Embed presentation
Downloaded 126 times


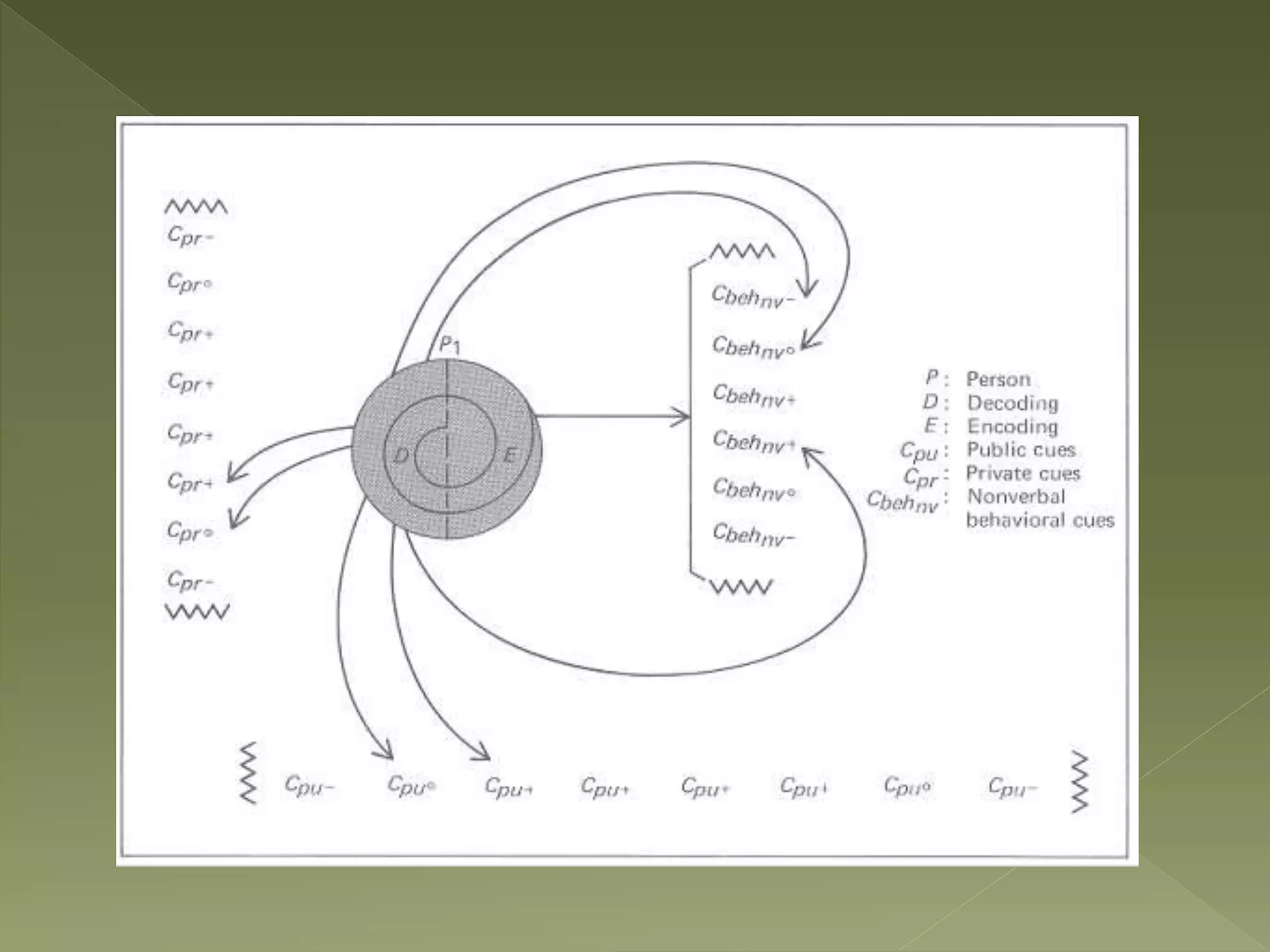
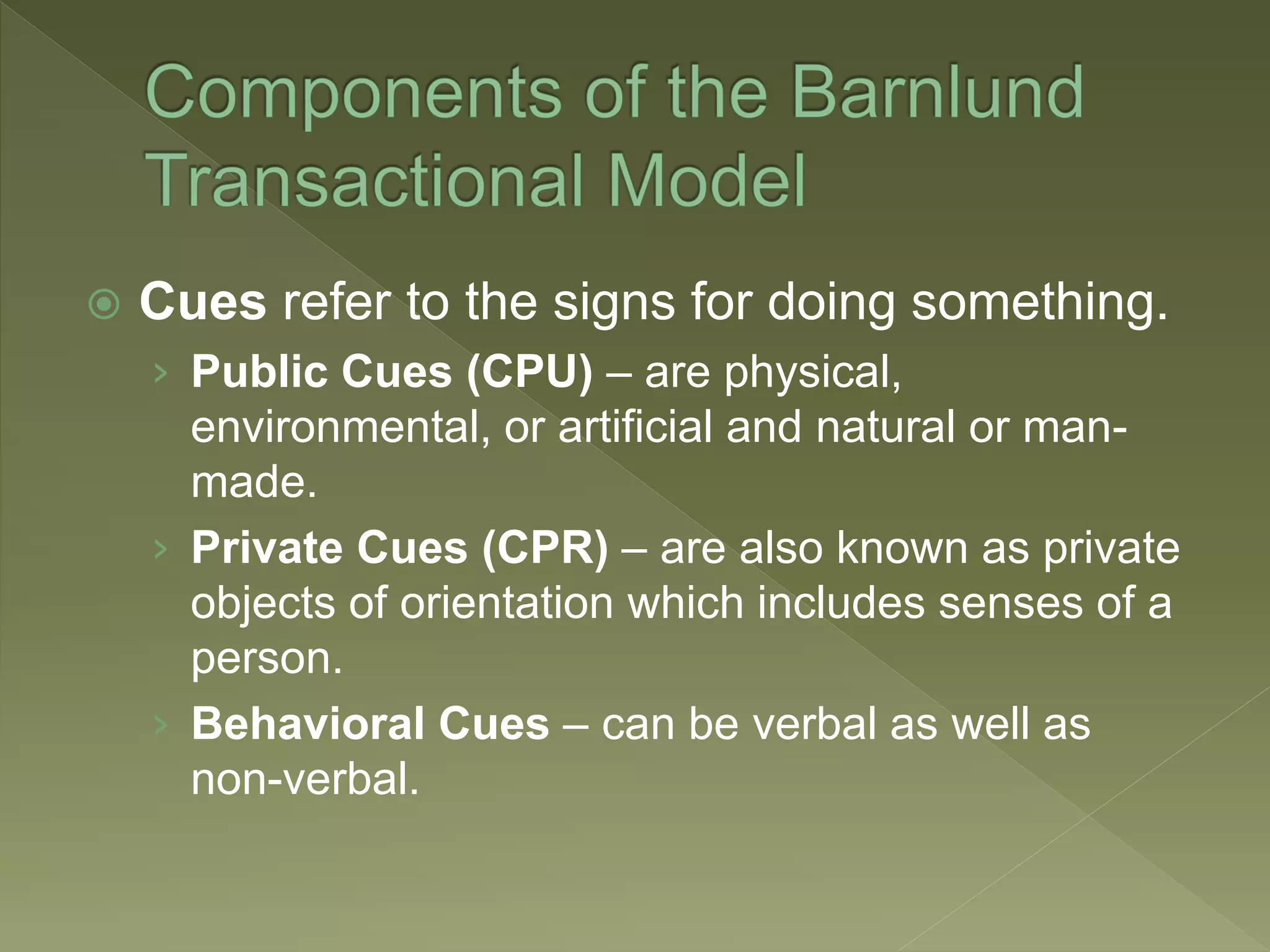
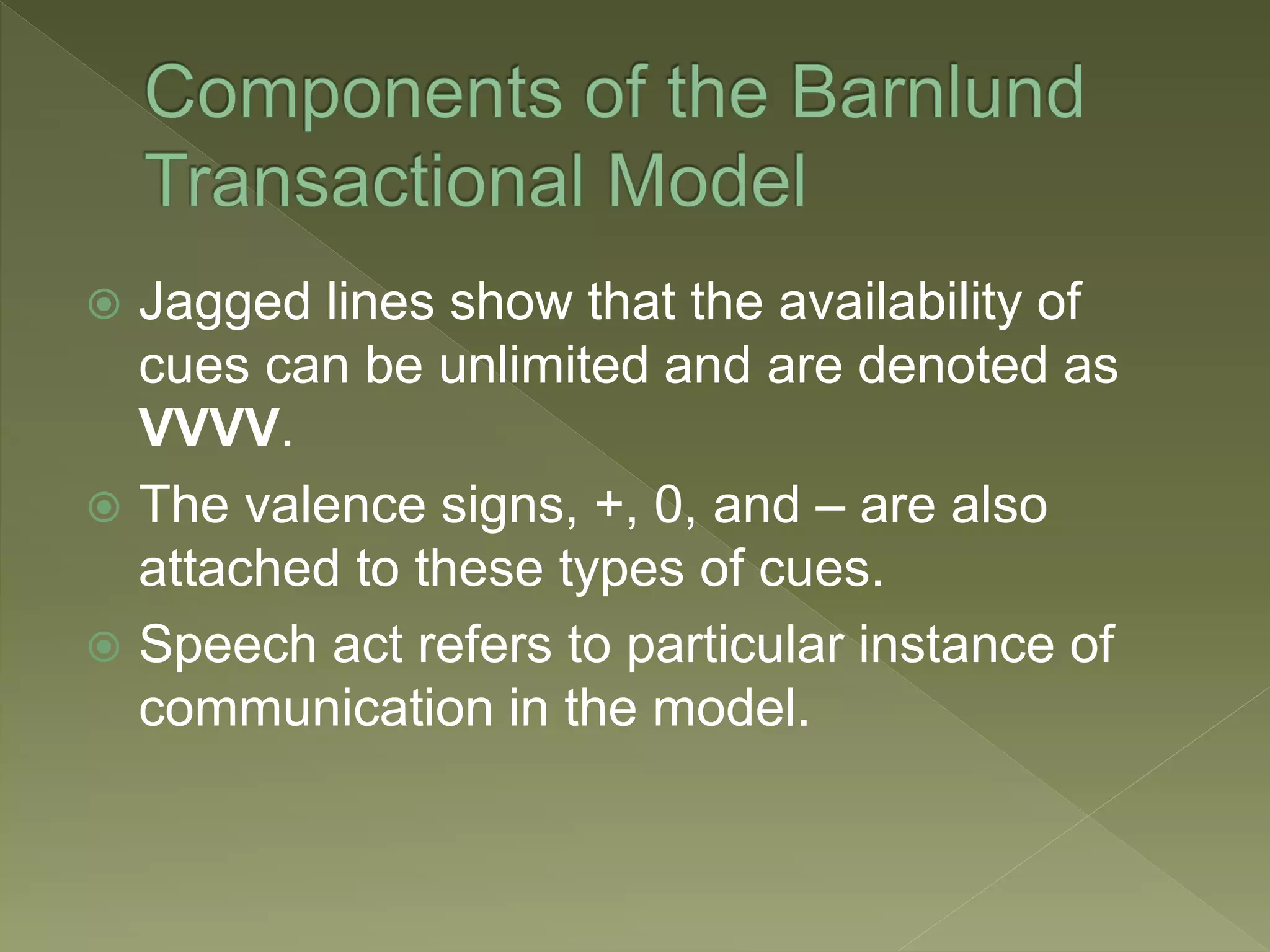

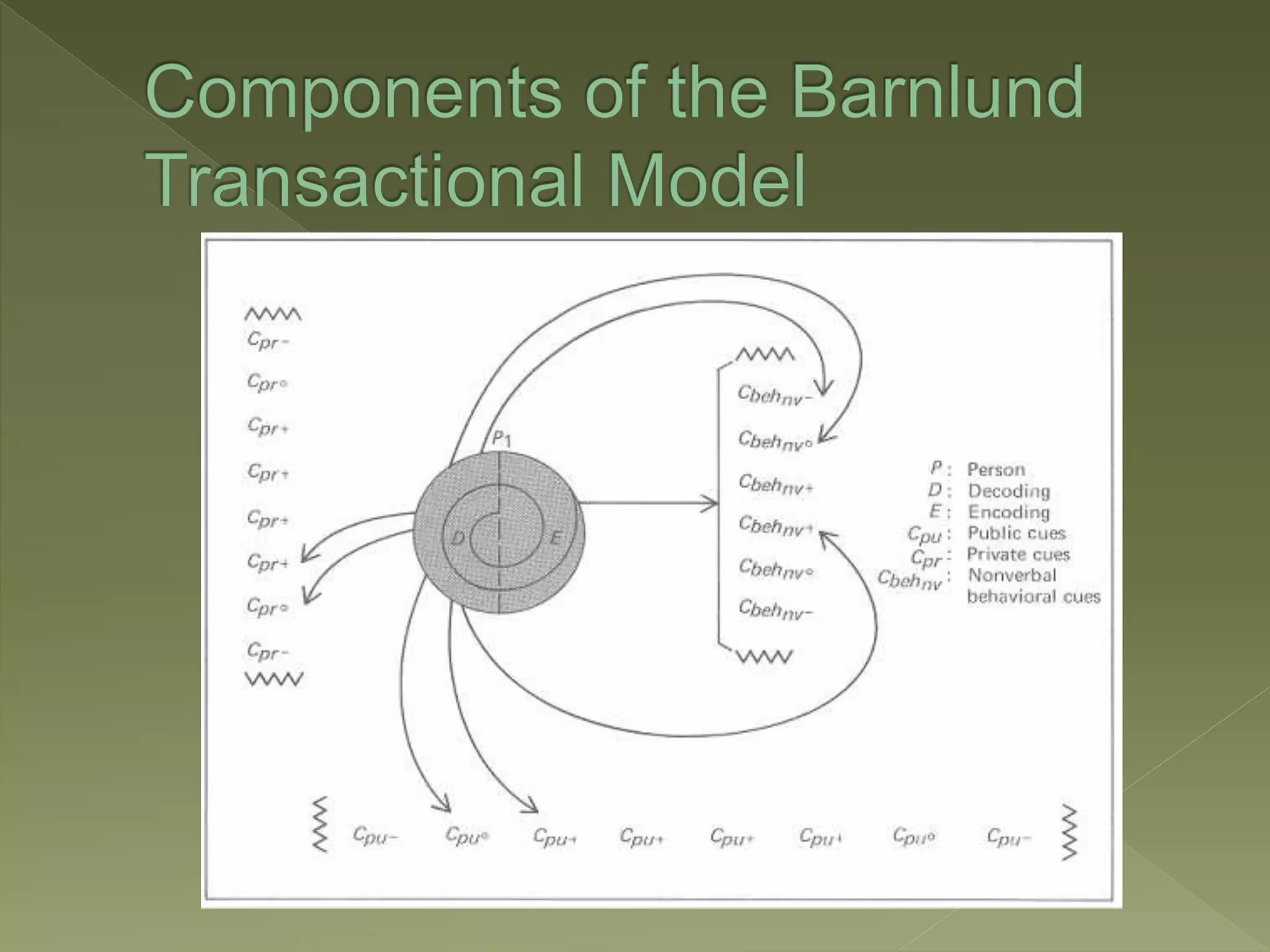


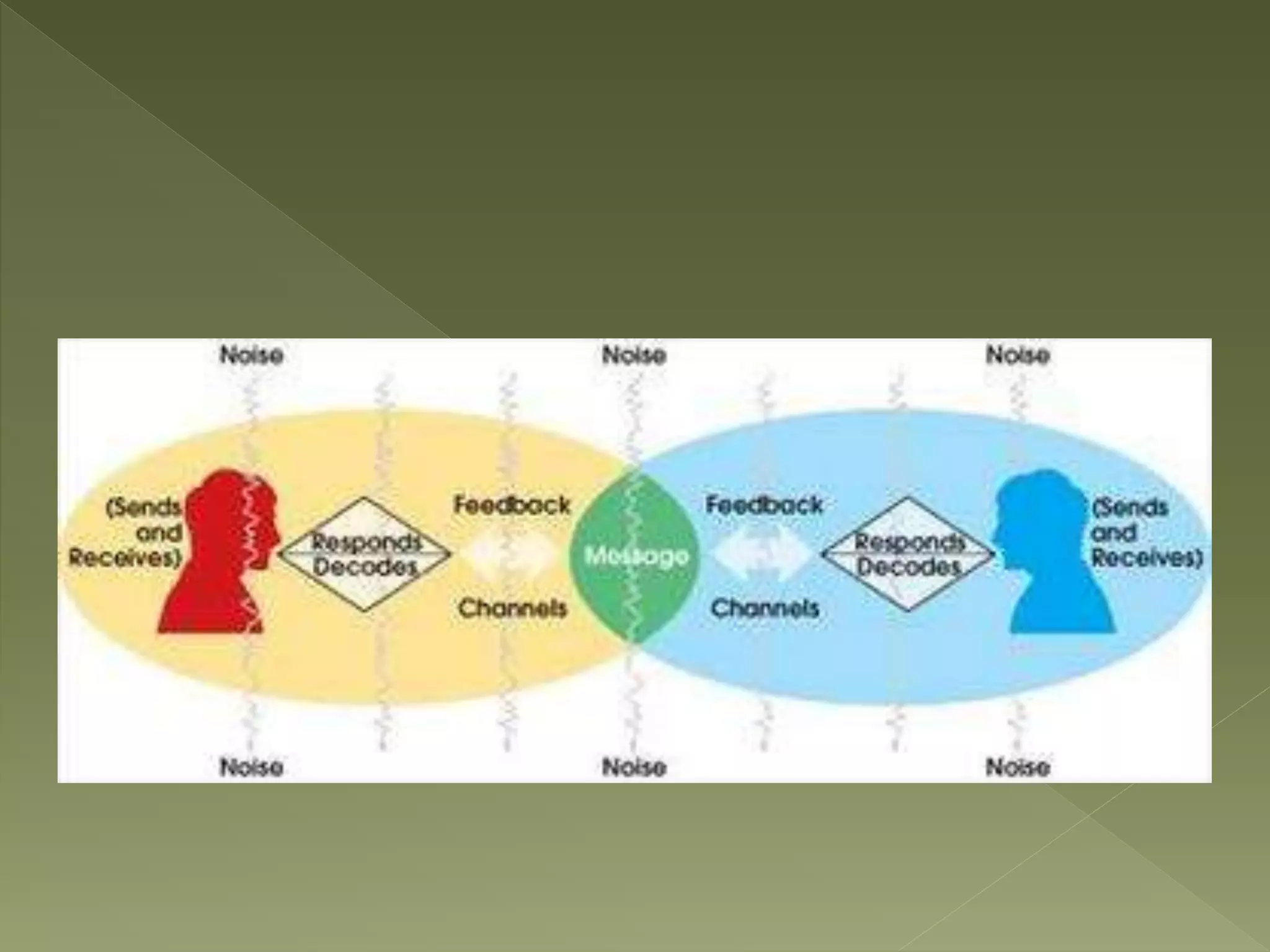
Barnlund's transactional model of communication was proposed in 1970 and presents a multi-layered feedback system where anyone can be a sender and receiver. It includes both verbal and non-verbal layers of feedback and is considered the most systematic of the functional models. The model accounts for public cues, private cues, behavioral cues, filters, noise and feedback in the communication process between sender and receiver.









