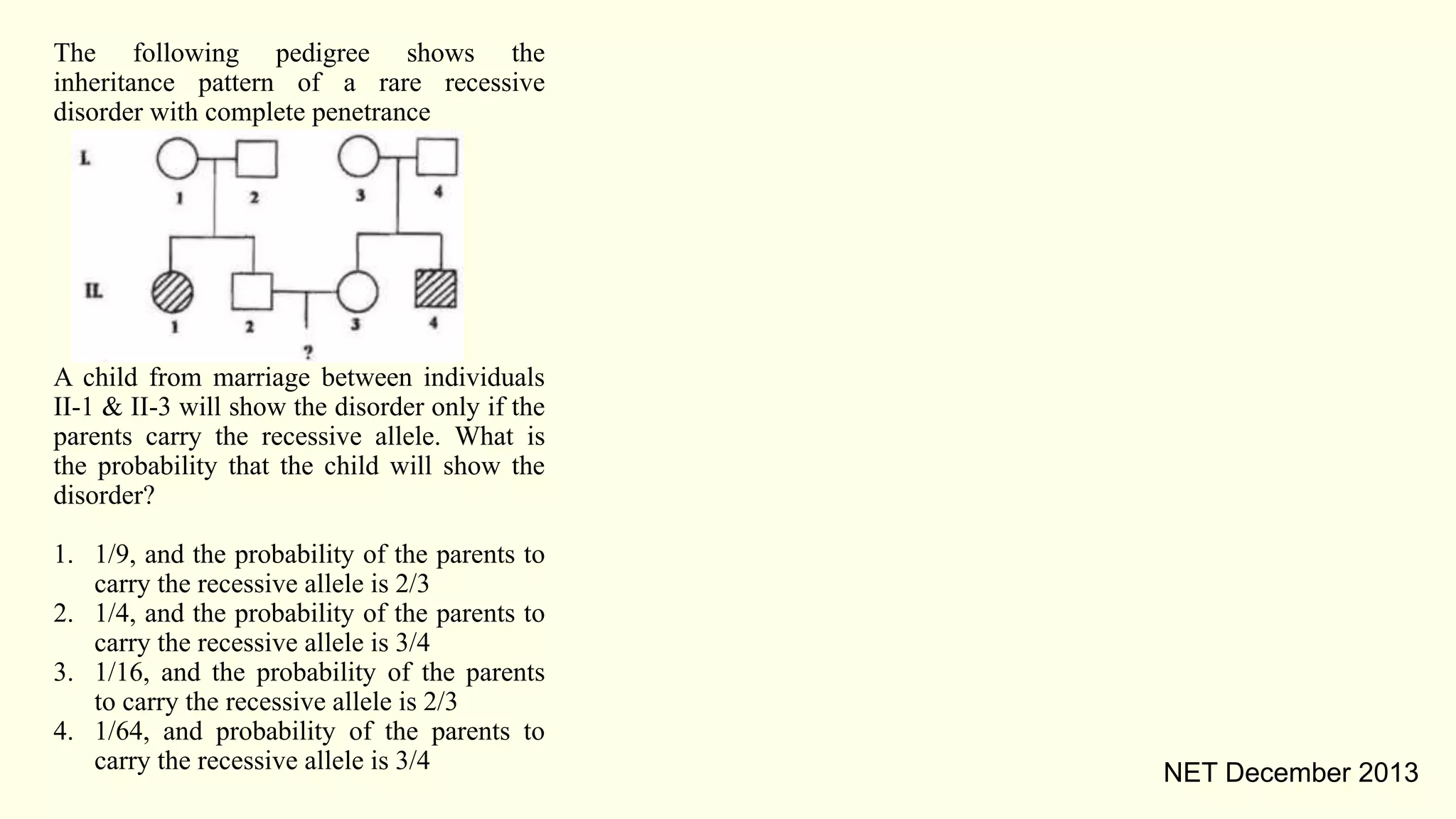
This document summarizes several pedigree analyses involving inheritance patterns of traits:
1. A pedigree is presented where a woman has a 100% chance of passing on a defective gene to her daughter based on her genotype. Calculations are shown for determining the probability that her grandson will have the defective gene.
2. Multiple pedigrees demonstrate autosomal recessive inheritance patterns based on affected and unaffected family members. X-linked inheritance is ruled out.
3. The mode of inheritance is determined to be autosomal recessive for a pedigree where an affected mother passes the trait to all her children. Mitochondrial inheritance and variable expression are discussed.
4. Probabilities are calculated for heterozygous parents and