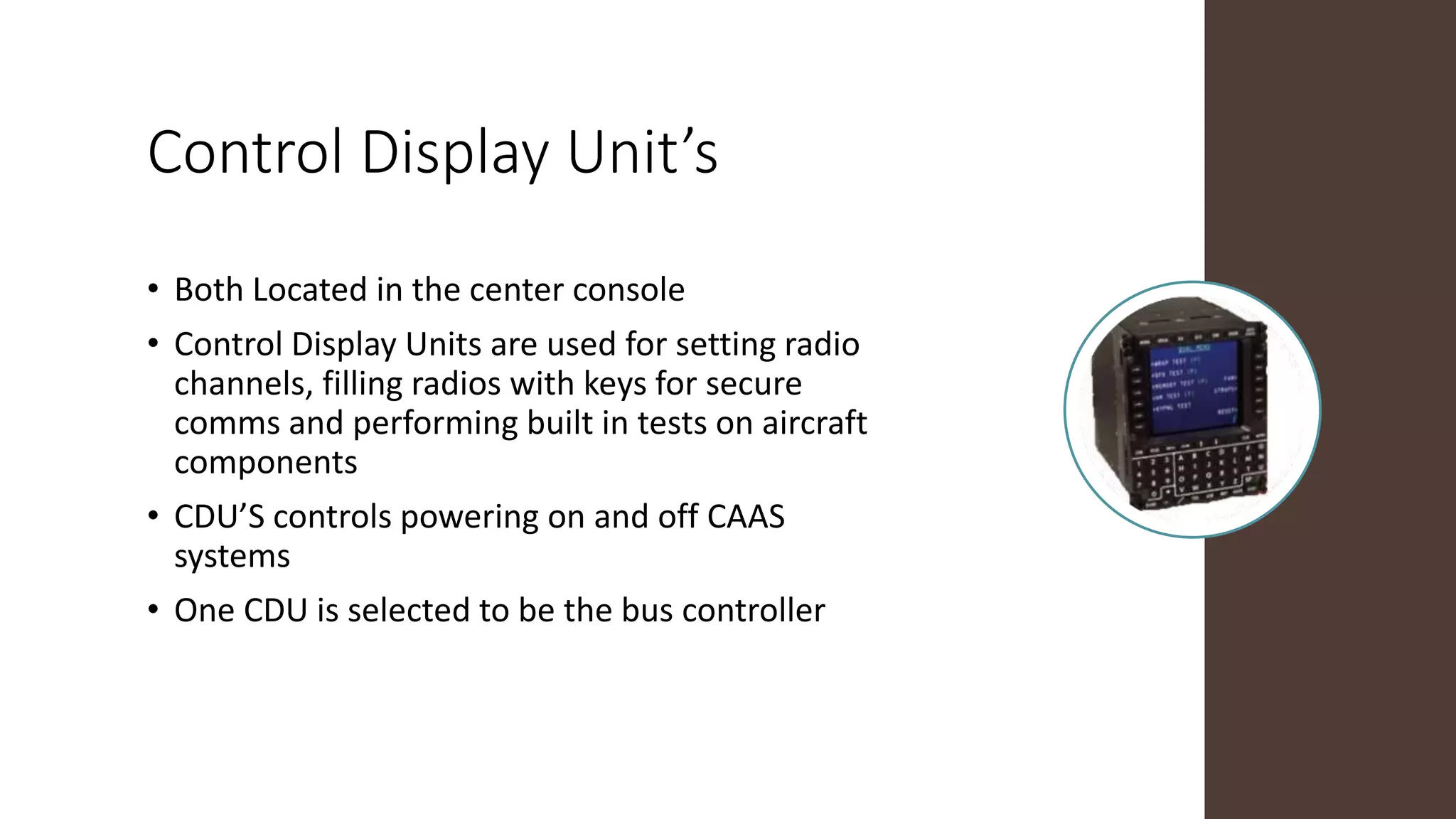
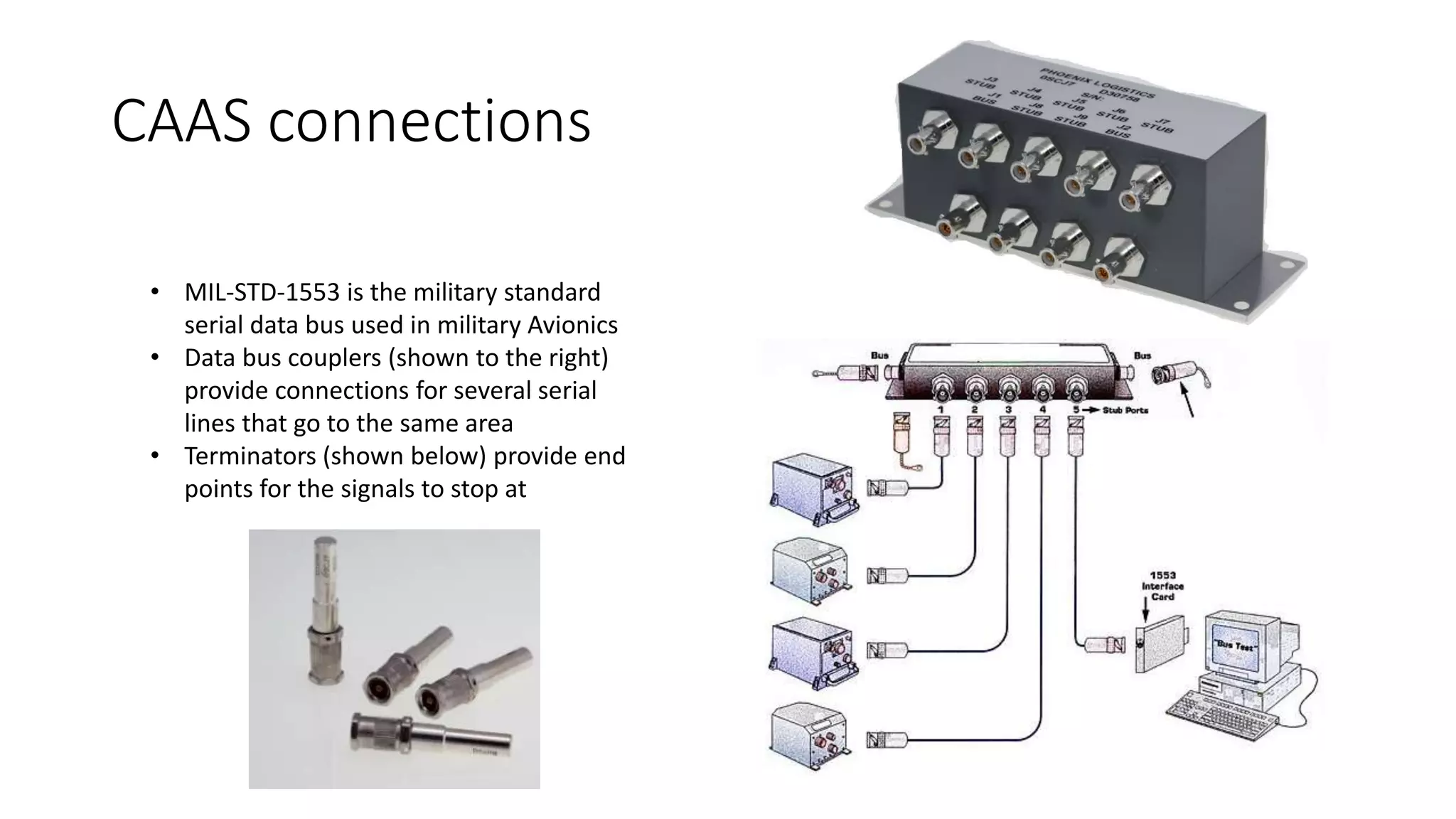
The Common Avionics Architecture System (CAAS) provides a digital interface for navigation, flight, and communication systems that is interchangeable between the MH-60 and MH-47 helicopter models. CAAS components include 4 multi-function displays, 2 control display units, 2 power switching modules, 2 video processing modules, and 1 data transfer unit. These components work together to process and display critical flight data, control aircraft systems, and transfer data and video.