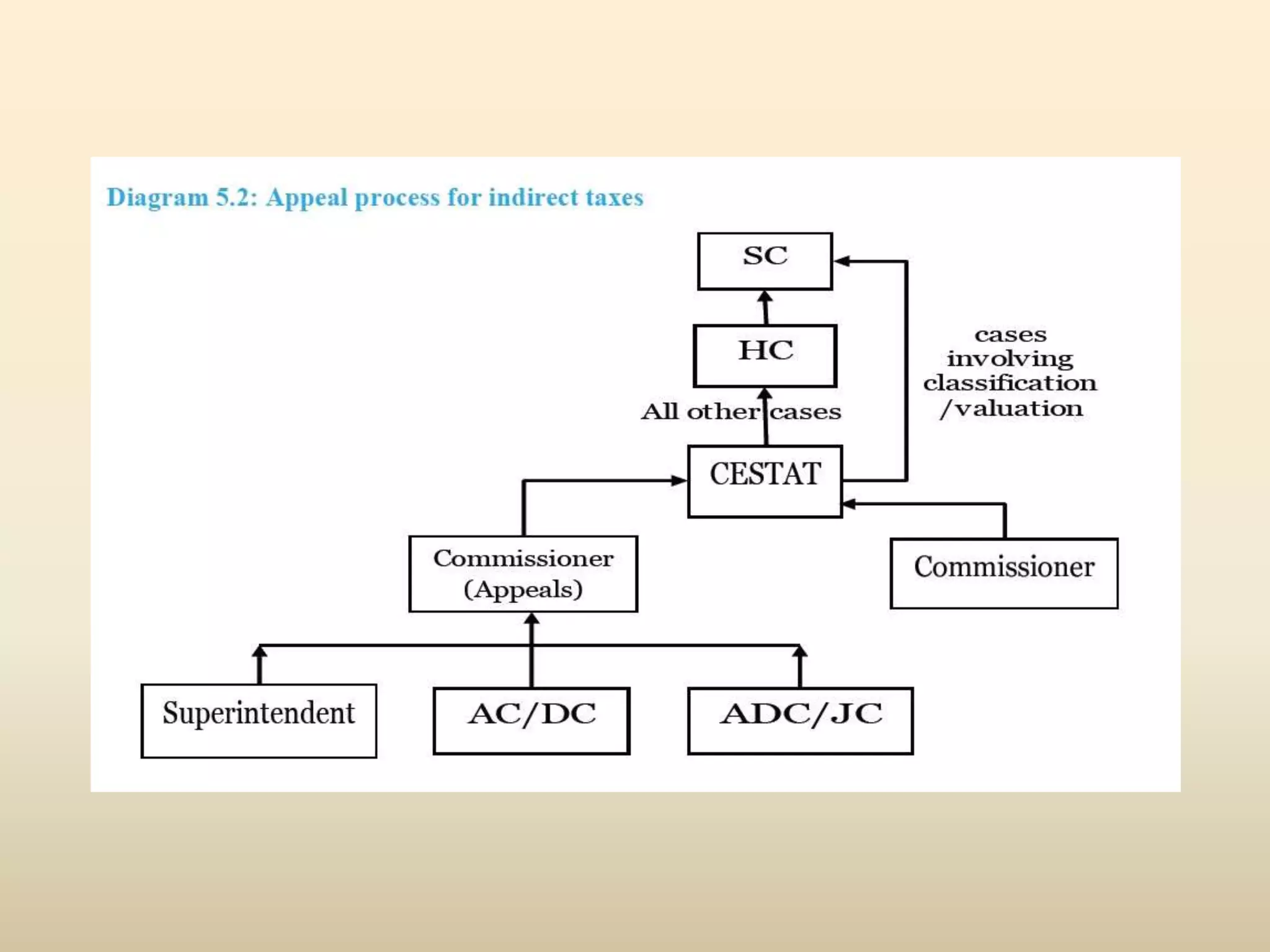
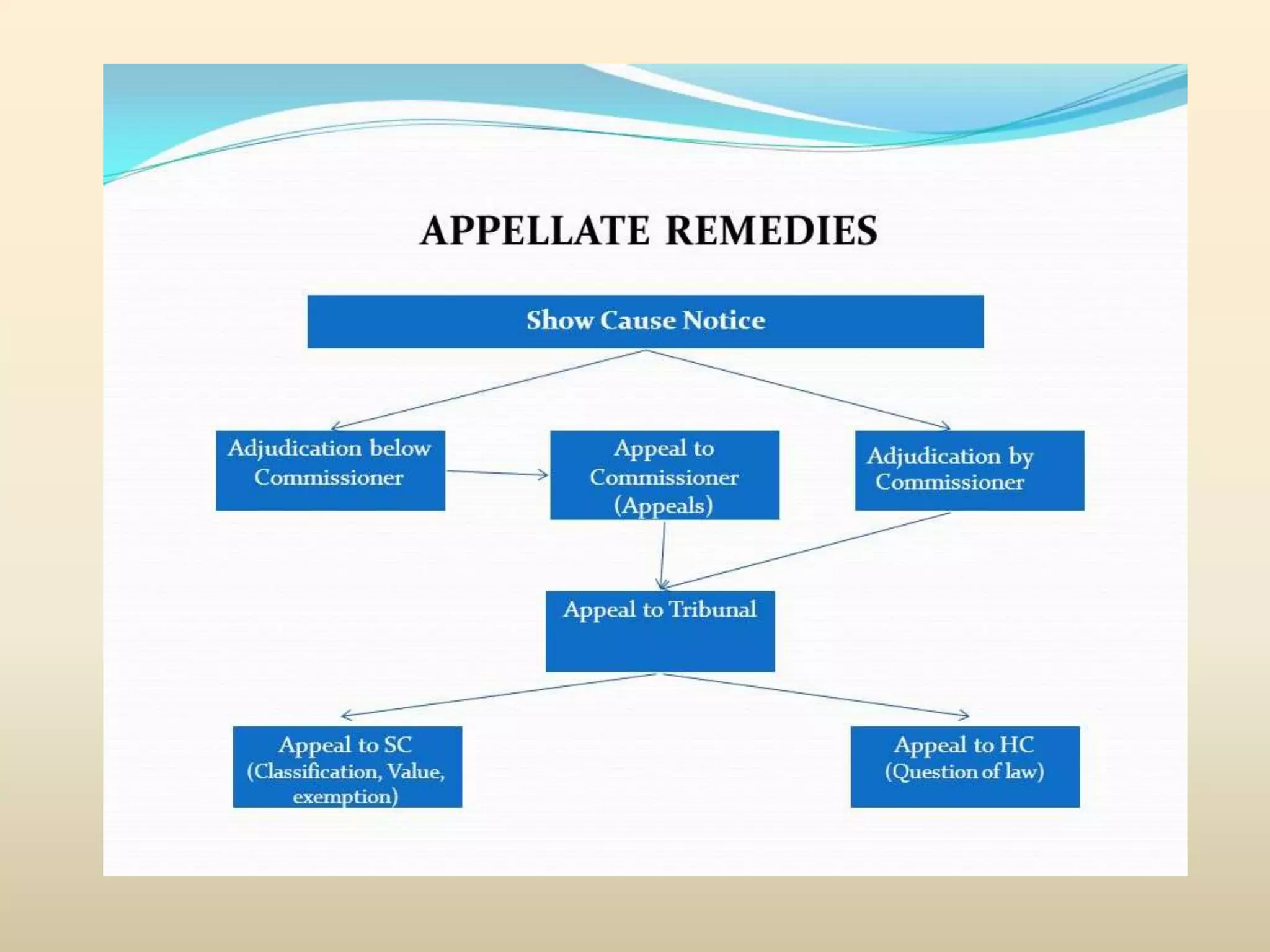
This document discusses penalties, offenses, and appeals related to central excise duties in India. It notes that penalties can be imposed for non-payment or underpayment of duties, unauthorized manufacture or storage of goods, and other violations. It outlines penalties as a percentage of unpaid duties and potential imprisonment. The document also describes the process for appeals, which can be made to the Commissioner (Appeals), Appellate Tribunal, High Court, and Supreme Court. It provides details on the timeline, form, and fees for each level of appeal.