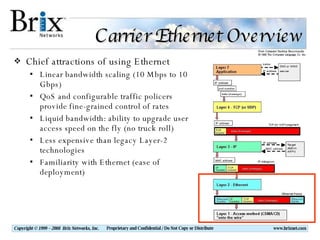
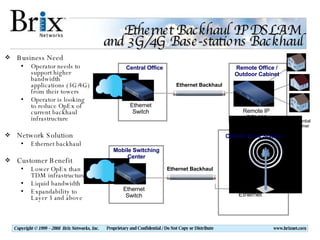
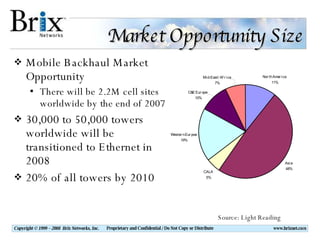
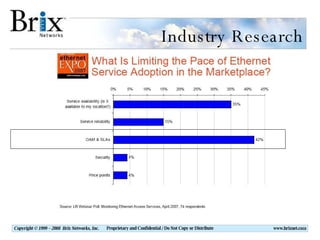
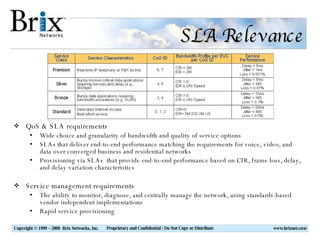
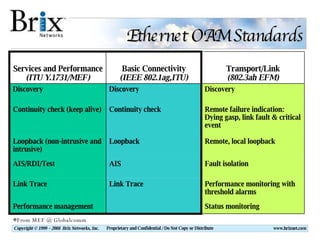
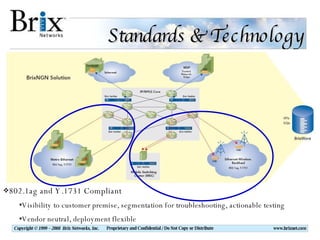
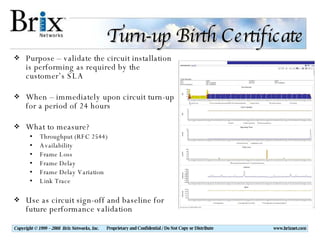
Carrier Ethernet is a standardized Ethernet service that provides bandwidth scaling and quality of service guarantees. Typical deployments include Ethernet backhaul for mobile networks and business Ethernet access across multiple business sites. Service level agreements are important for Carrier Ethernet services to ensure performance for applications like voice and video. Standards-based solutions exist for validating service level agreements through turn-up testing, ongoing monitoring, and troubleshooting network issues. When choosing a service assurance solution, considerations include multi-vendor flexibility, operational capabilities, data analysis and reporting tools, and the ability to integrate with other network management systems.