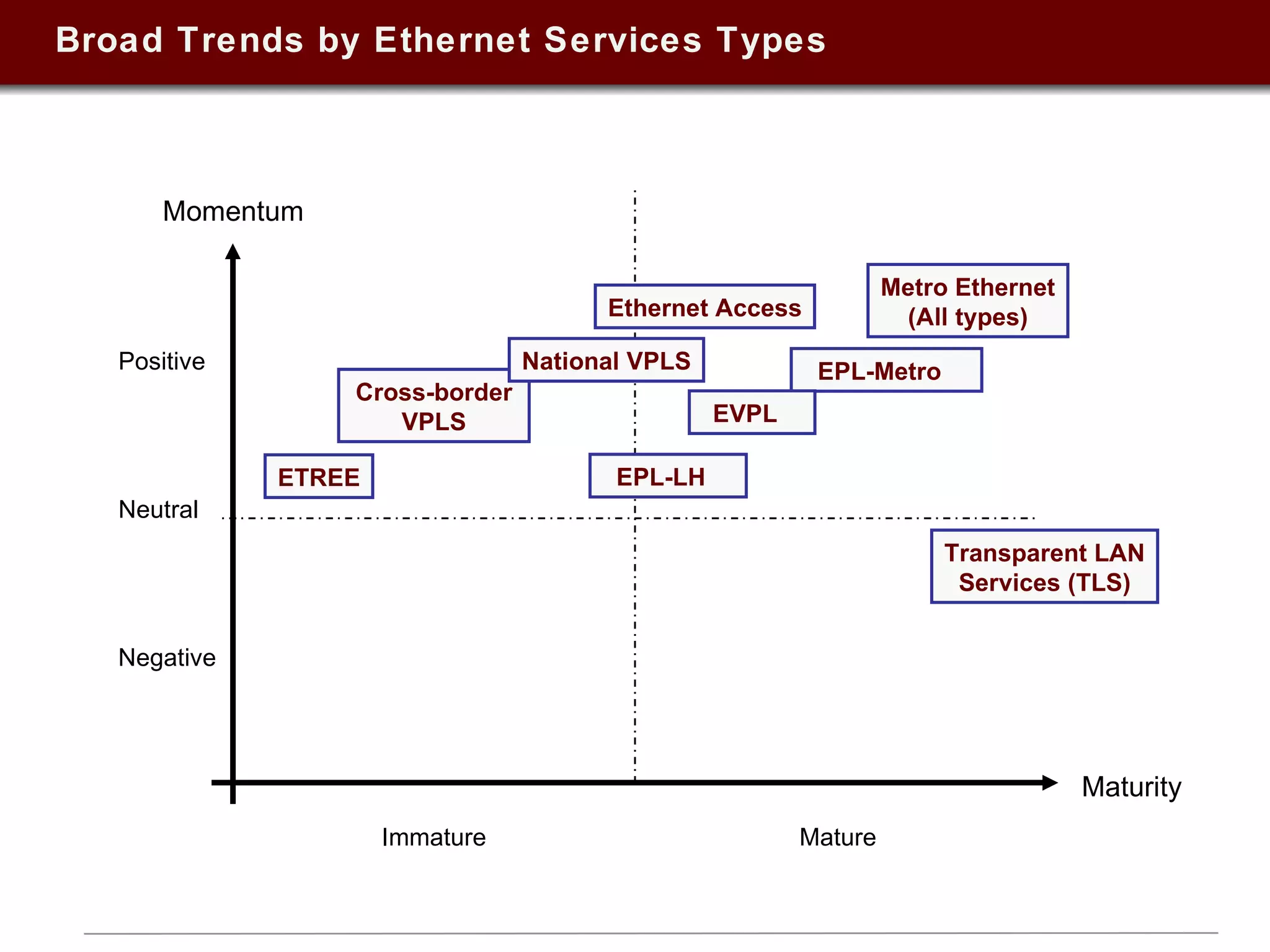
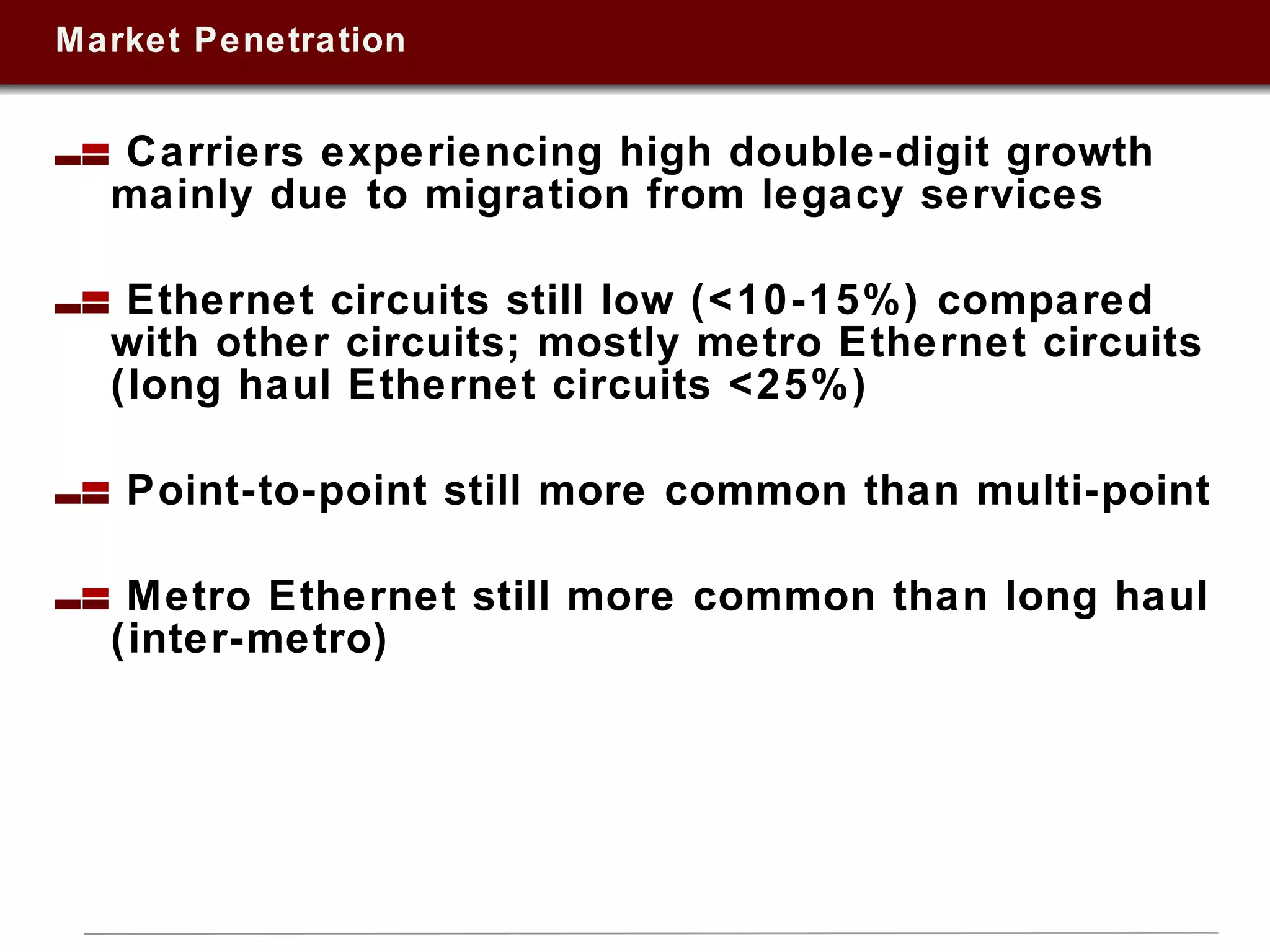
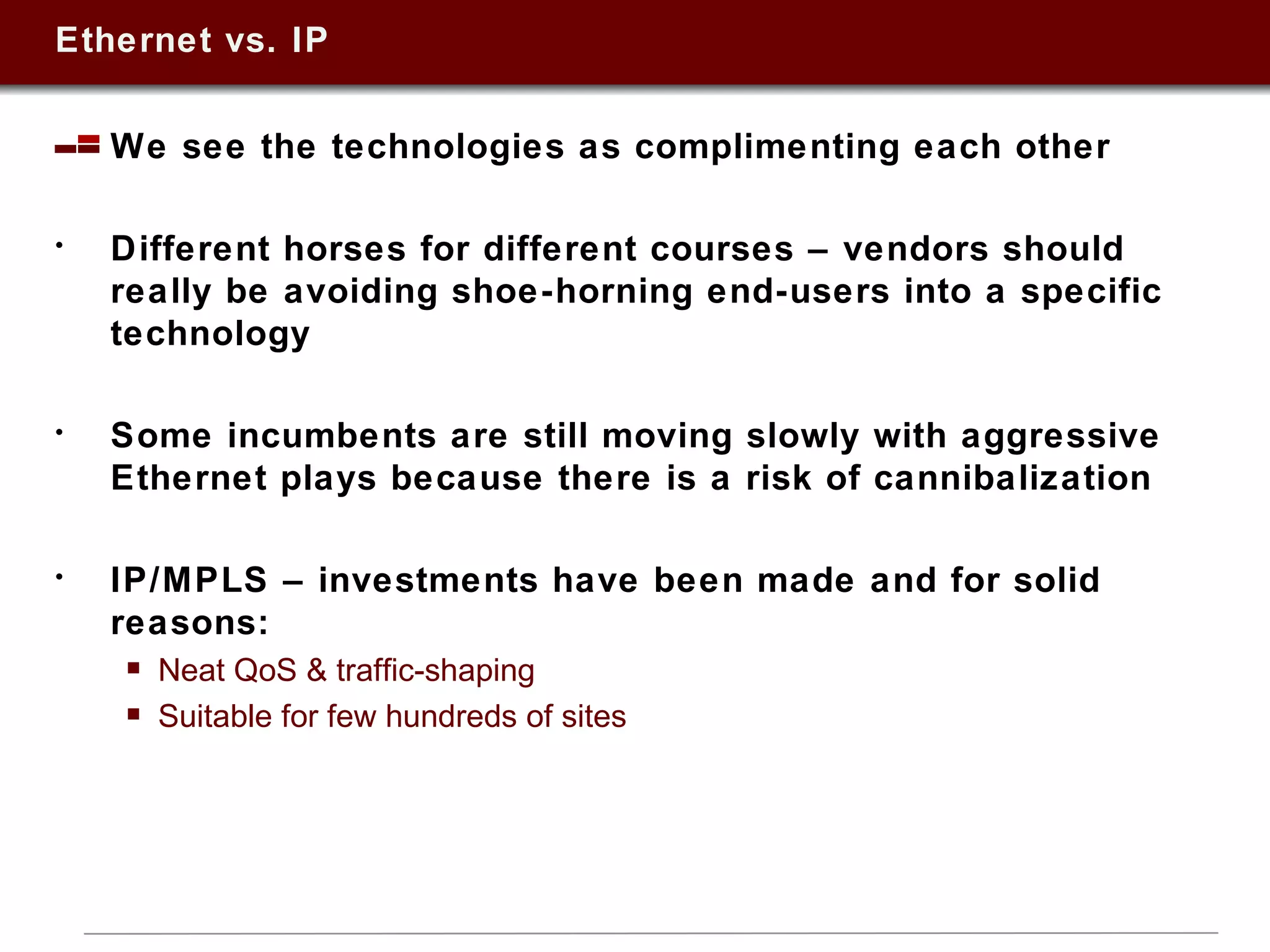
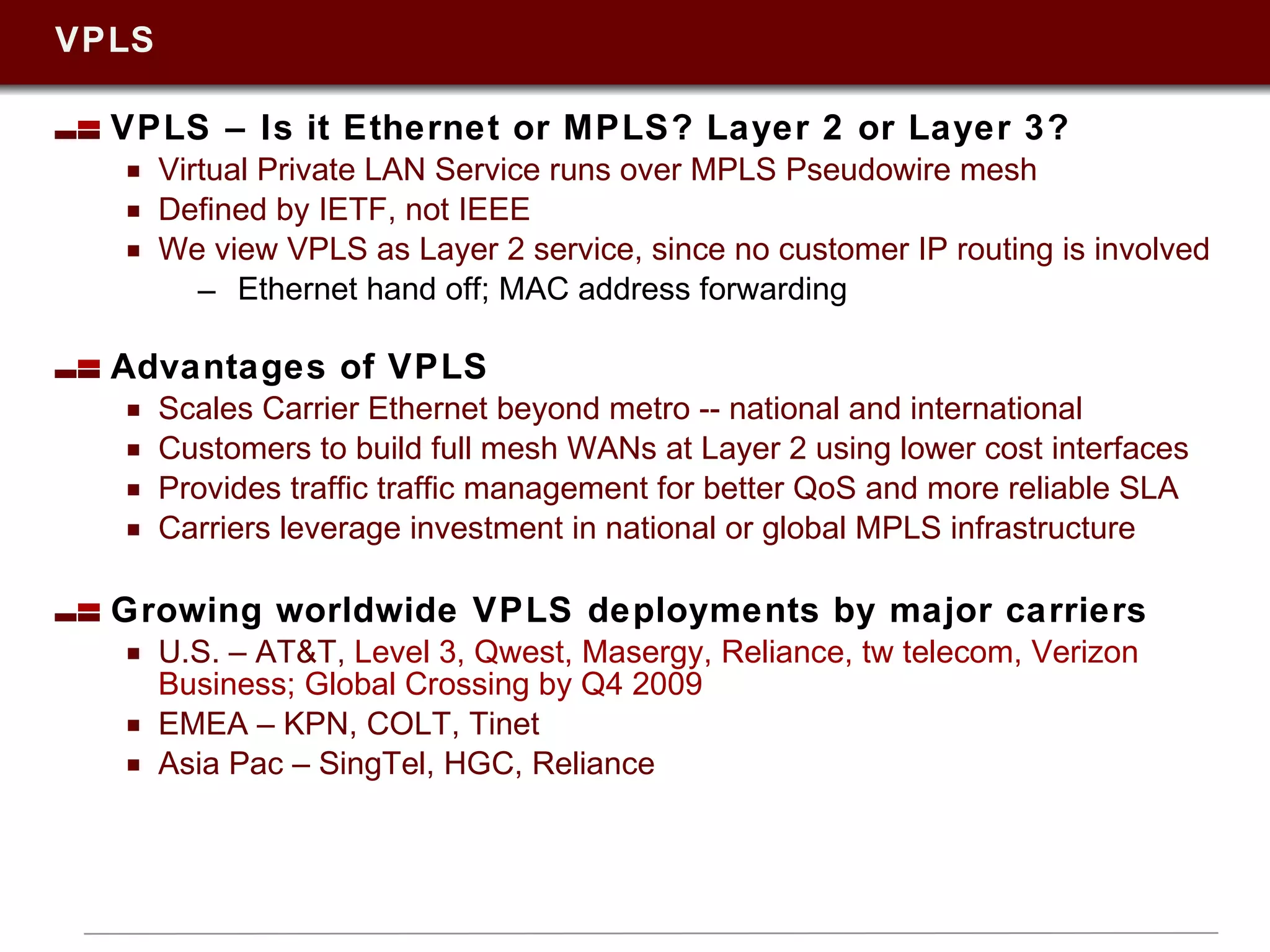
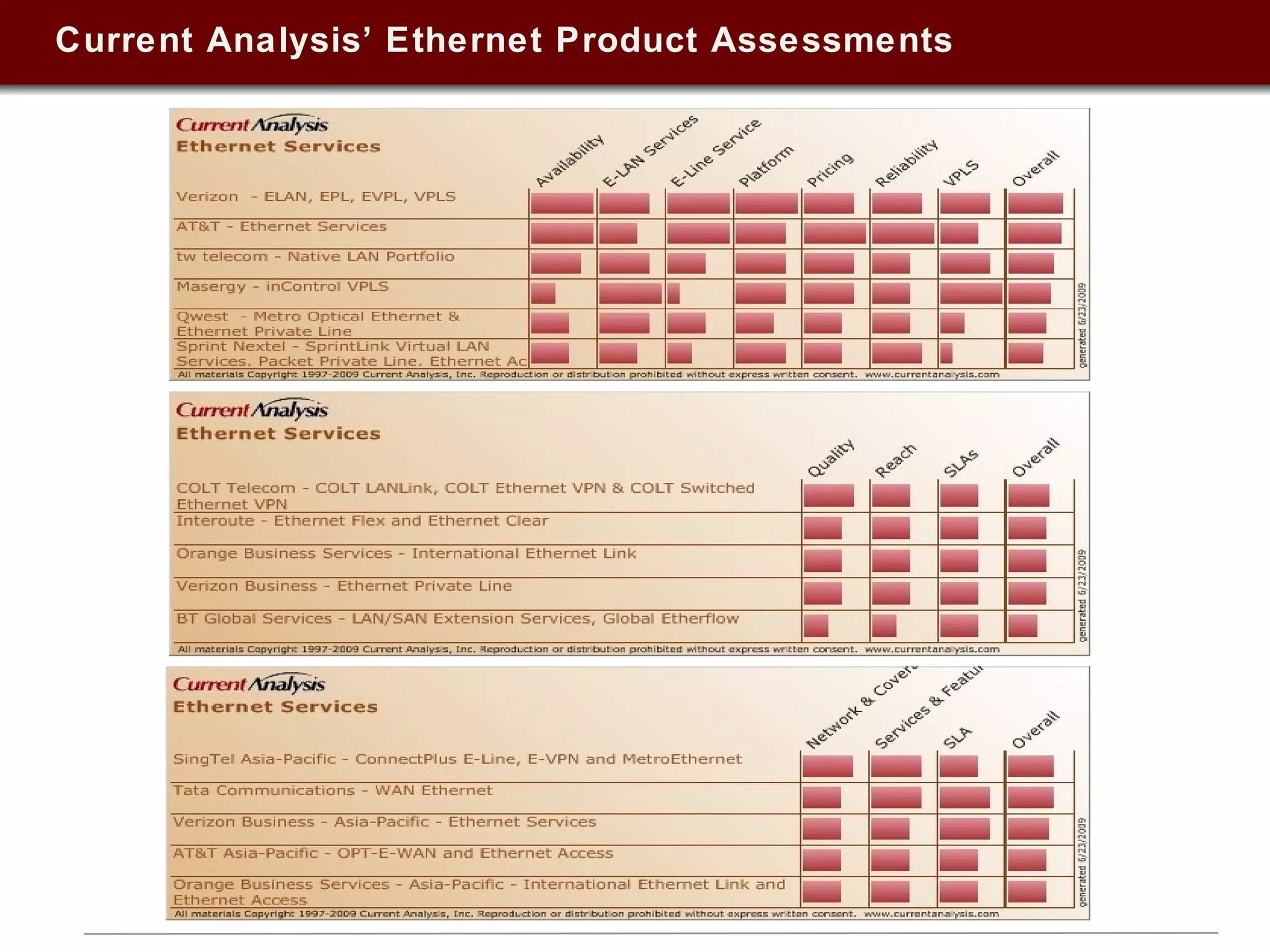
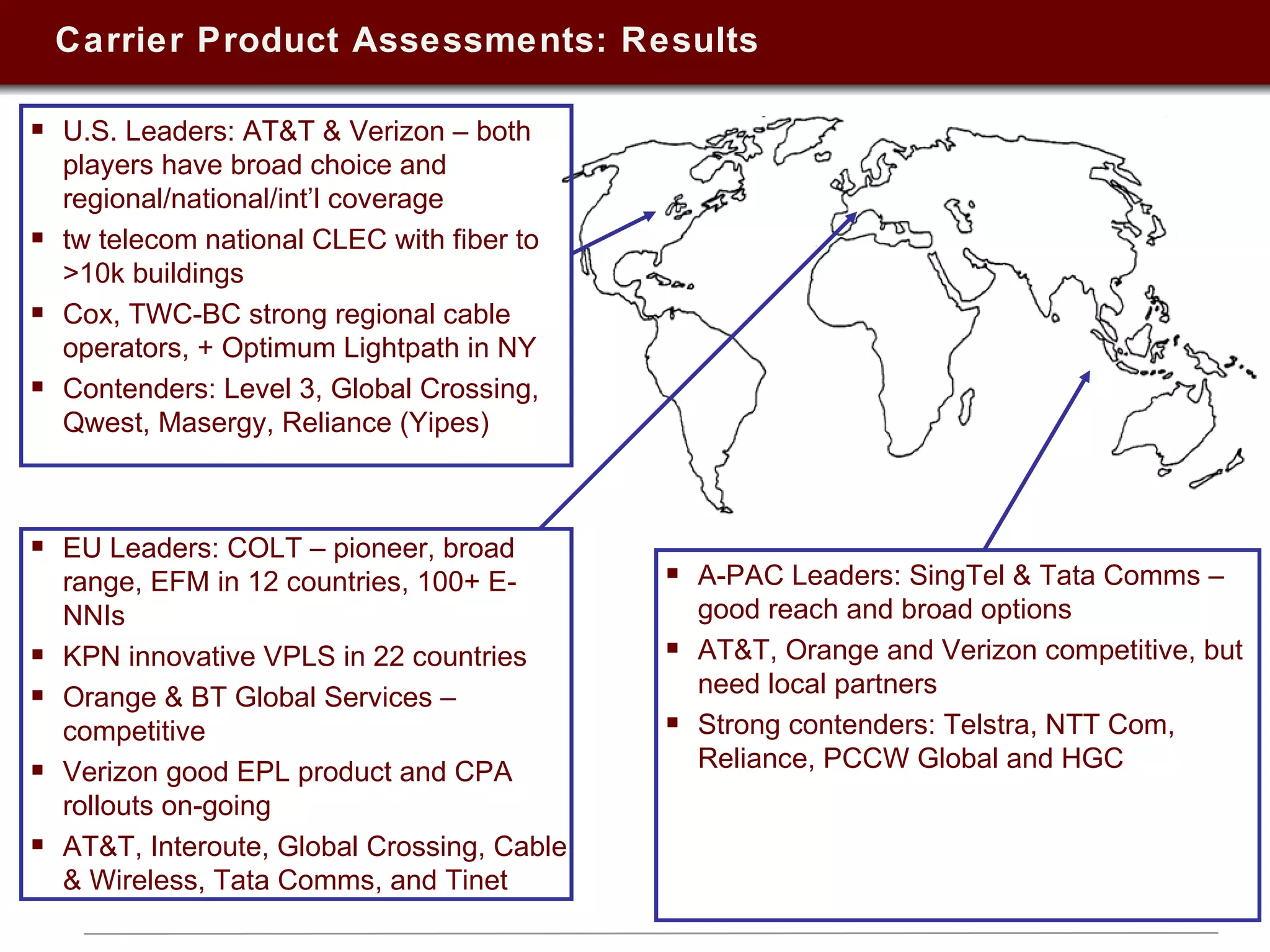
This document summarizes a presentation on Ethernet services given in 2009. It discusses trends in Ethernet market penetration globally, controversies around Ethernet vs. IP technologies, how carriers are expanding Ethernet access through fiber, bonded copper, and E-NNIs. Key vertical markets and applications driving adoption are described. Factors for evaluating successful Ethernet service provider portfolios are outlined. Leaders in Ethernet services in the US, Europe, and Asia-Pacific are identified based on network reach and service breadth. Future directions for carriers are also summarized.