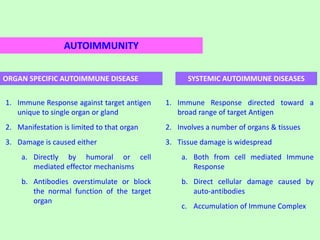
This document discusses autoimmunity, which occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues and organs. It describes how Paul Ehrlich first proposed the concept of "horror autotoxicus" to explain this phenomenon. The mechanisms of self-tolerance that normally prevent autoimmunity can fail, leading to either organ-specific or systemic autoimmune diseases. Examples of organ-specific diseases include Hashimoto's thyroiditis, pernicious anemia, and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis are examples of systemic autoimmune diseases provided.