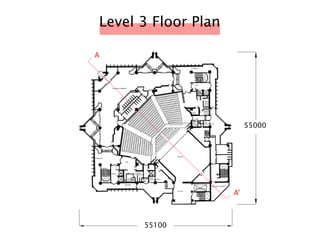
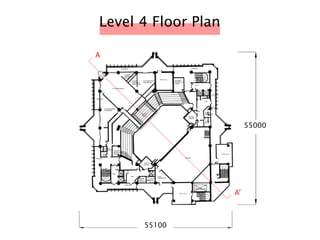
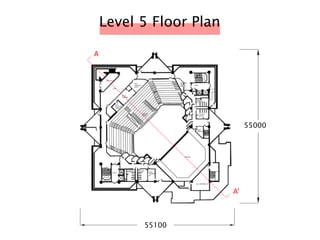
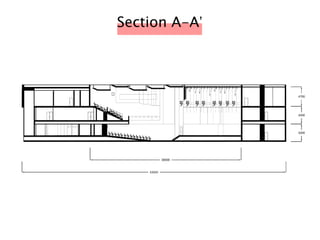
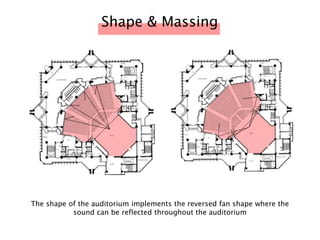
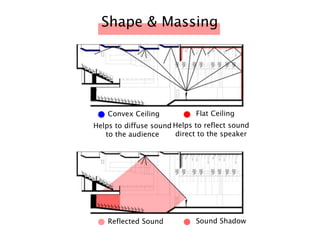
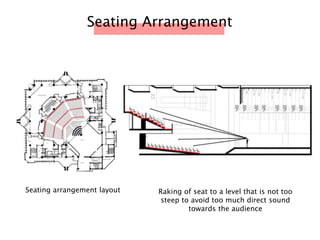
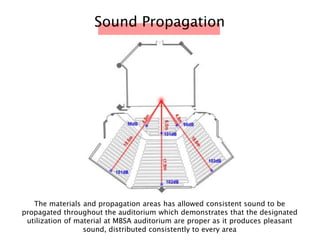
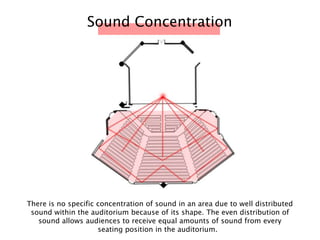
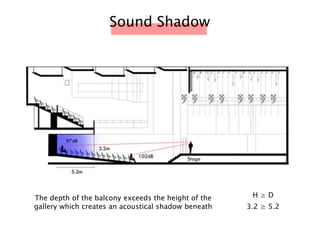
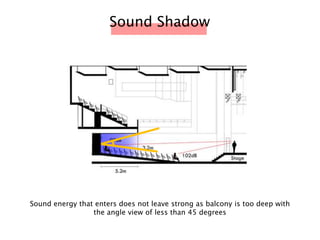
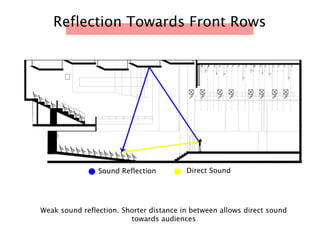
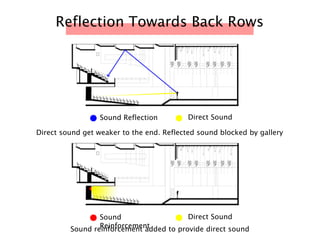
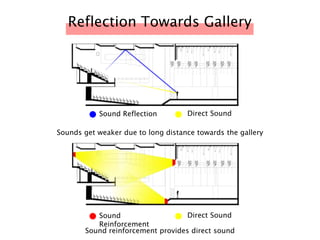
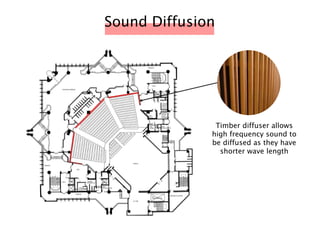
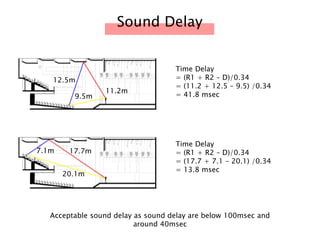
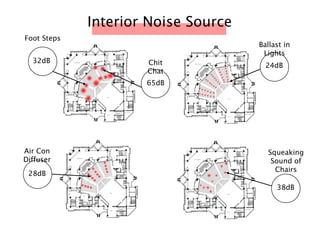
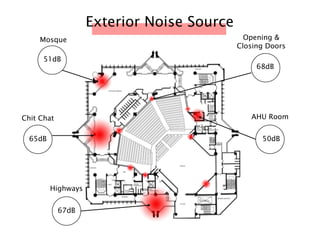
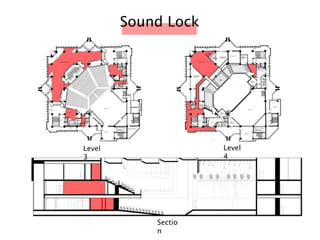
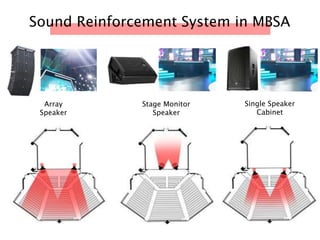
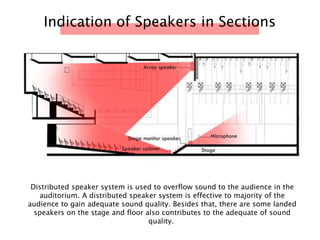
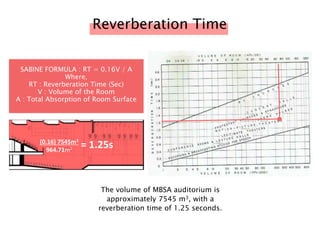
The document discusses the acoustic design of the MBSA Auditorium located in Wisma MBSA, Shah Alam. Key aspects of the design include the reversed fan shape of the auditorium which helps diffuse sound to audiences. Materials like timber and carpet are used to absorb and diffuse sound. The seating arrangement is raked at a shallow angle to avoid direct sound towards audiences. The design aims to distribute sound evenly without concentrations and uses sound reinforcement systems. Reverberation time calculations show the design meets standards.