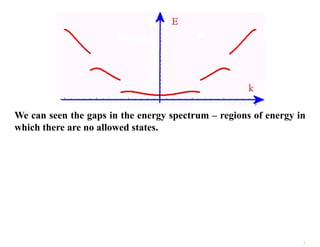
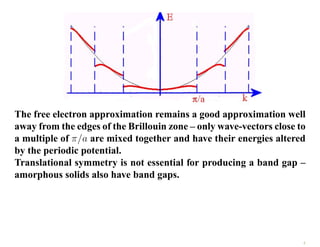
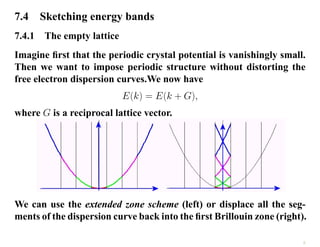
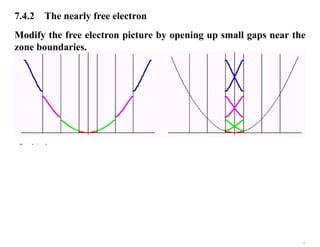
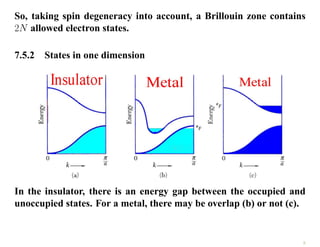
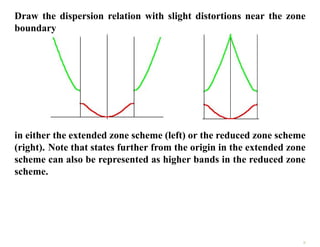
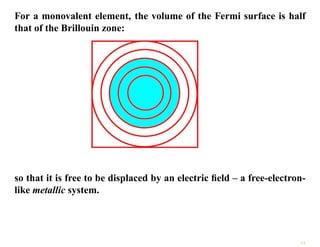
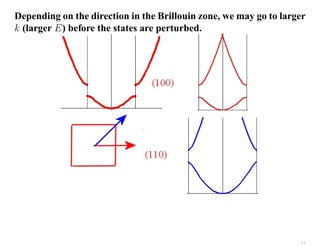
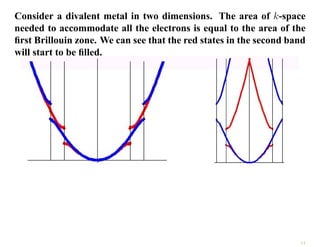
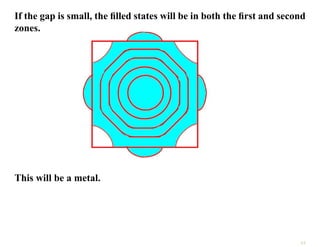
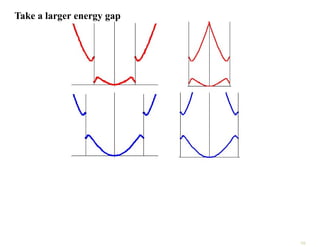
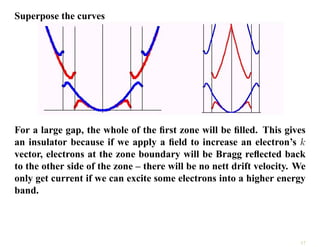
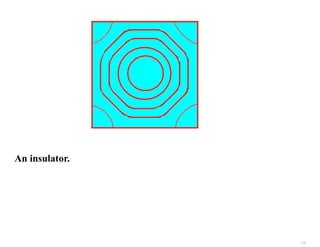
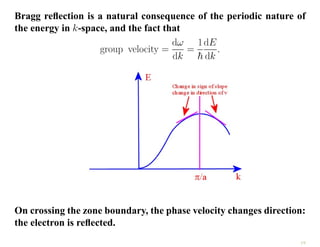
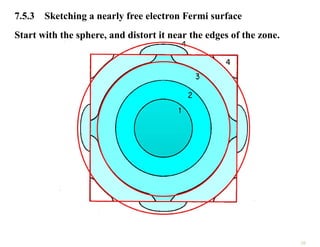
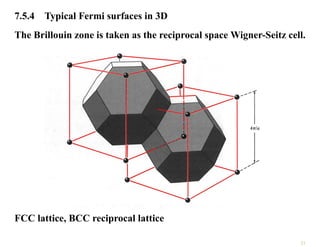
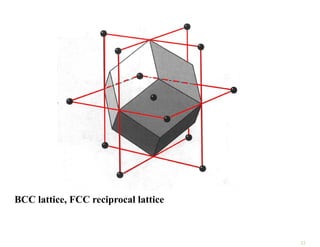
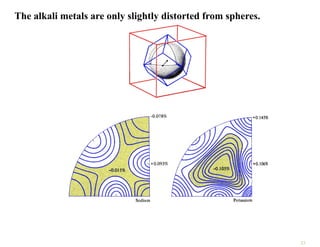
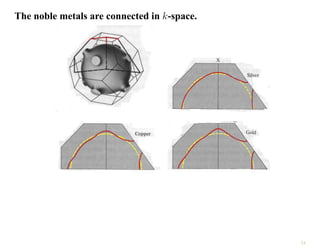
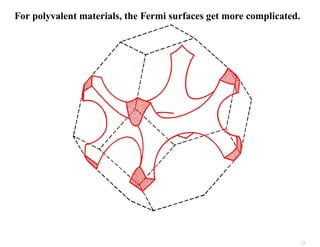
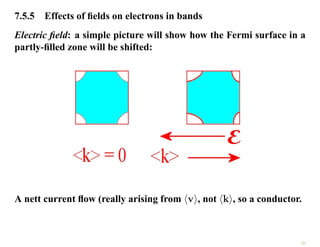
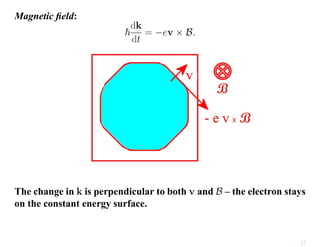
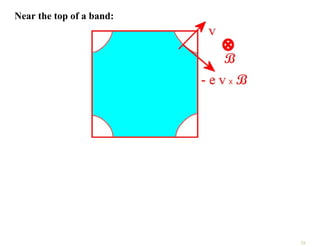
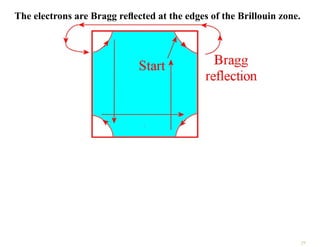
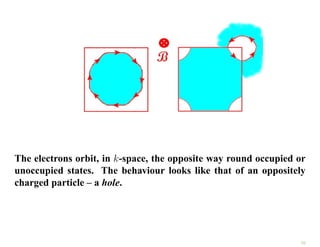
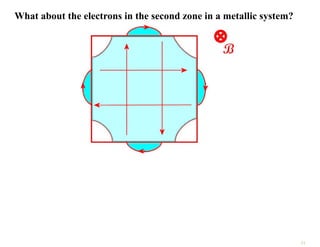
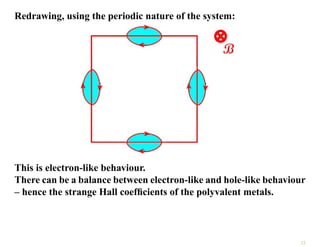
The document discusses the nearly free electron model in solid state physics, detailing concepts such as energy gaps in the electronic structure, the density of states, and the characteristics of Fermi surfaces. It explains how band structure arises due to periodic potentials and the implications of gaps for semiconductors and insulators. Additionally, it examines the effects of electric and magnetic fields on electrons in bands and the behavior of electrons near the Brillouin zone boundaries.