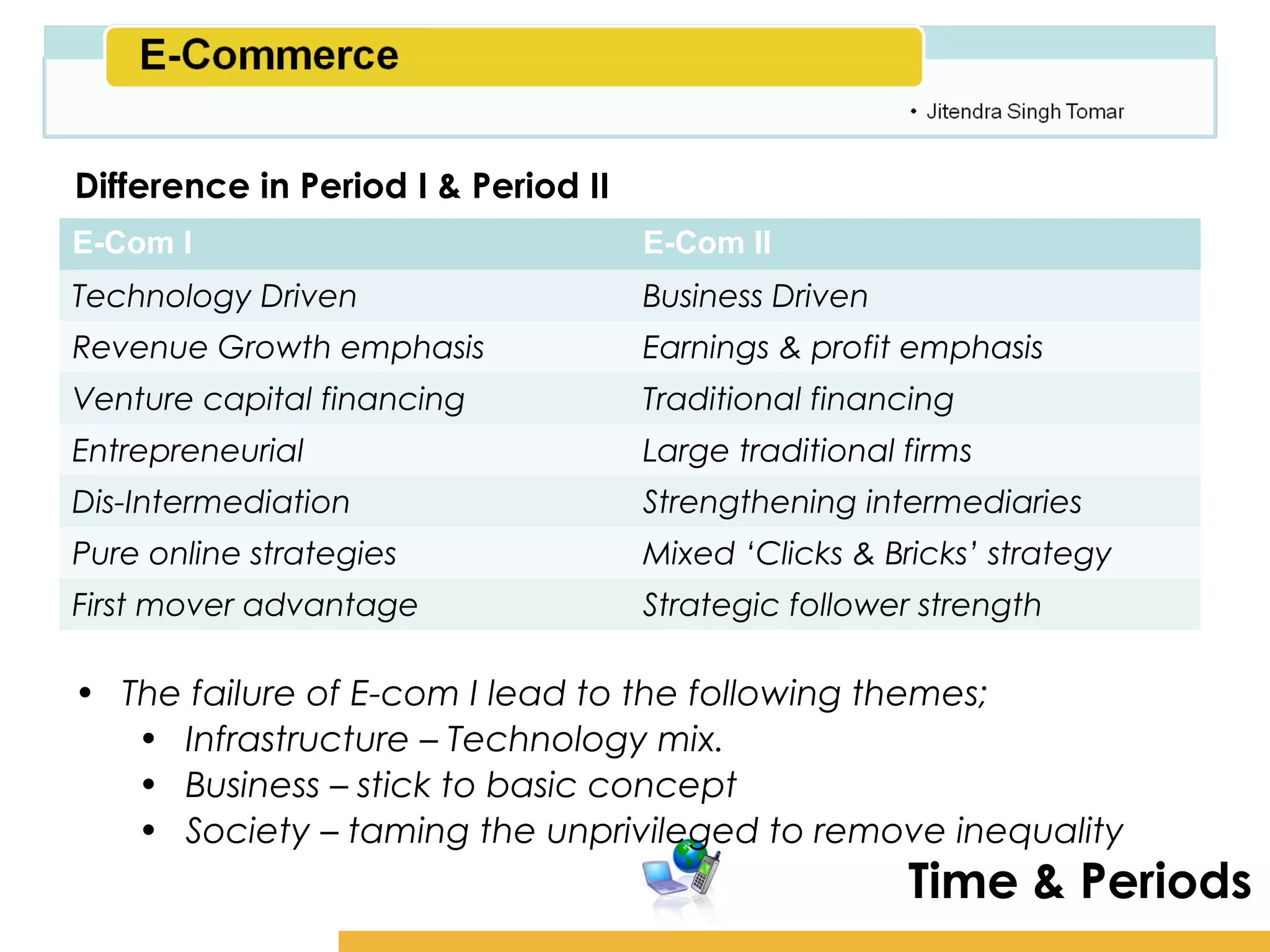
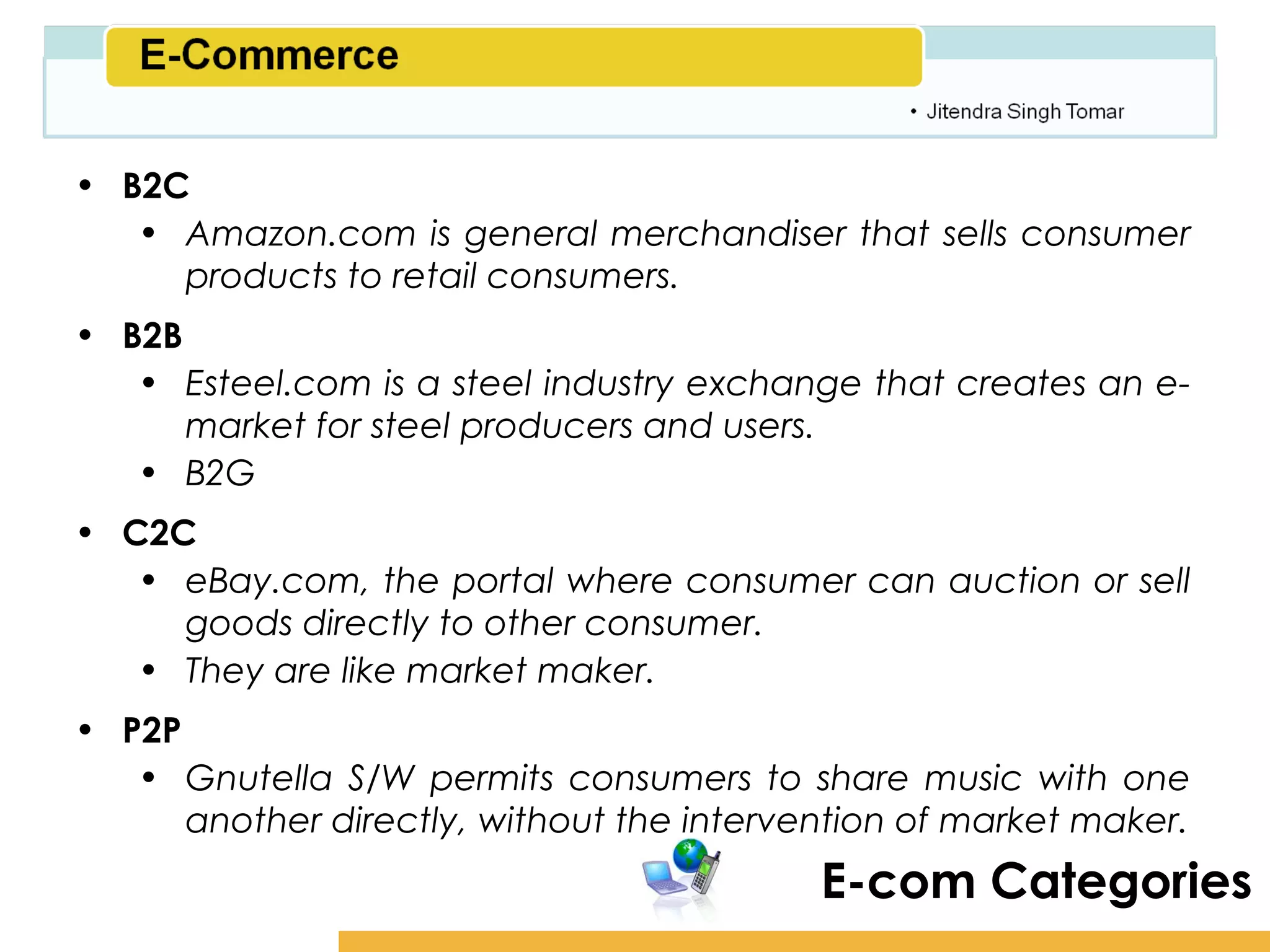
The document provides an overview of e-commerce, including definitions, types, history and driving forces. It defines e-commerce as the use of digital technologies to conduct business transactions online. The document outlines the major types of e-commerce like B2C, B2B, C2C and discusses the phases of development from the early 1990s to the present. The key driving forces behind the growth of e-commerce are also summarized such as digital convergence, availability anywhere at any time, organizational changes and demand for customized products.