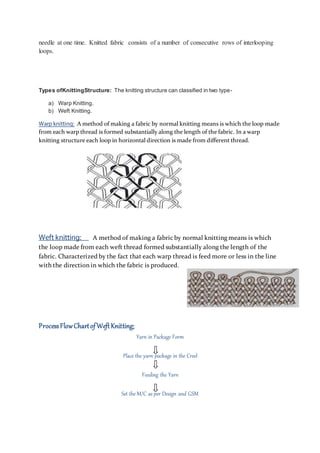
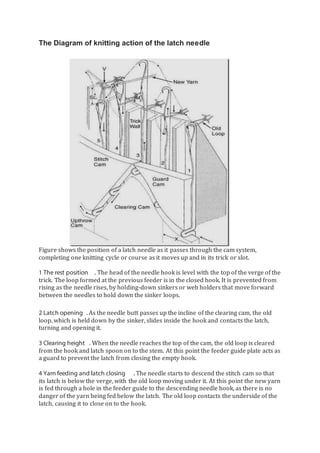
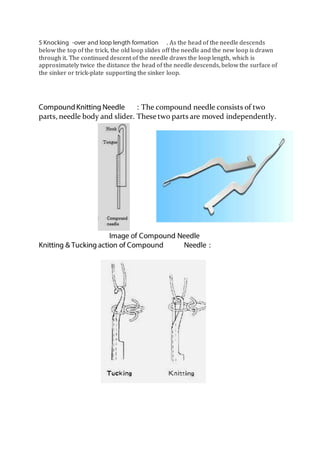
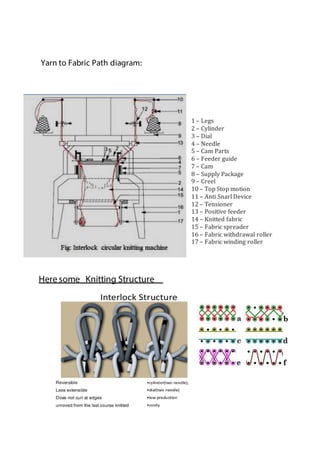
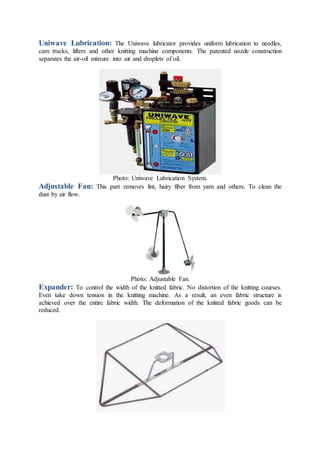
The document discusses different types of textiles including yarn, fabrics, and the processes used to make them. It provides information on:
1) Yarn is a continuous length of interlocked fibers that can be used to make textiles through processes like weaving, knitting, and spinning.
2) Fabrics are made by interlacing yarns through weaving or knitting. Woven fabrics use two sets of yarns (warp and weft) that intersect at right angles. Knitted fabrics use interlocking loops of yarn.
3) There are different types of structures for woven and knitted fabrics depending on how the yarns are interlaced. Key processes