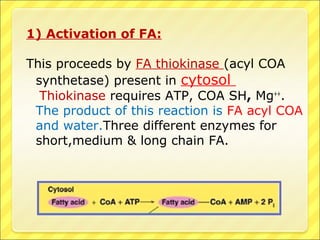
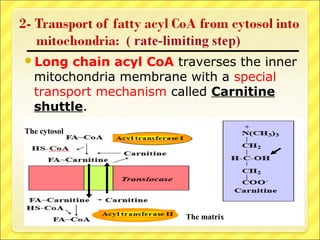
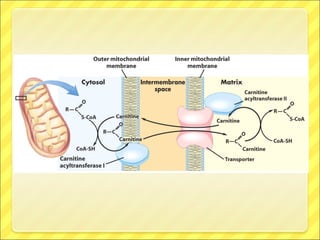
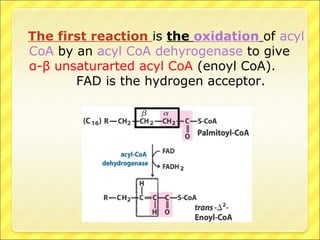
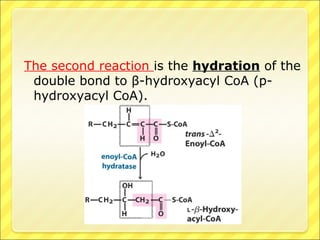
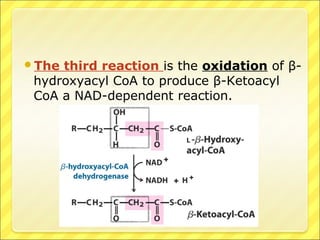
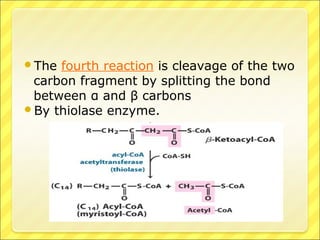
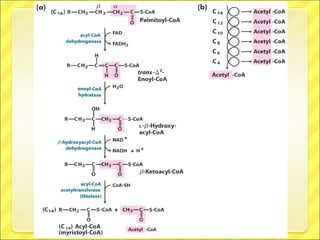
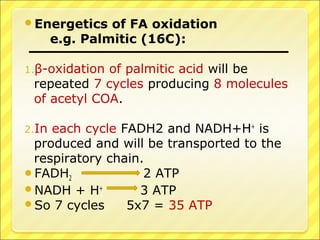
The document summarizes the process of beta oxidation, where fatty acids are broken down in the mitochondria to generate acetyl-CoA. There are four steps: 1) activation of fatty acids to fatty acyl-CoA in the cytosol, 2) transport into the mitochondrial matrix using carnitine shuttle, 3) beta oxidation proper involving oxidation, hydration, and thiolytic cleavage reactions to remove two-carbon acetyl-CoA units, 4) repetition of steps 3 until the fatty acid is fully broken down to acetyl-CoA, which feeds into the citric acid cycle. The process generates large amounts of ATP through production of FADH2 and NADH. Deficiencies in enzymes involved can