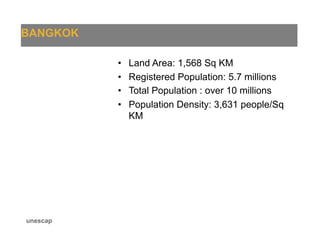
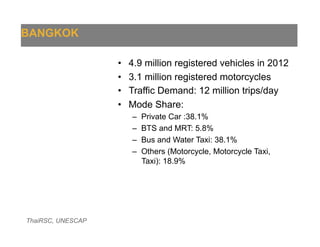
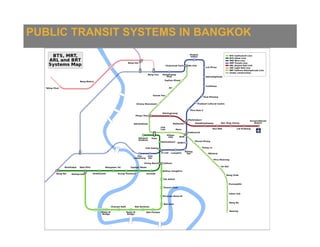
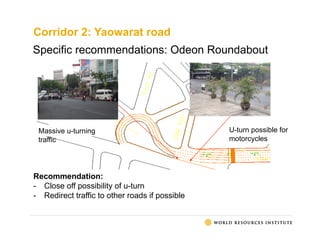
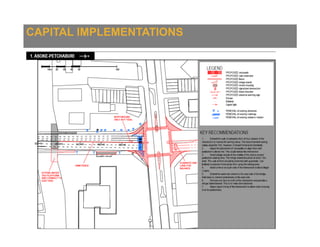
The document presents an overview of traffic issues in Bangkok, highlighting its significant population, vehicle registration, and traffic demand statistics. It outlines the high traffic fatality rate and the vulnerability of road users, especially motorcyclists, and provides a summary of key findings from road design inspections with specific recommendations for improvements. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of collaboration with various stakeholders and proposes short-term implementations to enhance road safety.