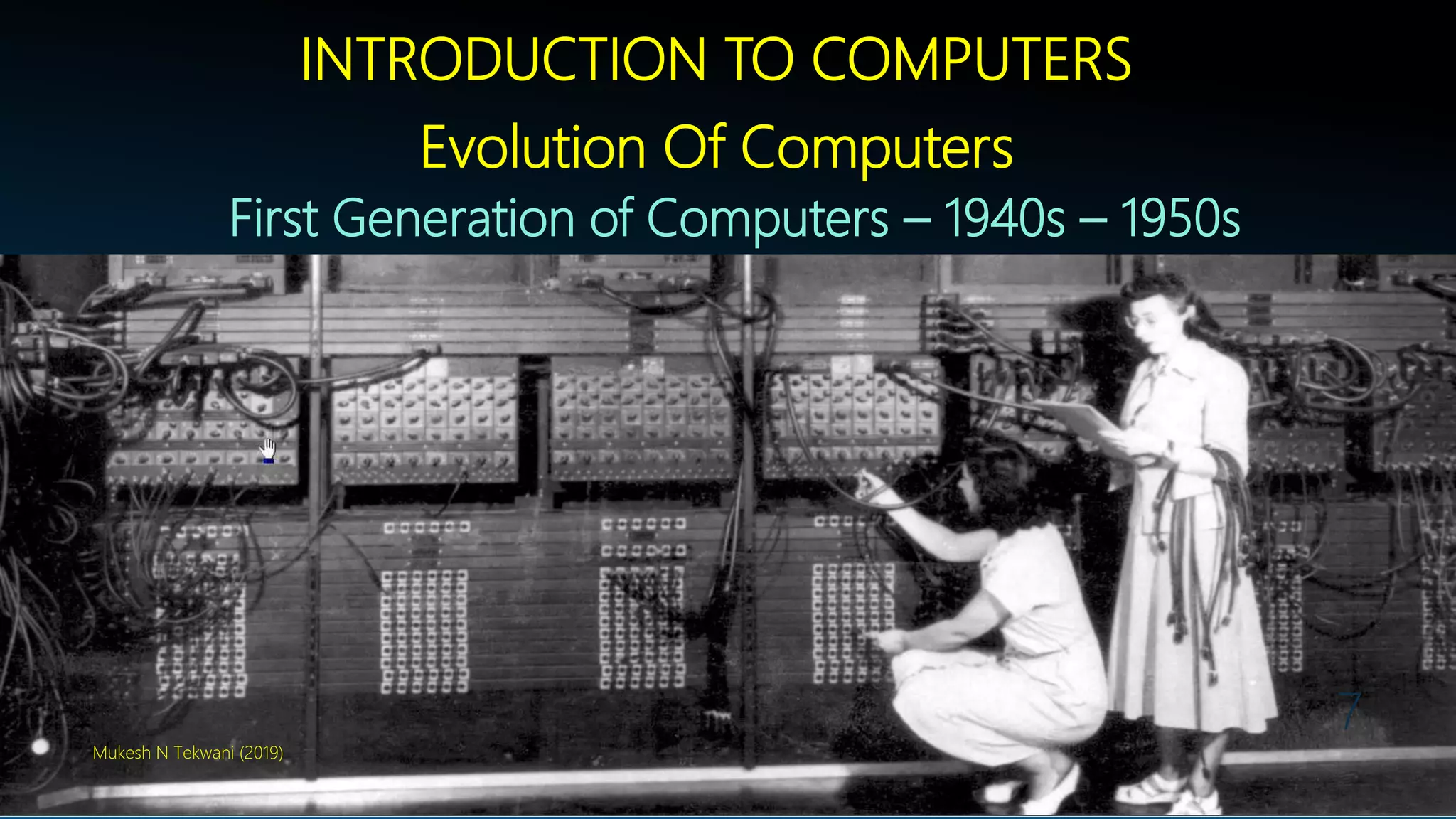
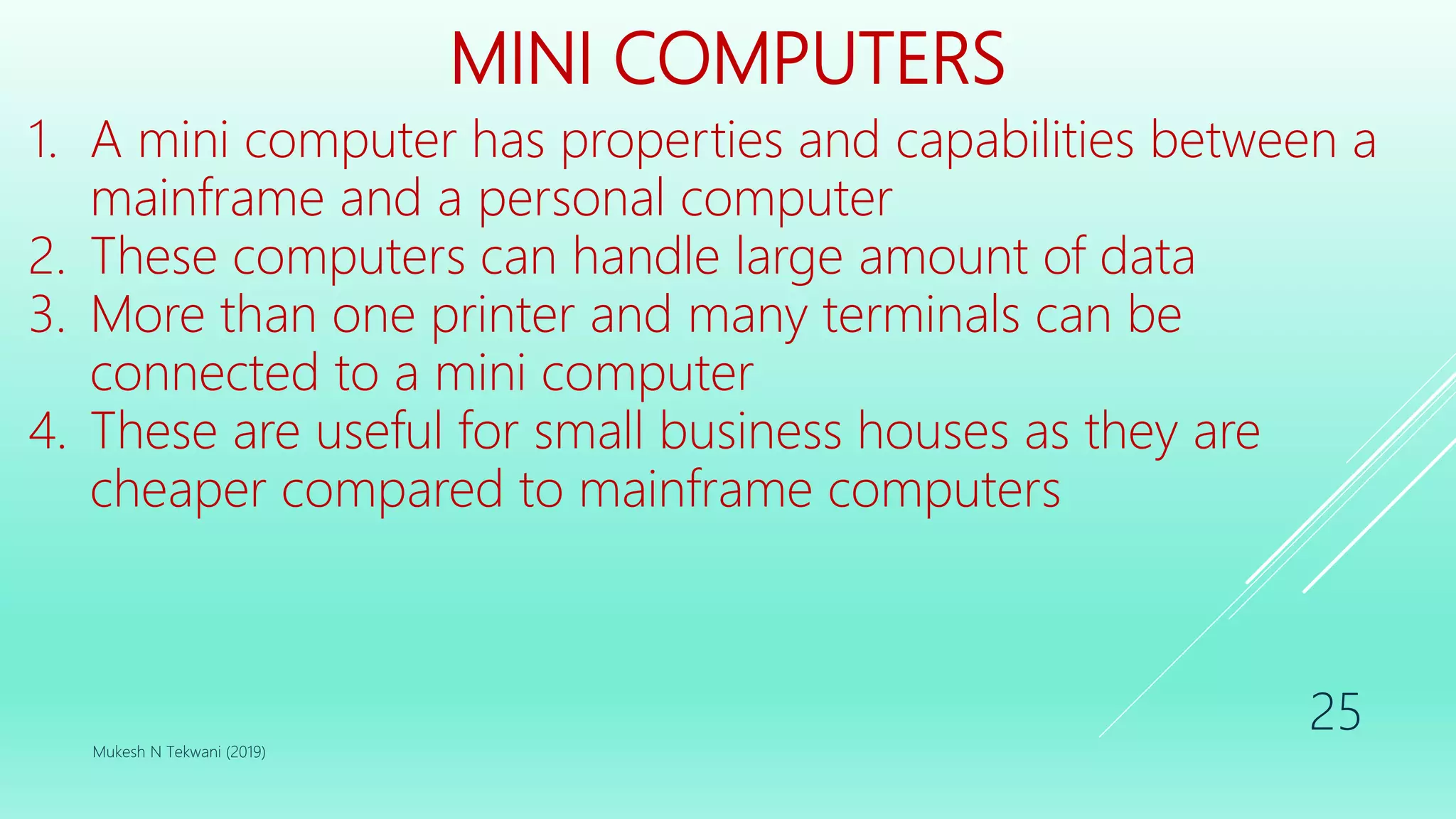
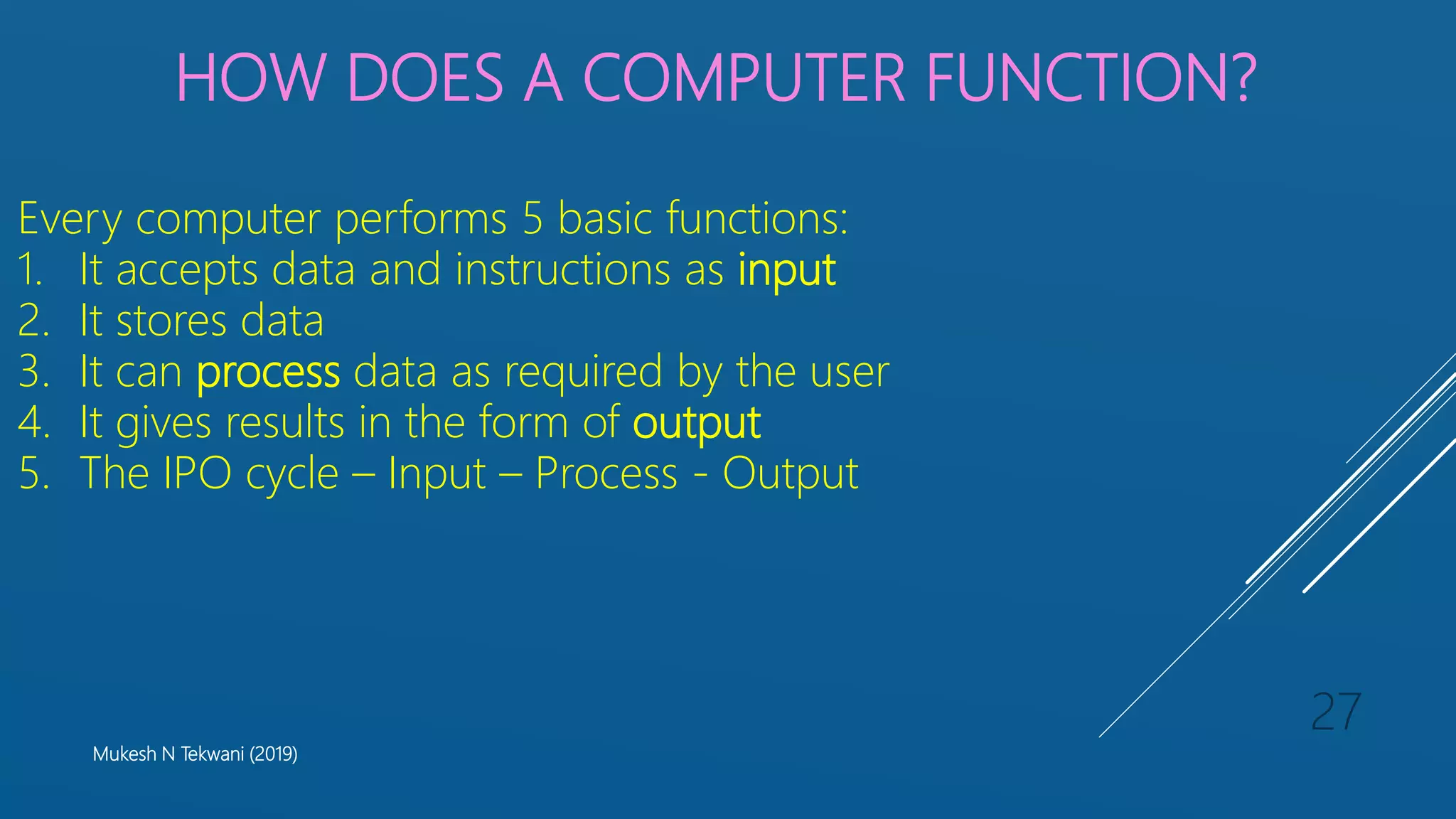
This document provides a syllabus and lecture materials for an introductory computing skills course. The syllabus covers introduction to computers, operating systems, internet usage, Microsoft Word, and Microsoft Excel. The lecture materials define the need for computers, describe their evolution through different generations using vacuum tubes, transistors, integrated circuits, and microprocessors. It also covers different types of computers like analog, digital and hybrid computers, as well as computers categorized by size as supercomputers, mainframes, mini computers, and personal computers. The document explains how a computer functions by accepting input, storing and processing data, and providing output.