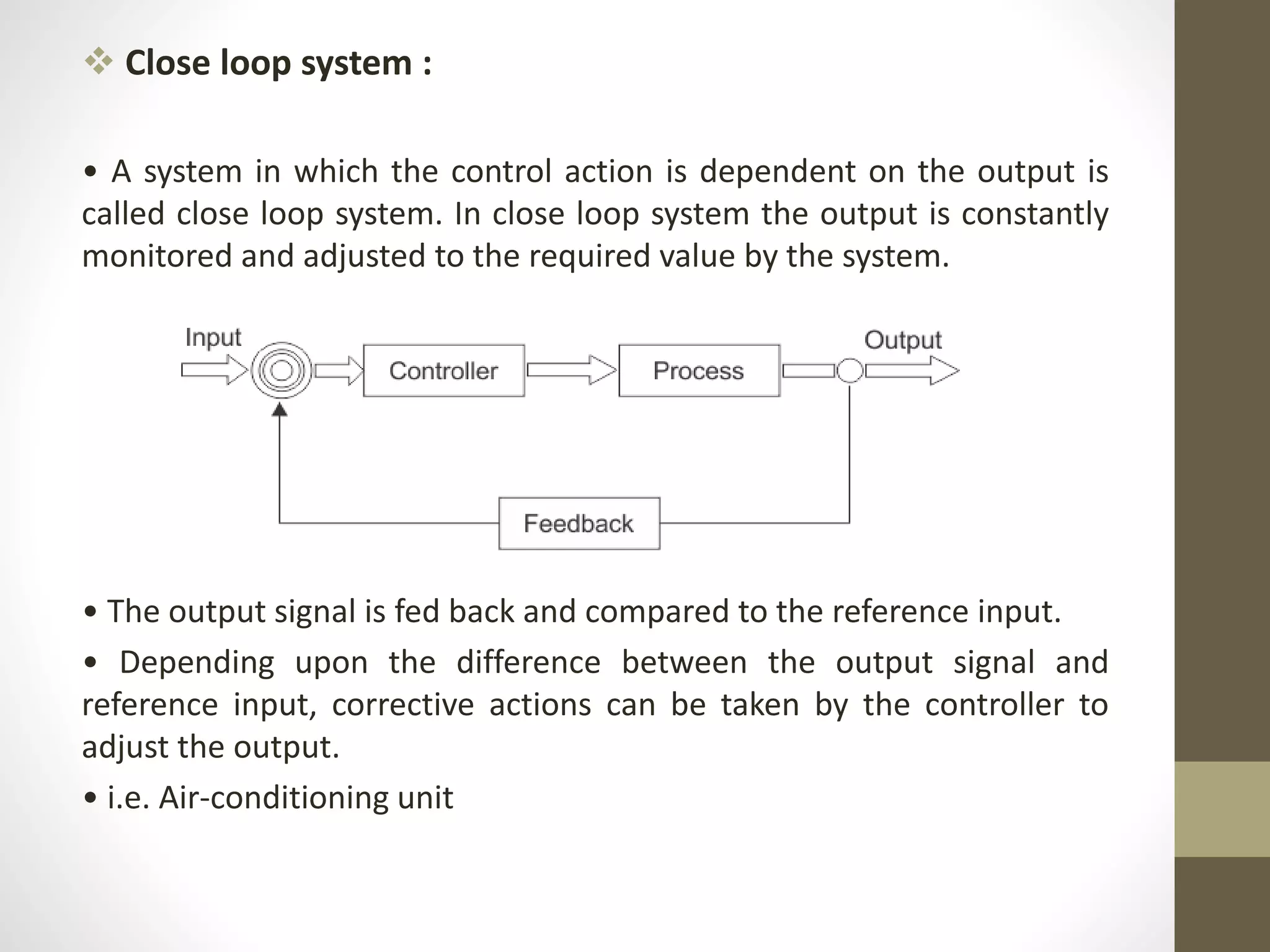
This document provides an overview of control systems. It defines a control system as an arrangement of components designed to achieve a specific objective. The document discusses open loop and closed loop systems. Open loop systems do not provide feedback, while closed loop systems constantly monitor and adjust the output based on feedback. Examples are given of each type of system. The key requirements, terms, types of systems, their comparison and design process are outlined over the course of the document.