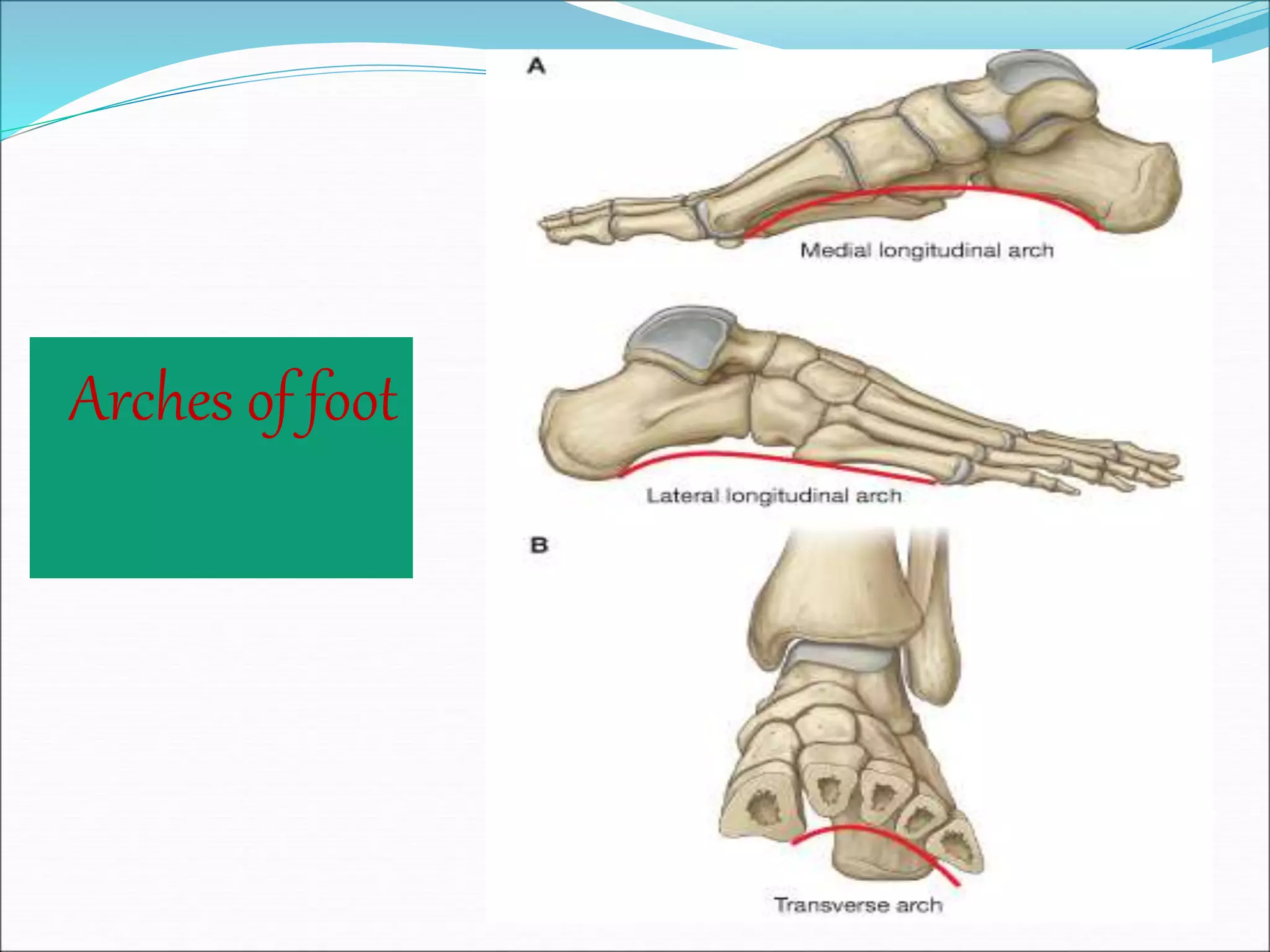
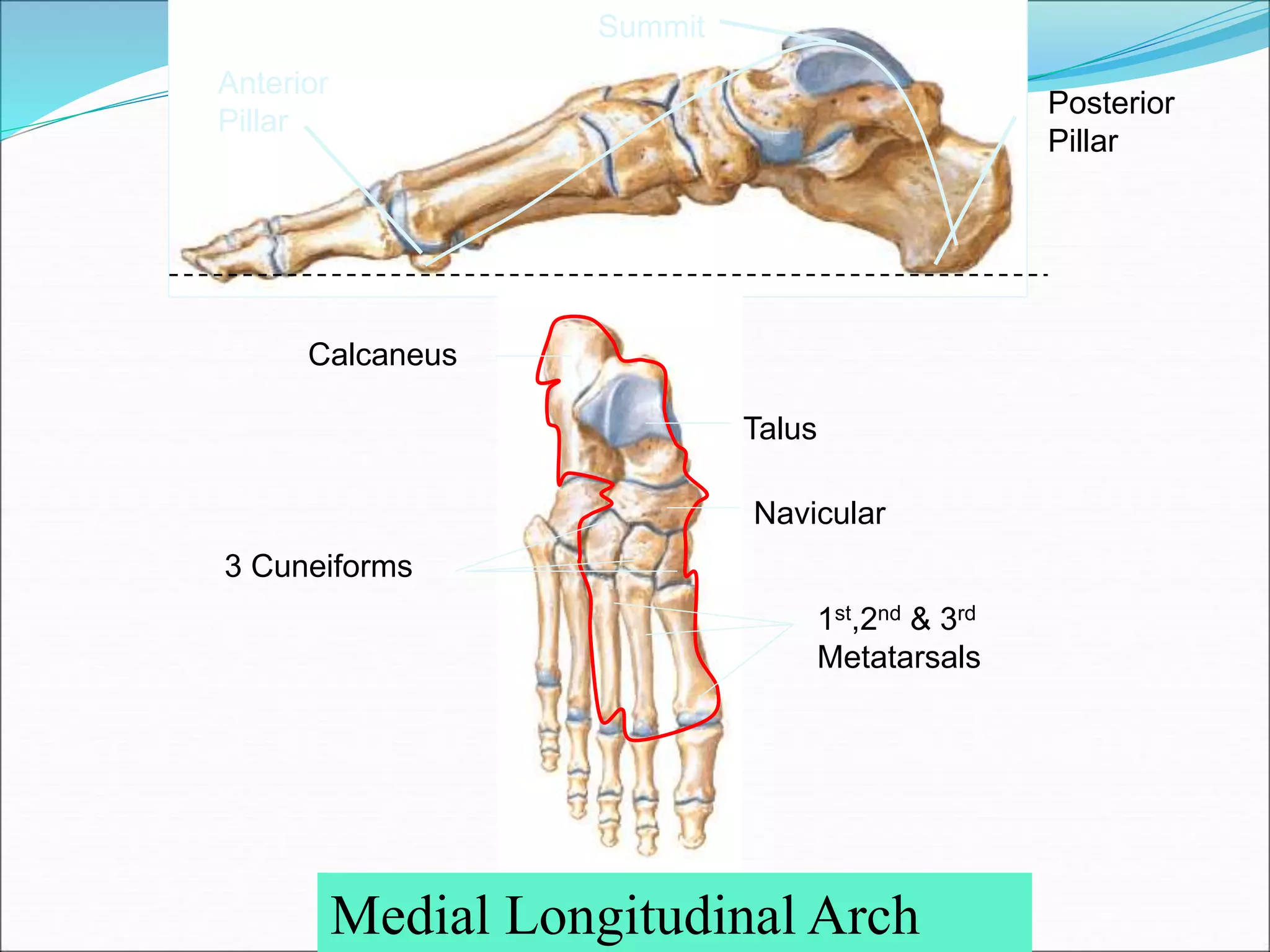
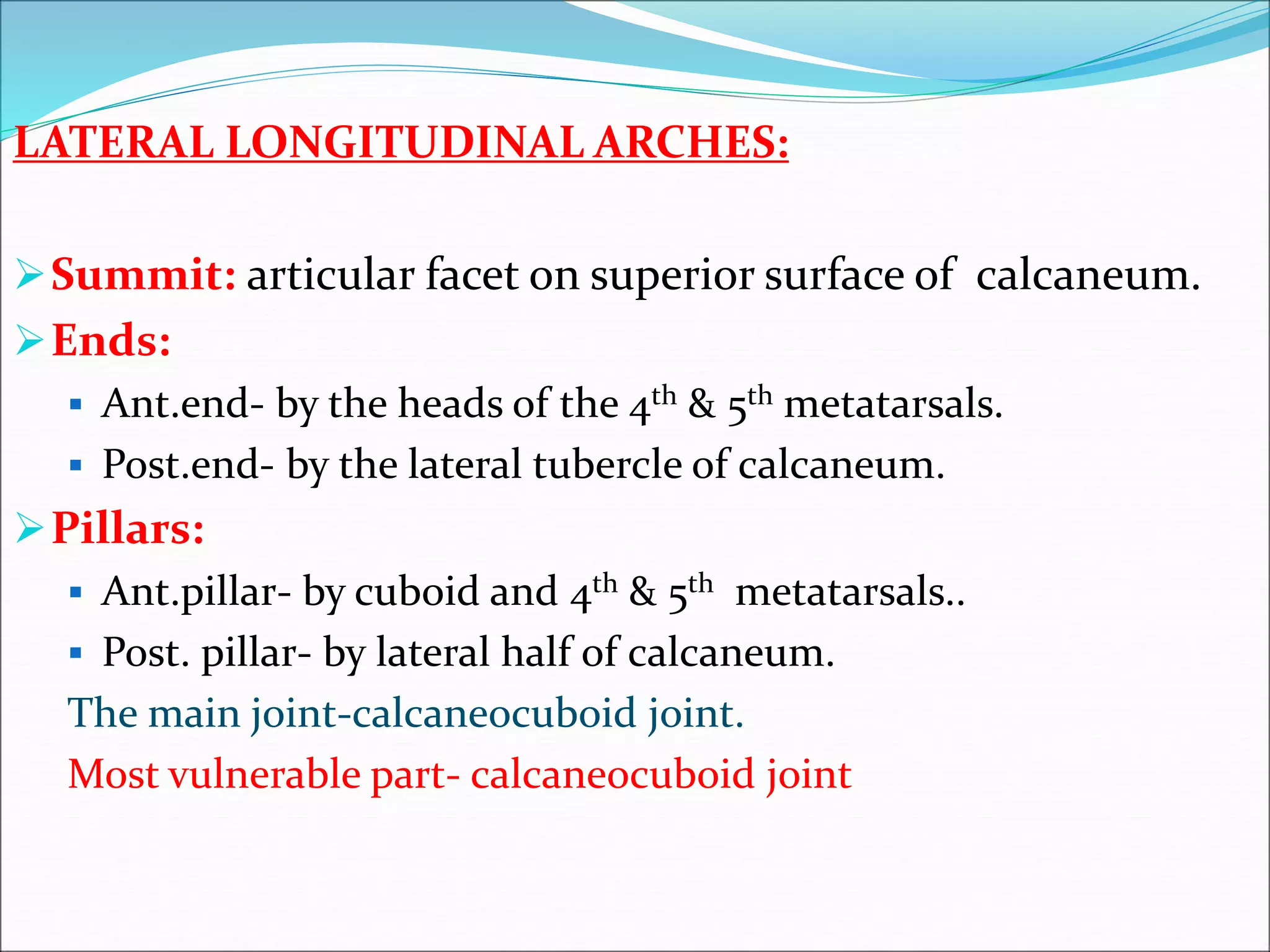
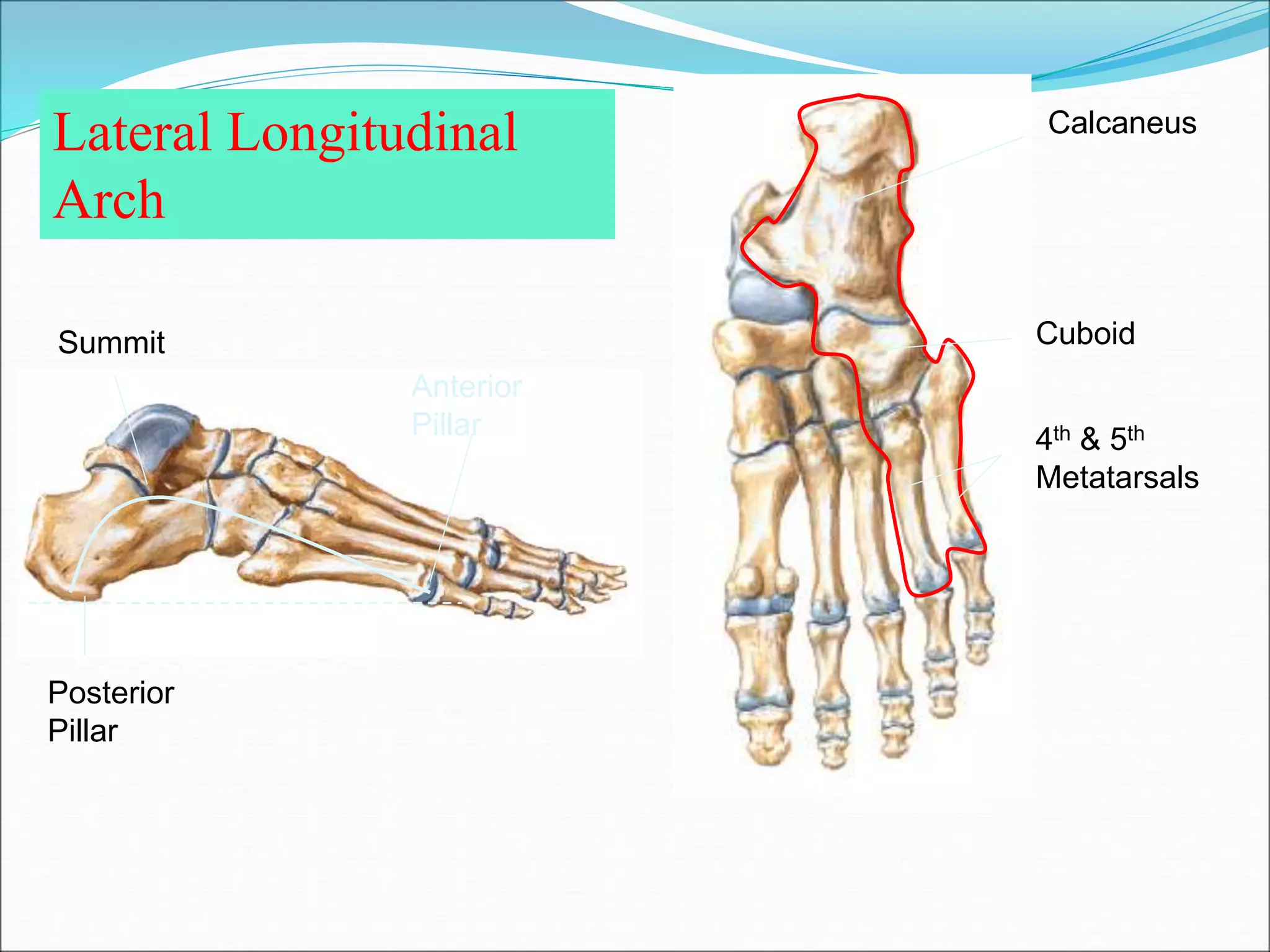
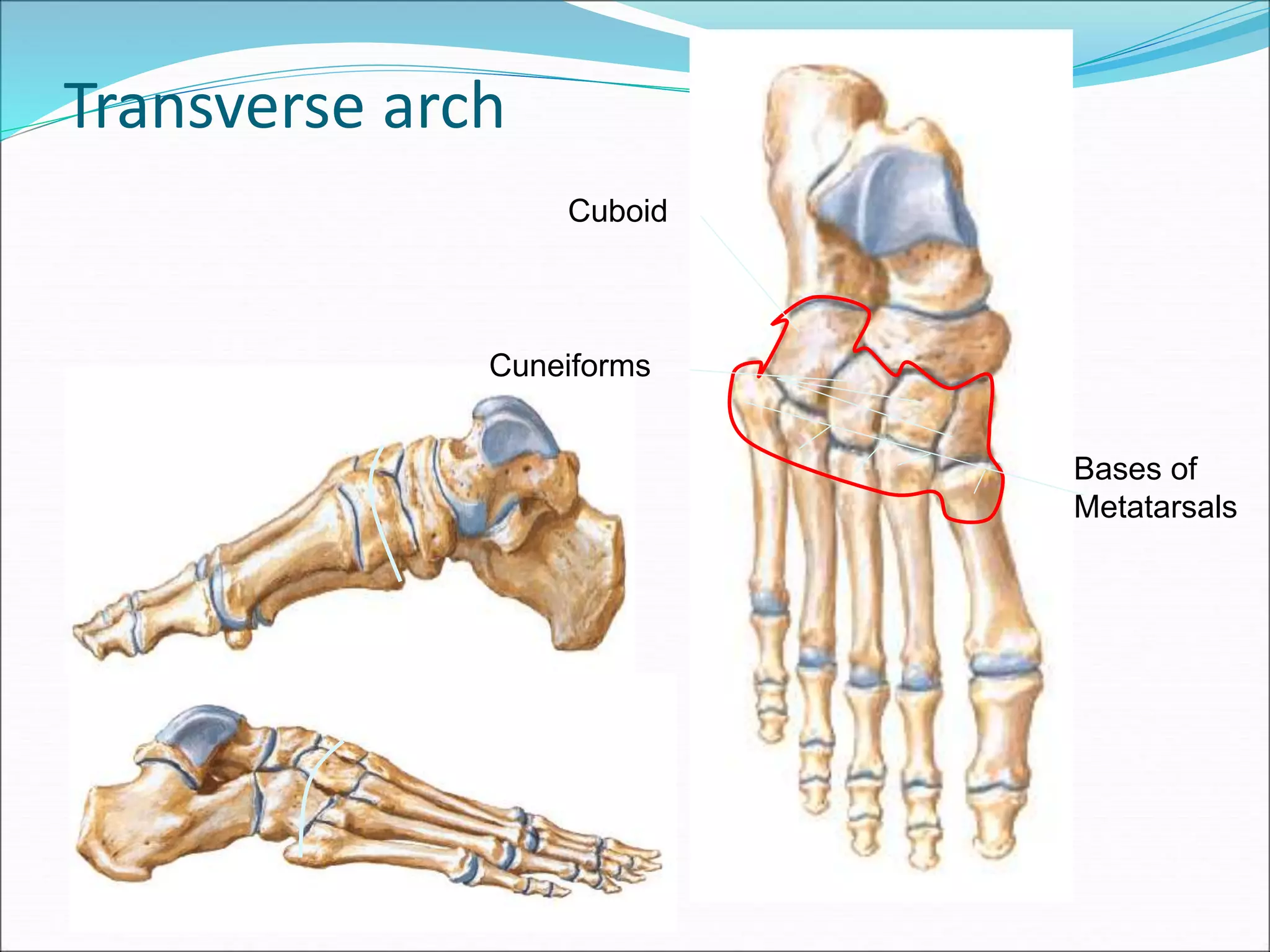
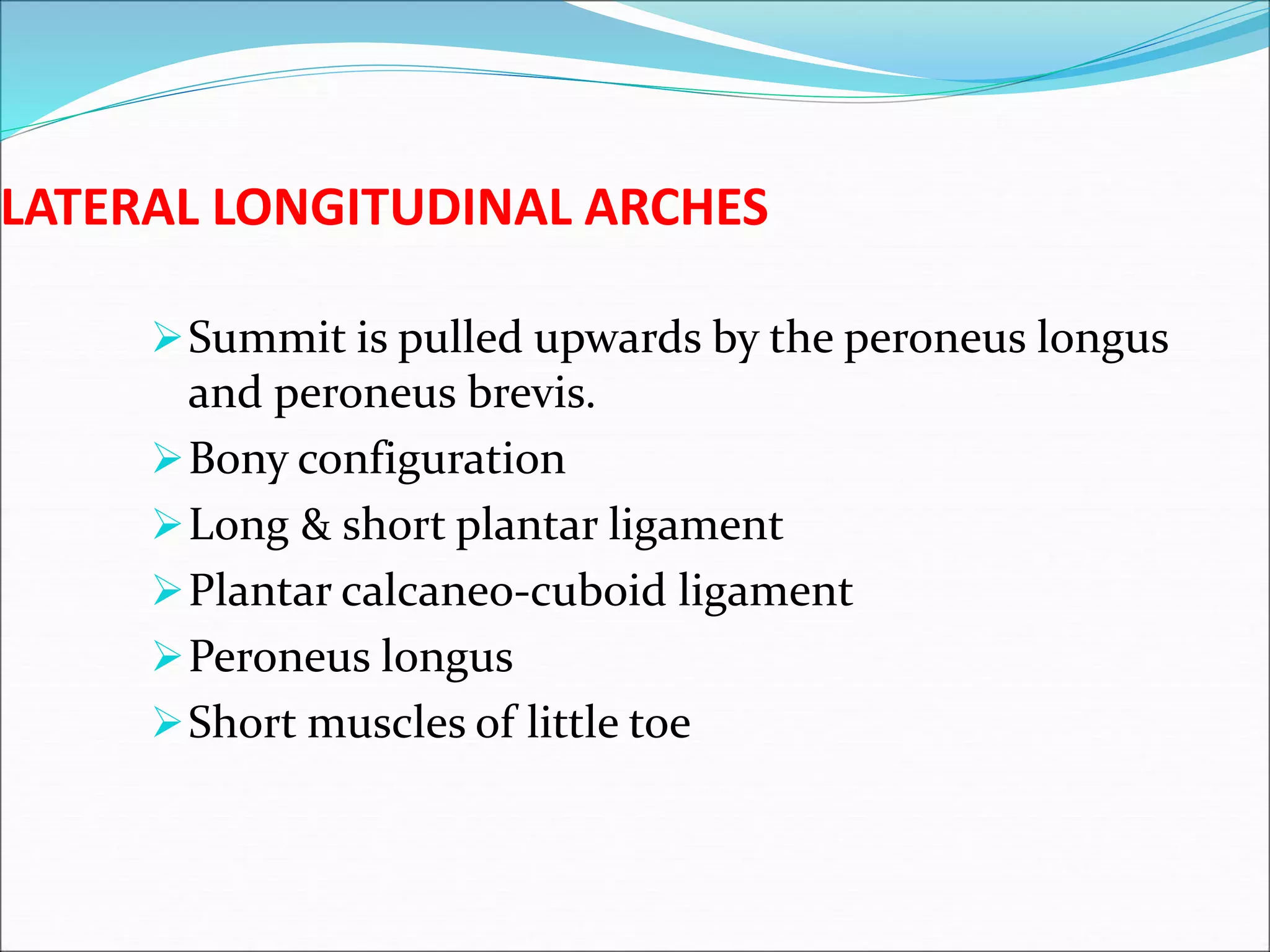
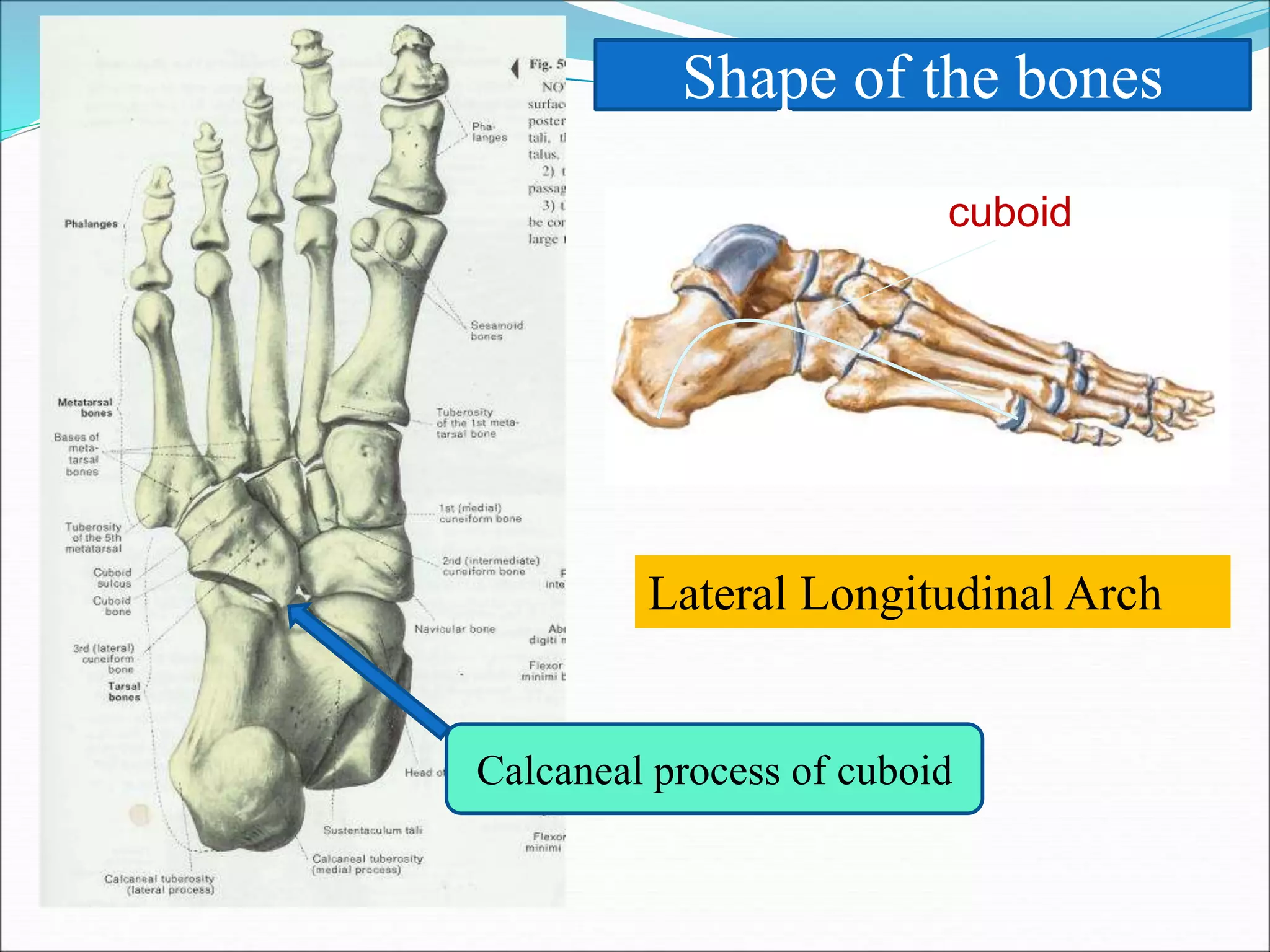
The human foot contains three arches - the medial and lateral longitudinal arches and the transverse arch. These arches are formed by tarsal and metatarsal bones and supported by ligaments, muscles, tendons and aponeurosis. The arches act as flexible platforms to support body weight and as levers to propel the body during walking and running. They also function as shock absorbers and protect soft tissues from pressure. The arches are maintained by bone shape, ligaments like the plantar ligaments, muscles like tibialis posterior, and the plantar aponeurosis. Loss of the arches can lead to conditions like flat feet while exaggerated arches cause pes cavus.