Embed presentation
Download to read offline


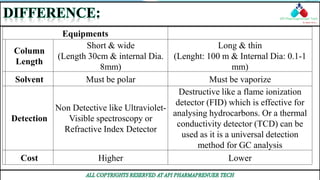
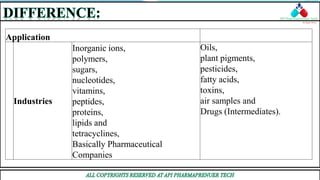

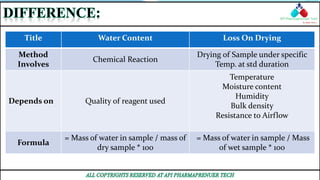


This document compares and contrasts two analytical chemistry techniques: HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) and GC (Gas Chromatography). HPLC uses liquid mobile phases to separate compounds based on polarity, while GC uses inert gases and separates compounds based on volatility. HPLC works at room temperature and has shorter, wider columns, while GC operates at higher temperatures and uses longer, thinner columns. HPLC is generally used in pharmaceutical industries for separation of non-volatile compounds, while GC is commonly used to analyze volatile compounds like oils and fuels. Overall, HPLC provides higher resolution for polar compounds but is more expensive than GC.






