1. The document discusses key quality indicators (KQIs) and quality of experience (QoE) metrics for evaluating network performance from the end user perspective.
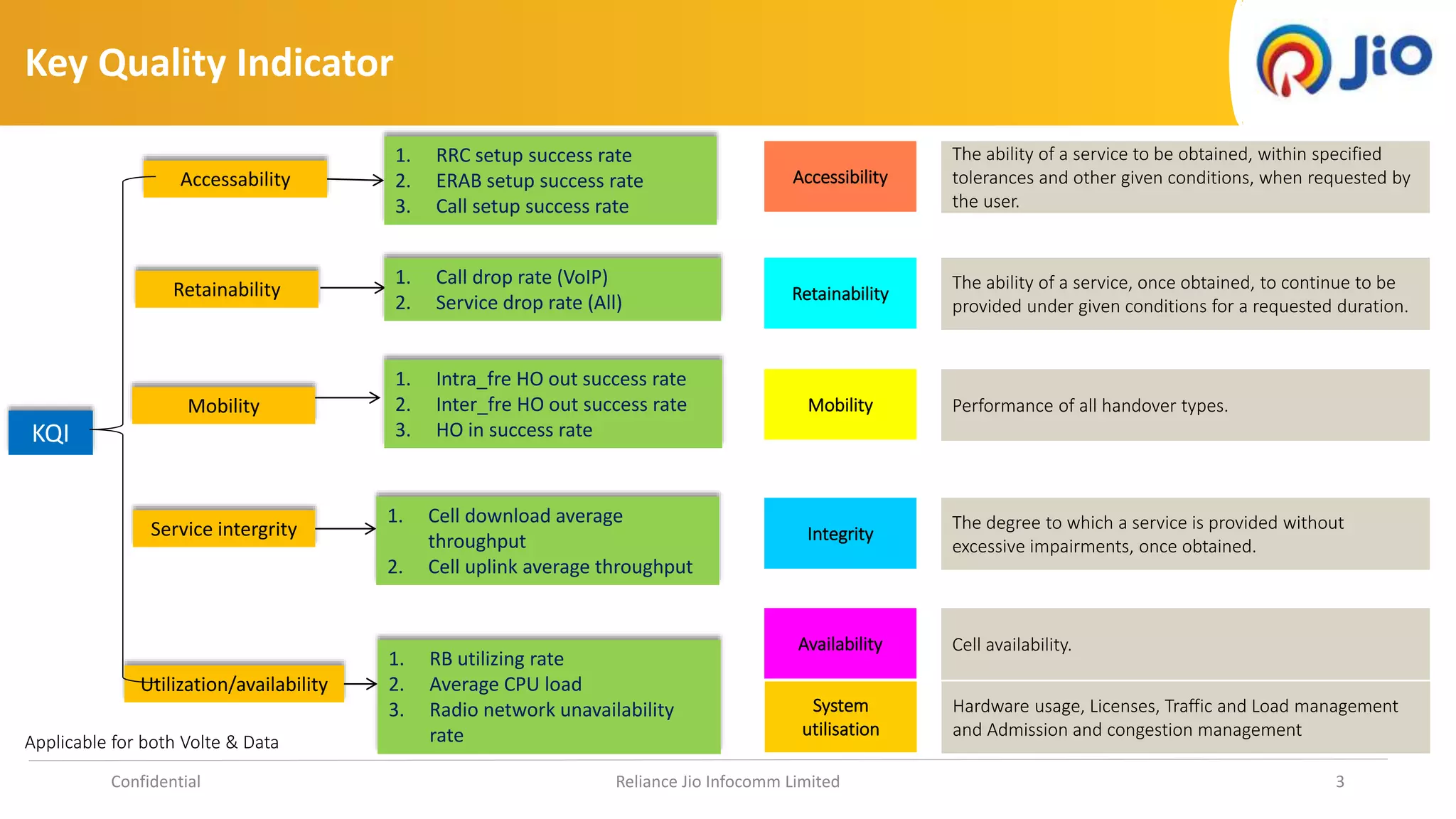
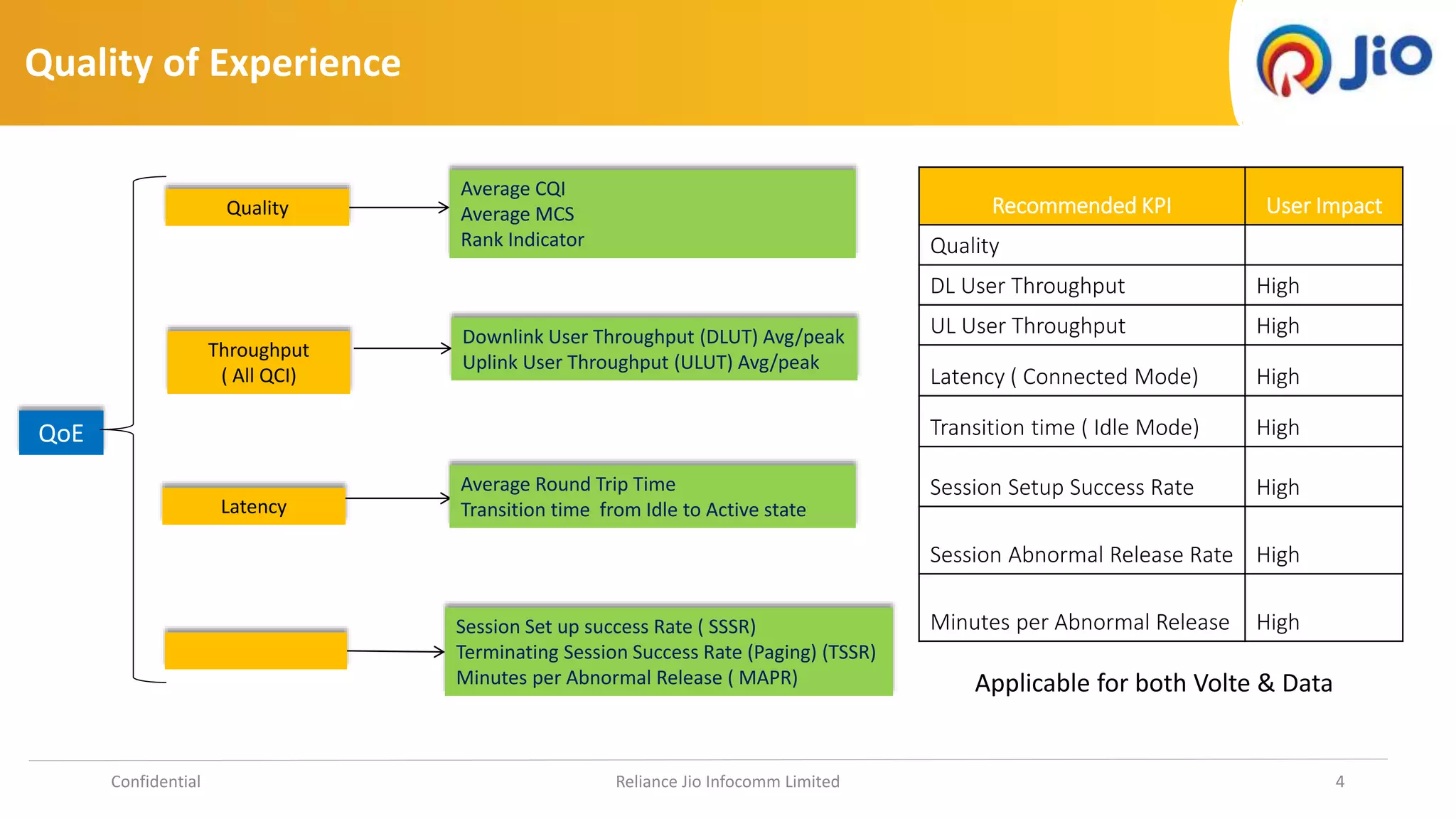
2. KQIs measure specific parts of the network system but don't necessarily impact user experience, while QoEs are calculated from performance metrics and indicate macro-level user perception.
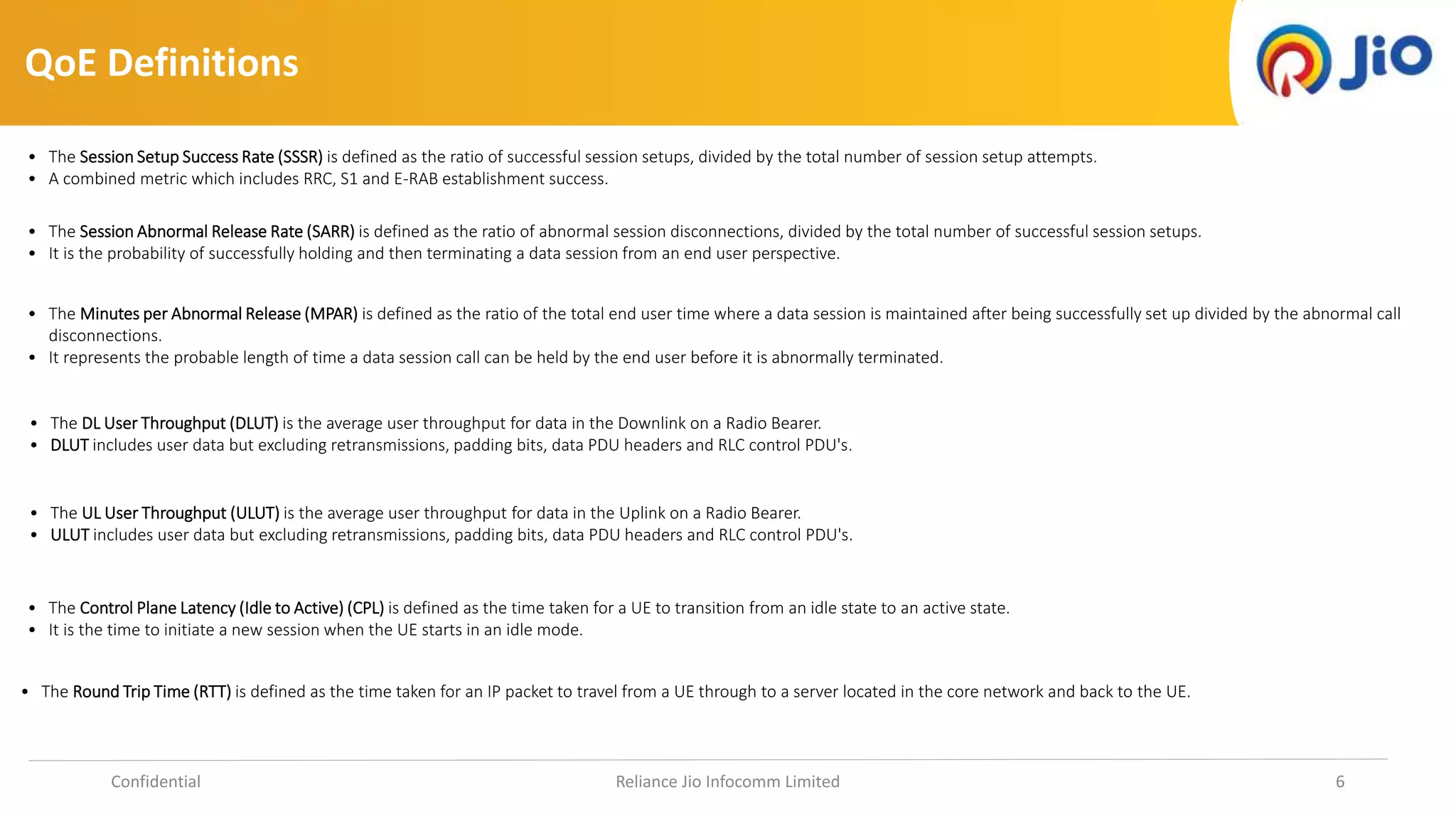
3. The document lists examples of KQIs and QoEs including session setup success rates, throughput measures, latency, and abnormal call release rates.