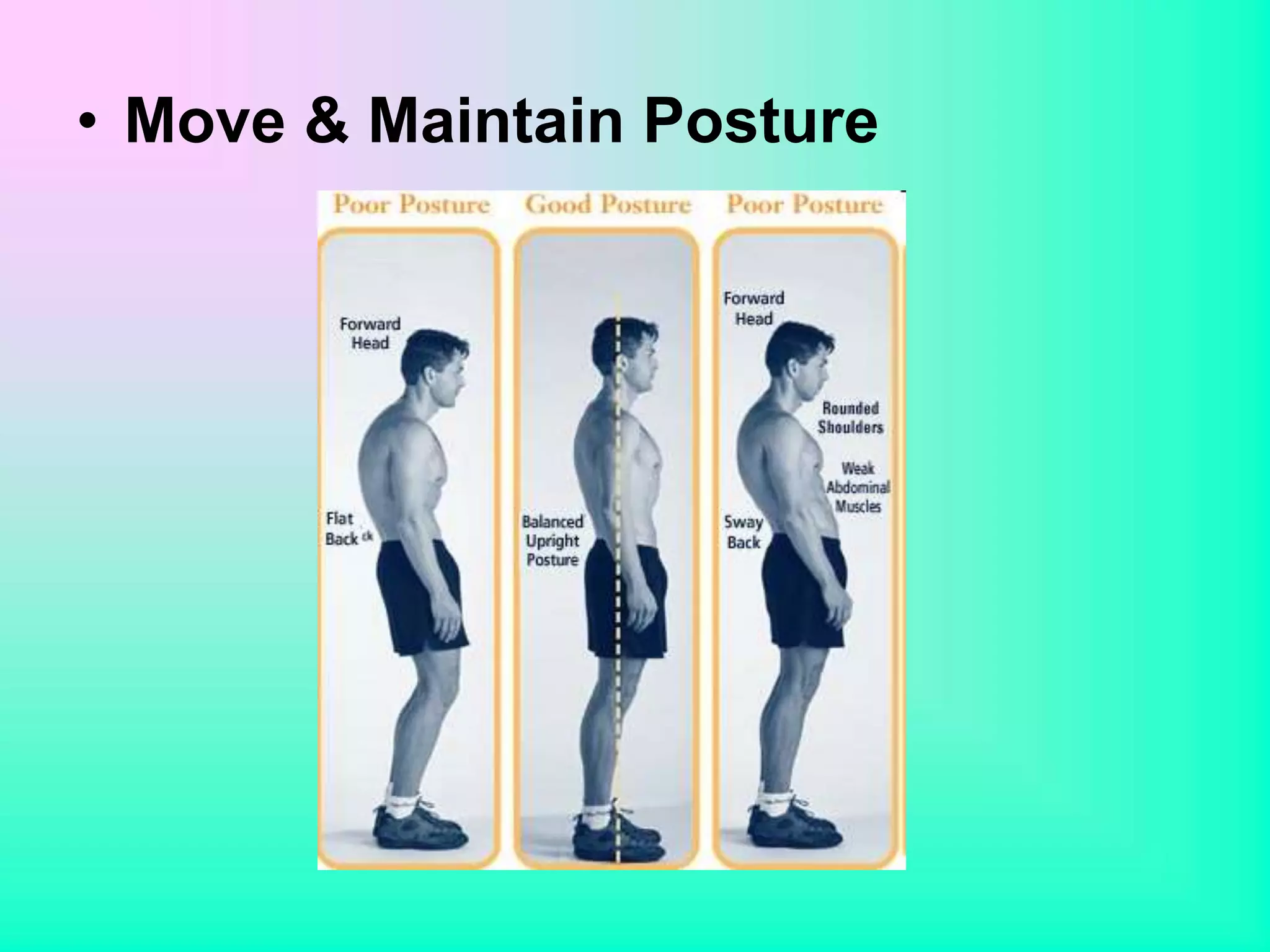
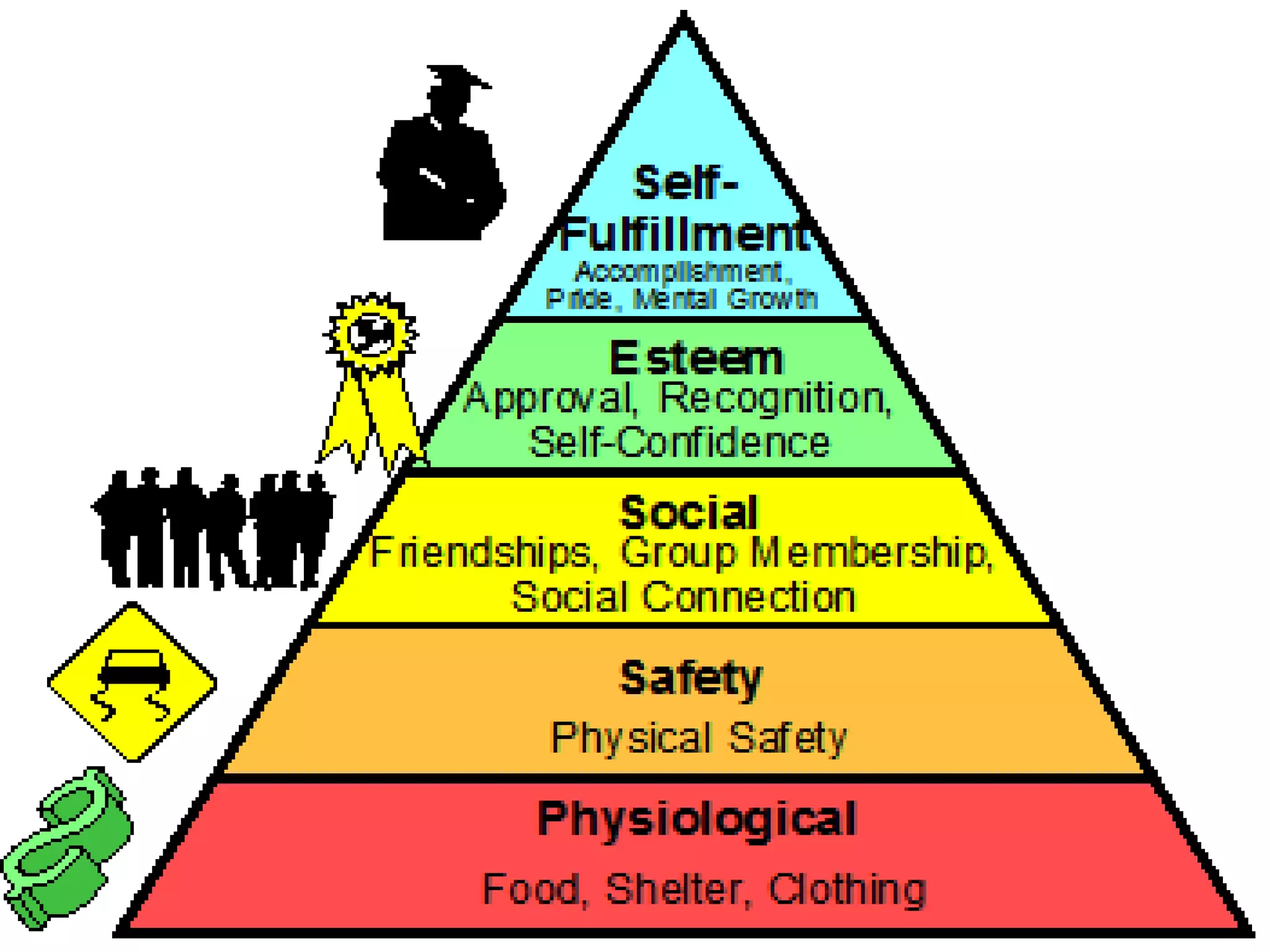
Human needs can be categorized into physiological, psychological, and sociological components. Physiological needs include breathing, eating, drinking, eliminating waste, sleeping, maintaining posture, keeping the body clean and avoiding dangers. Psychological needs involve communication, learning, and spiritual fulfillment. Sociological needs encompass work, recreation, and interpersonal relationships. Several theories describe the hierarchy of human needs, with physiological needs being the most basic. Nurses assess patients' needs using these frameworks to develop care plans that help individuals meet their needs and maintain health.