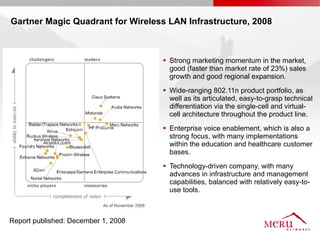
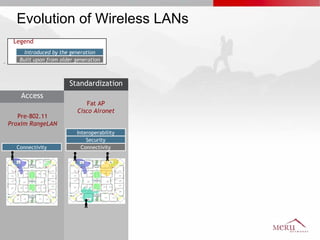
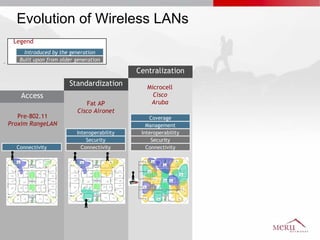
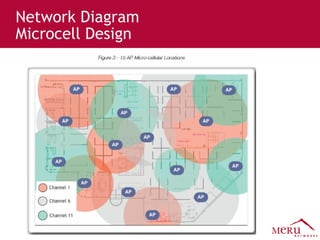
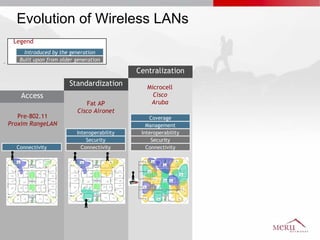
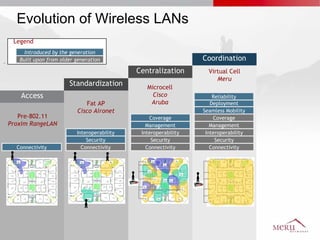
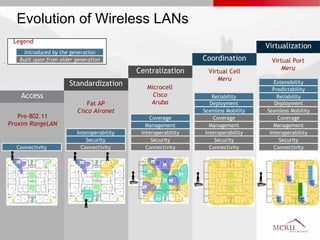
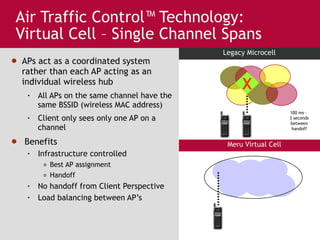
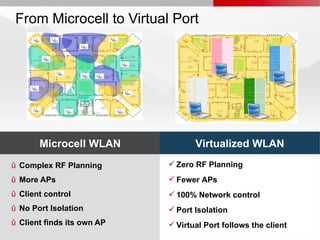
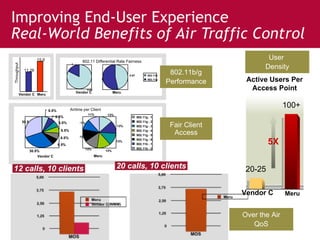
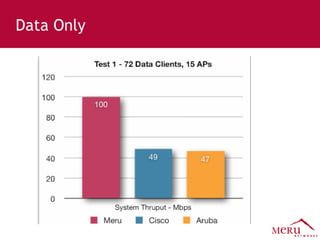
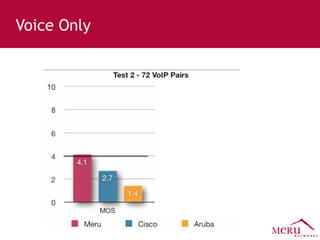
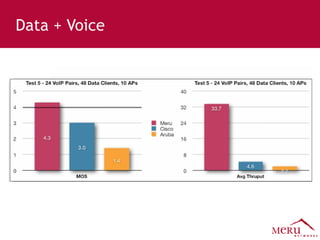
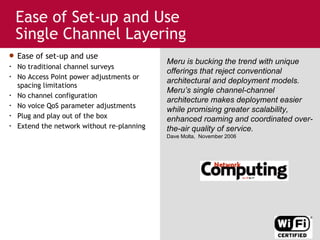
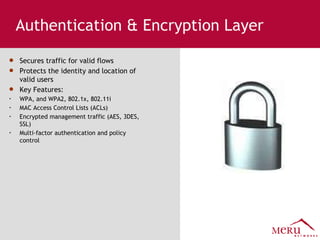
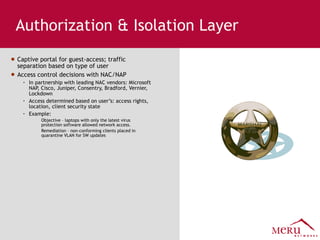
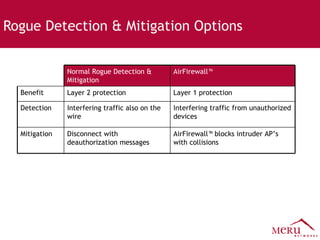
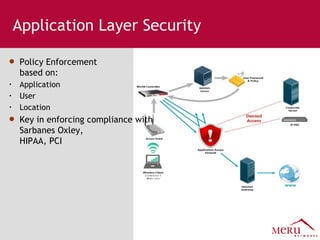
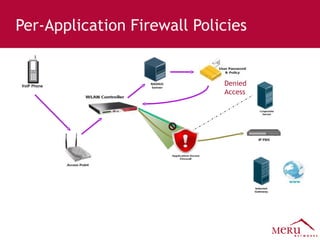
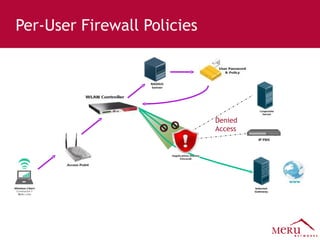
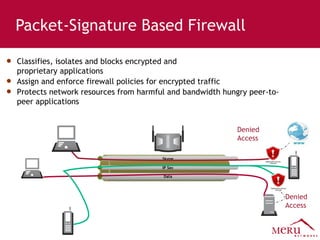
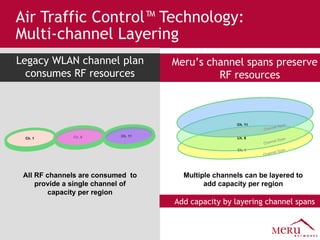
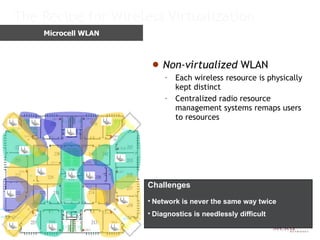
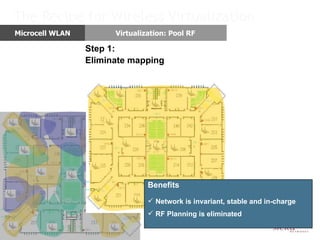
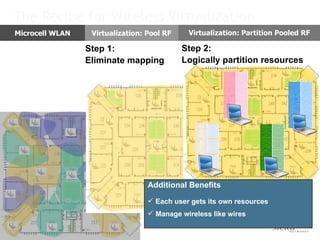
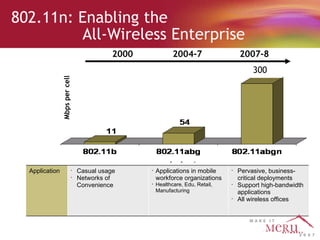
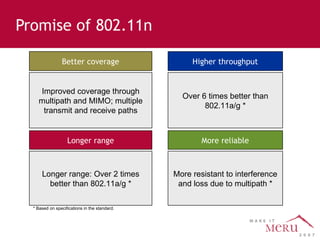
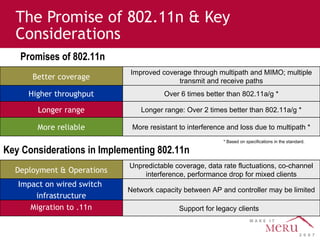
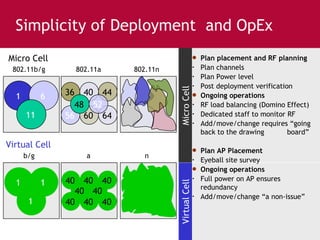
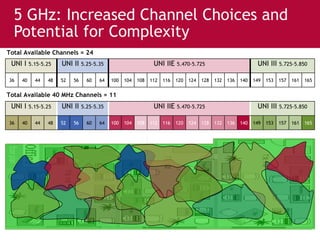
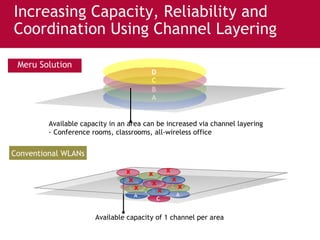
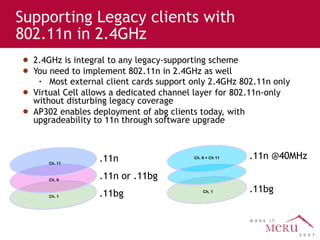
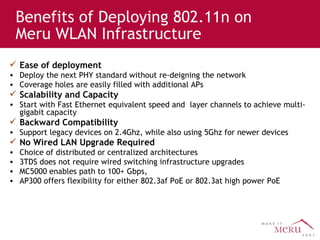
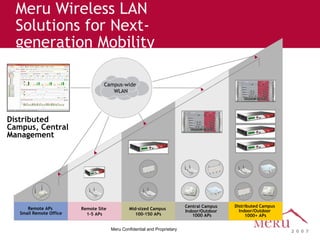
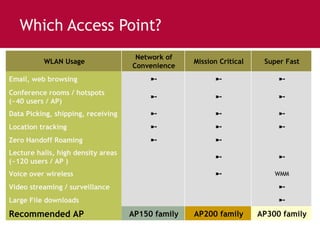
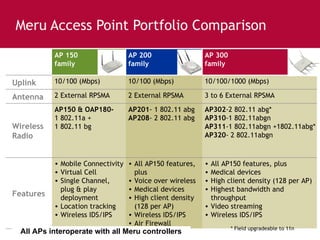
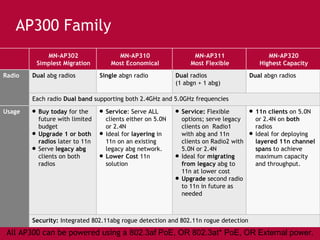
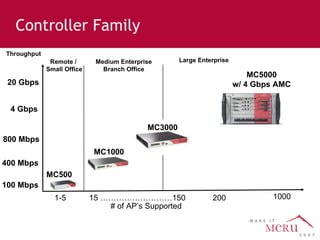
Meru's wireless LAN solutions emphasize a unique architecture enabling seamless connectivity, scalability, and efficient voice applications, showing strong growth and regional expansion in the market. The technology supports advanced features such as application-aware optimization, enhanced security, and innovative wireless management that simplify deployment and reduce operational costs. Notable deployments highlight the performance improvements and high user density capabilities offered by the Meru system.
![Wireless without Compromise™ Tim MacMillan Integra Data Systems Corp. 705-761-3645 [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/merupresentation-1271179694137-phpapp01/85/Meru-Presentation-1-320.jpg)








![For more information on WLAN virtualization and Meru product offerings, please visit www.merunetworks.com or contact me for a personal presentation: Tim MacMillan 705-761-3645 [email_address] Questions and Answers ? ? ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/merupresentation-1271179694137-phpapp01/85/Meru-Presentation-52-320.jpg)
