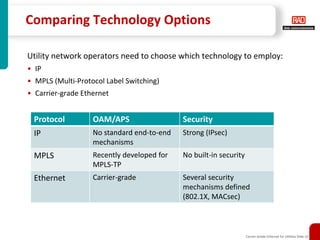
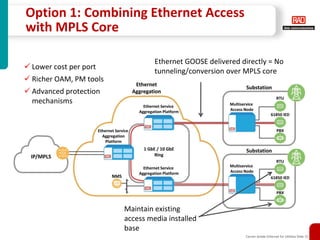
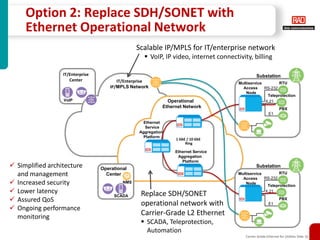
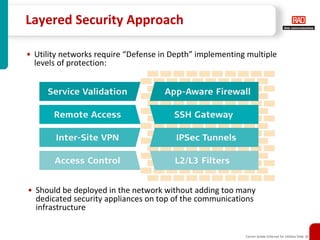
This document discusses how carrier-grade Ethernet can ensure reliable communications for utility networks transitioning to support smart grid applications. It covers Ethernet mechanisms that provide carrier-grade performance such as quality of service, resiliency, monitoring and timing synchronization. Choosing between IP, MPLS and Ethernet options is discussed. The document also addresses network security considerations and introduces RAD's carrier-grade Ethernet product portfolio for power utilities.