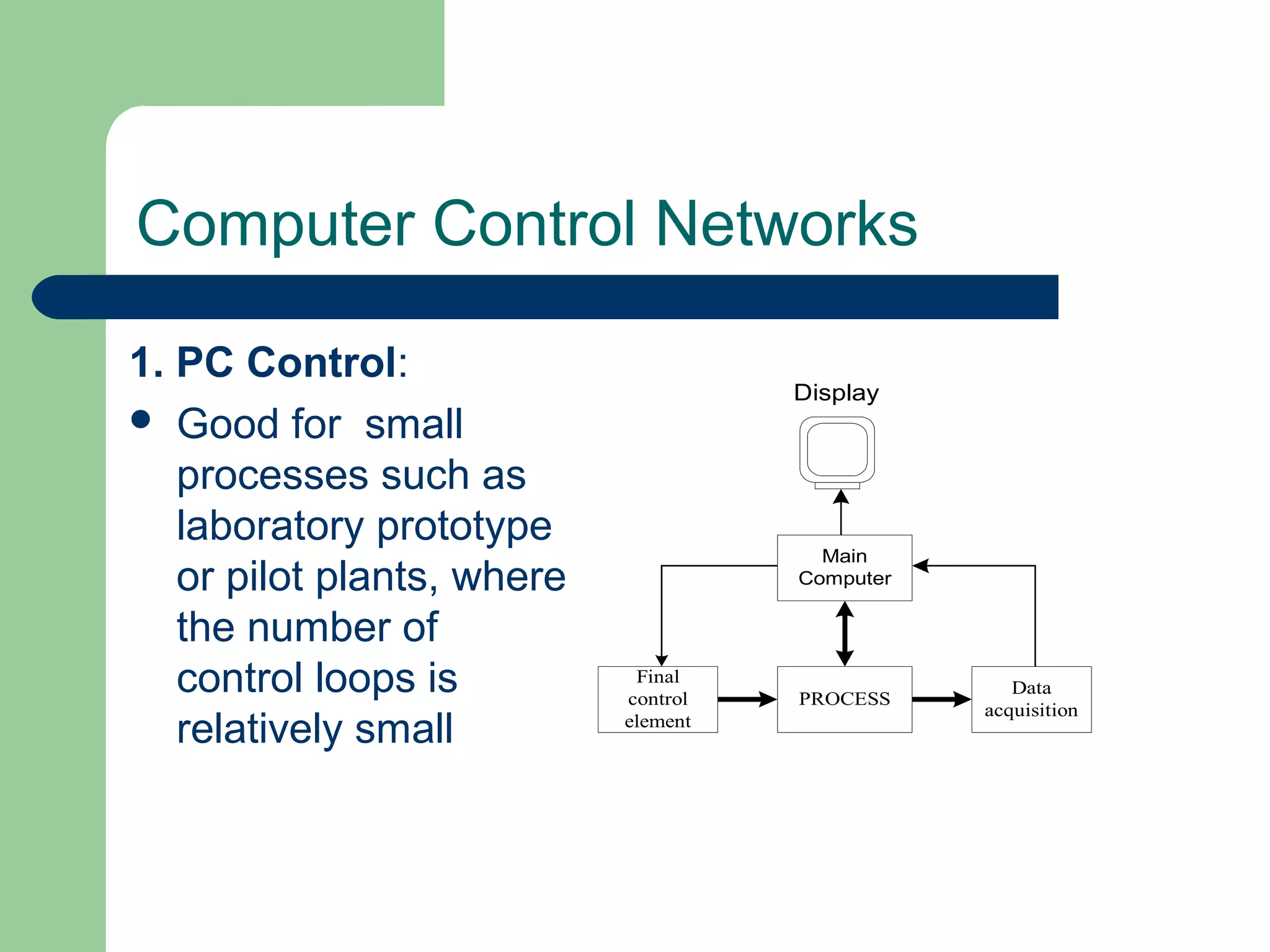
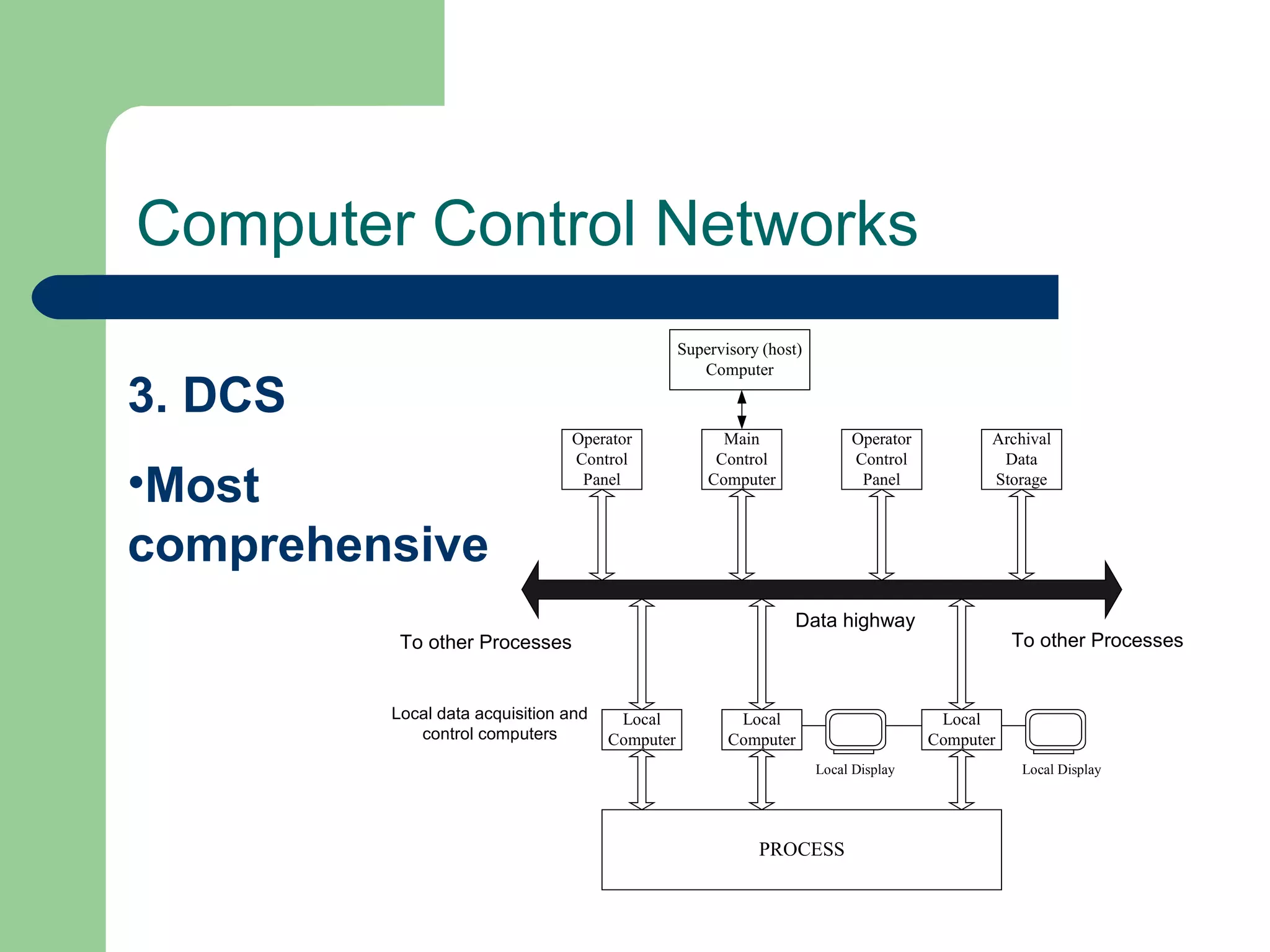
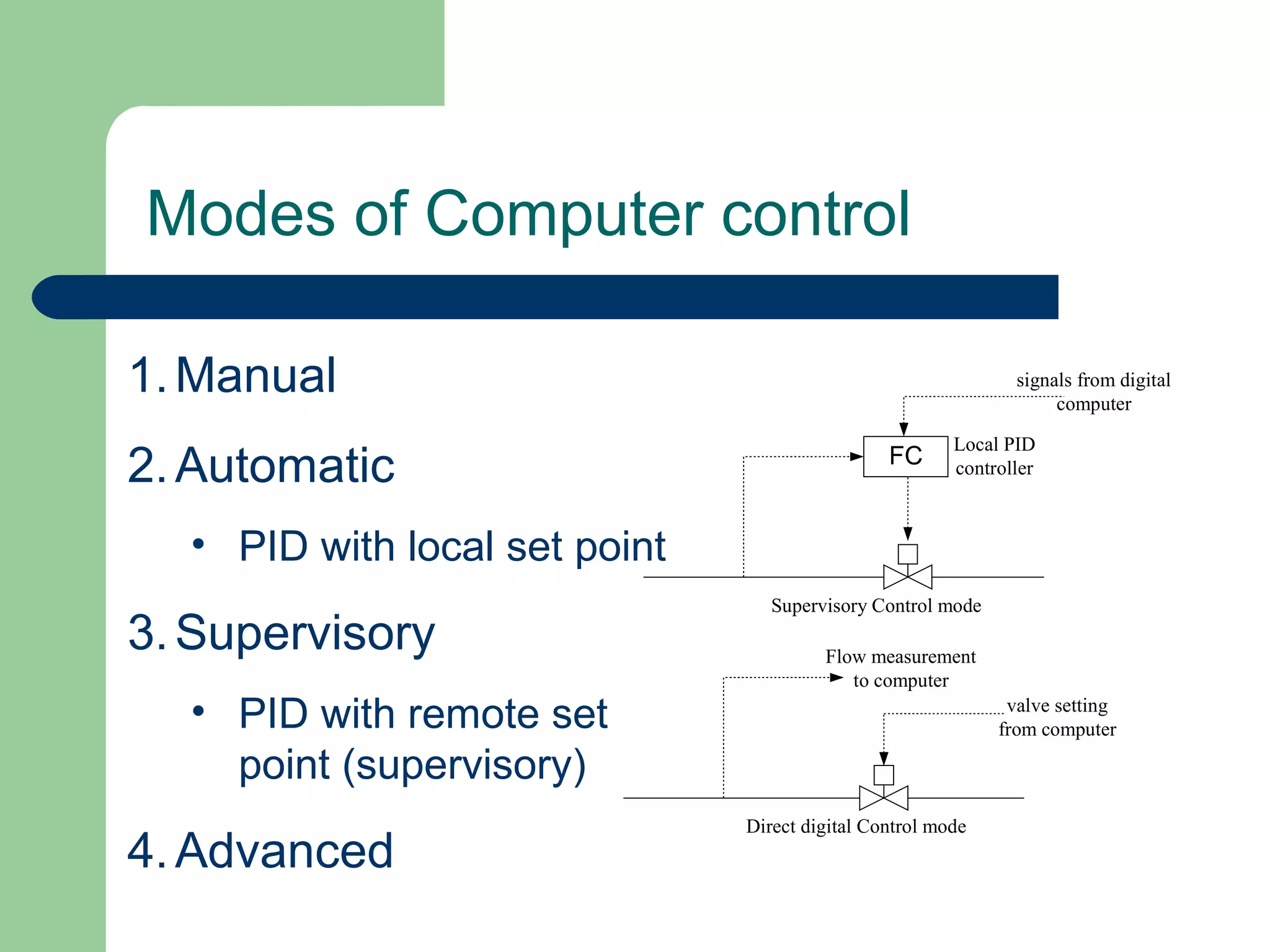
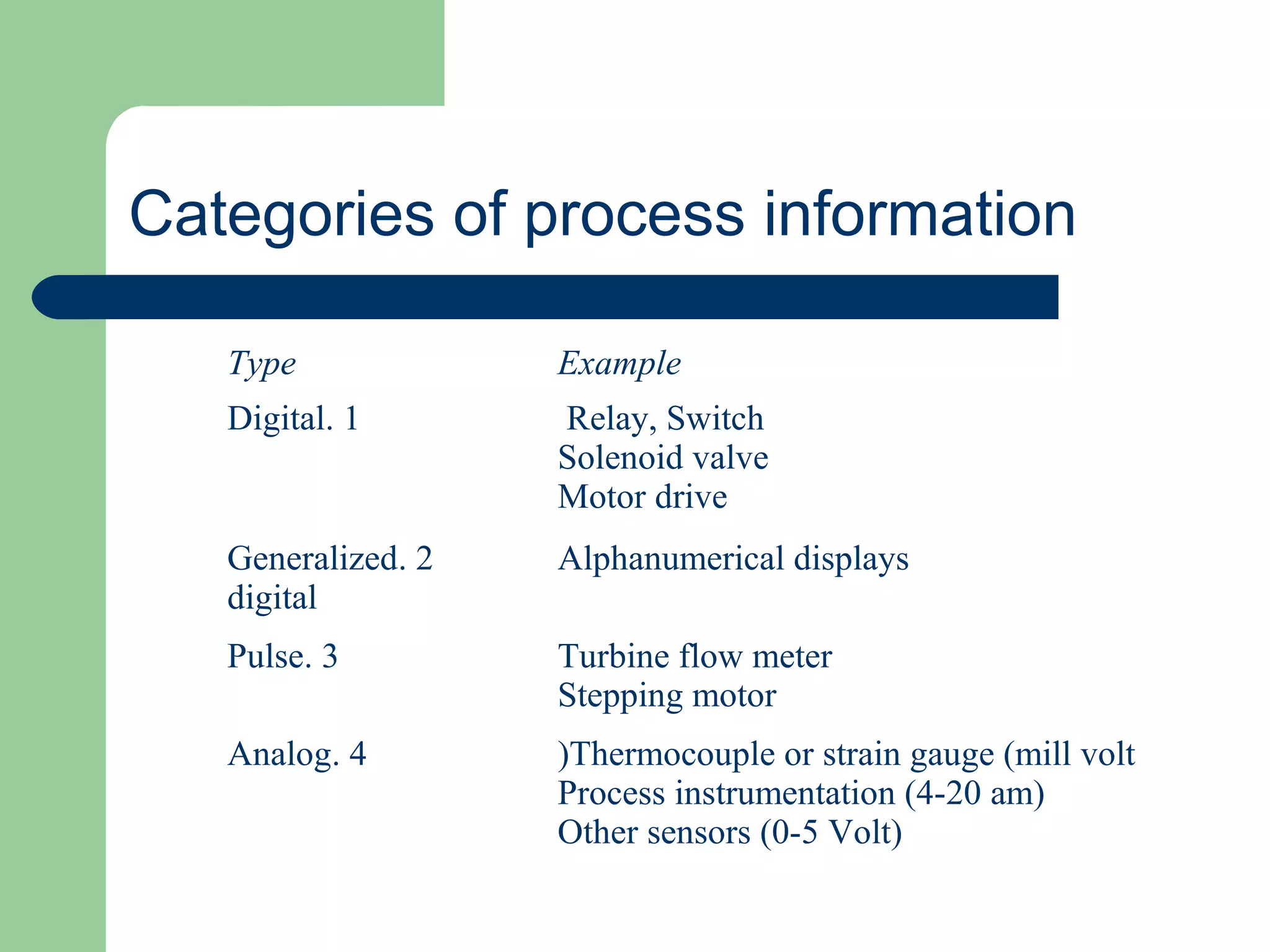
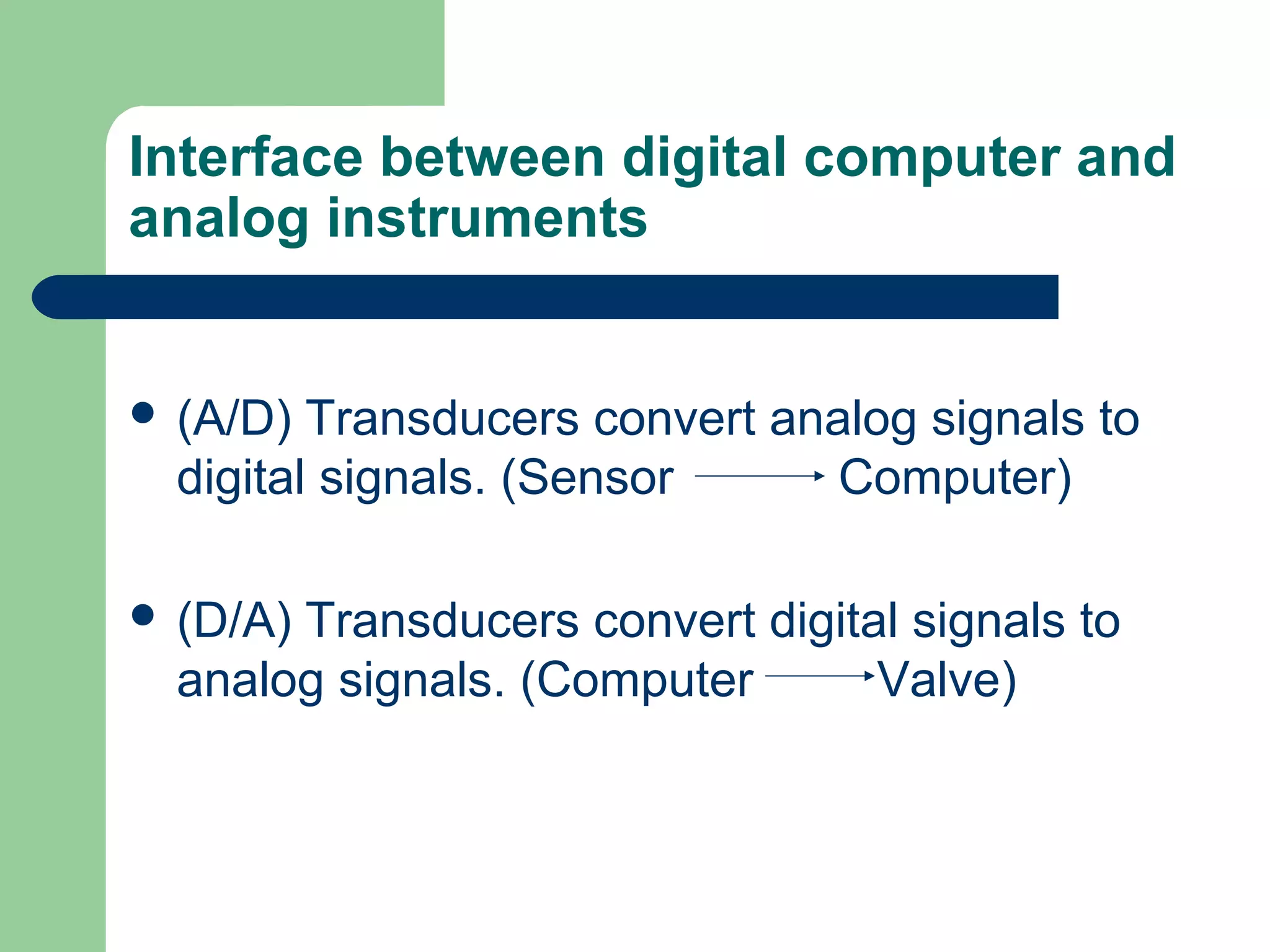
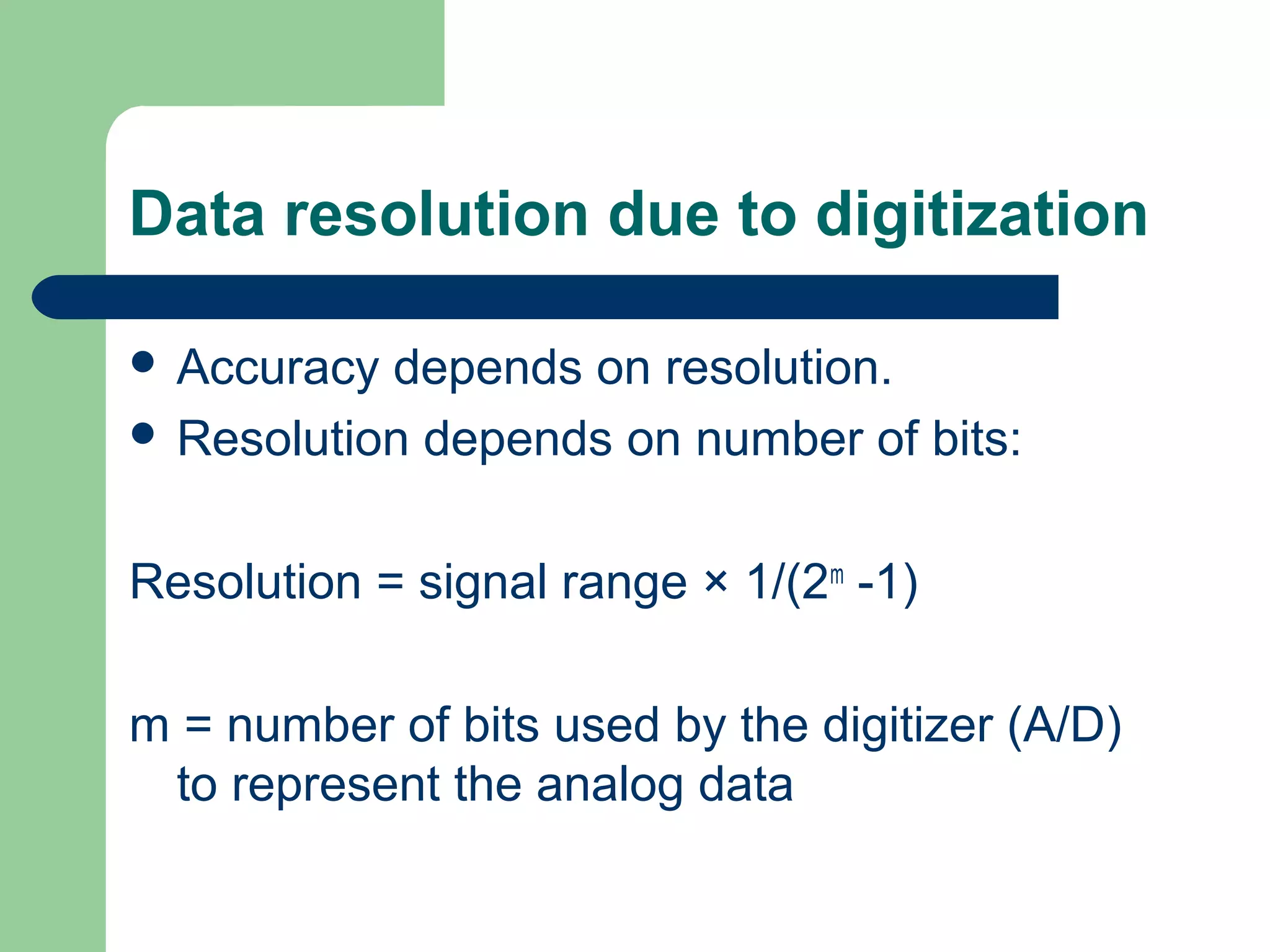
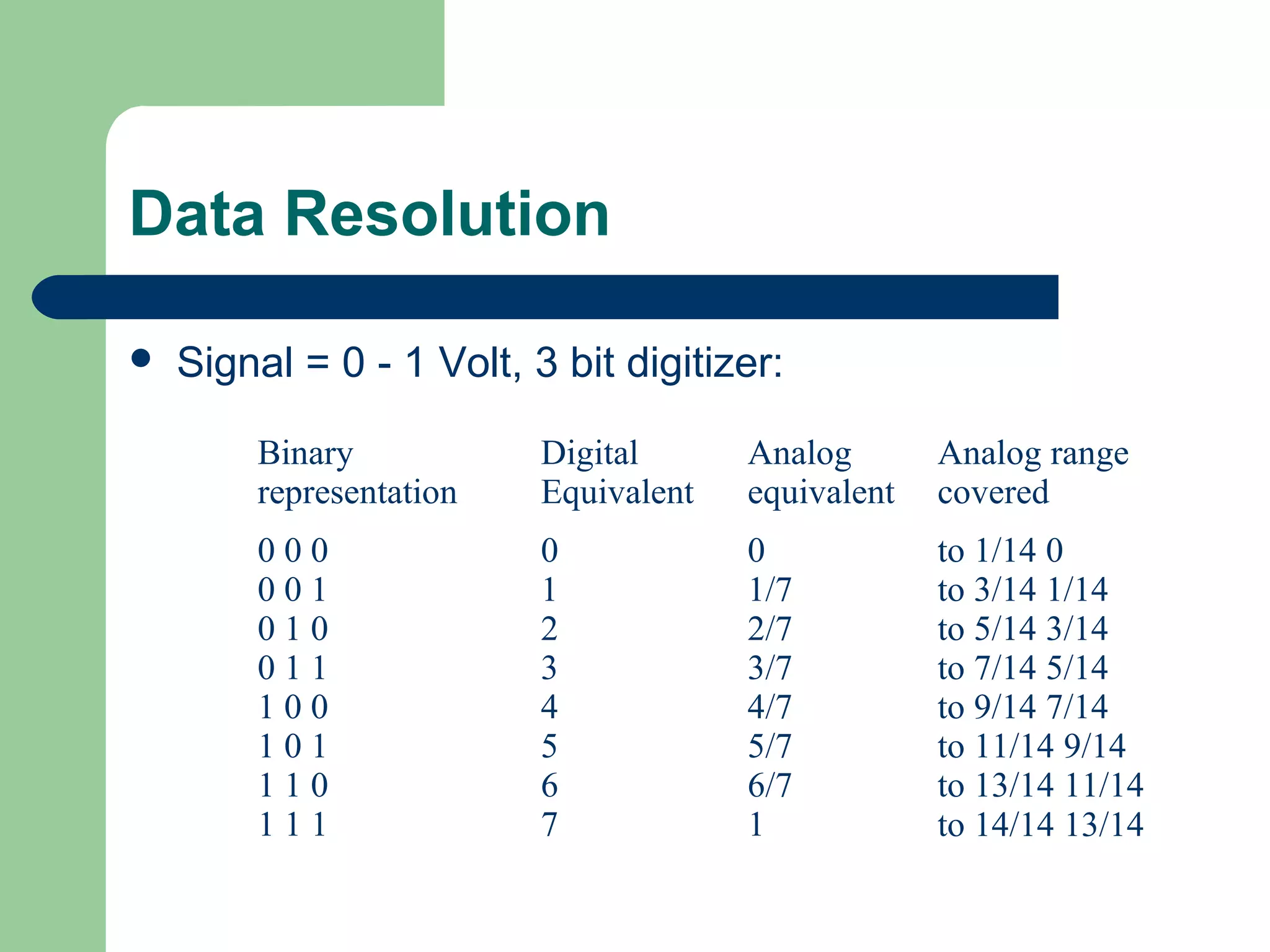
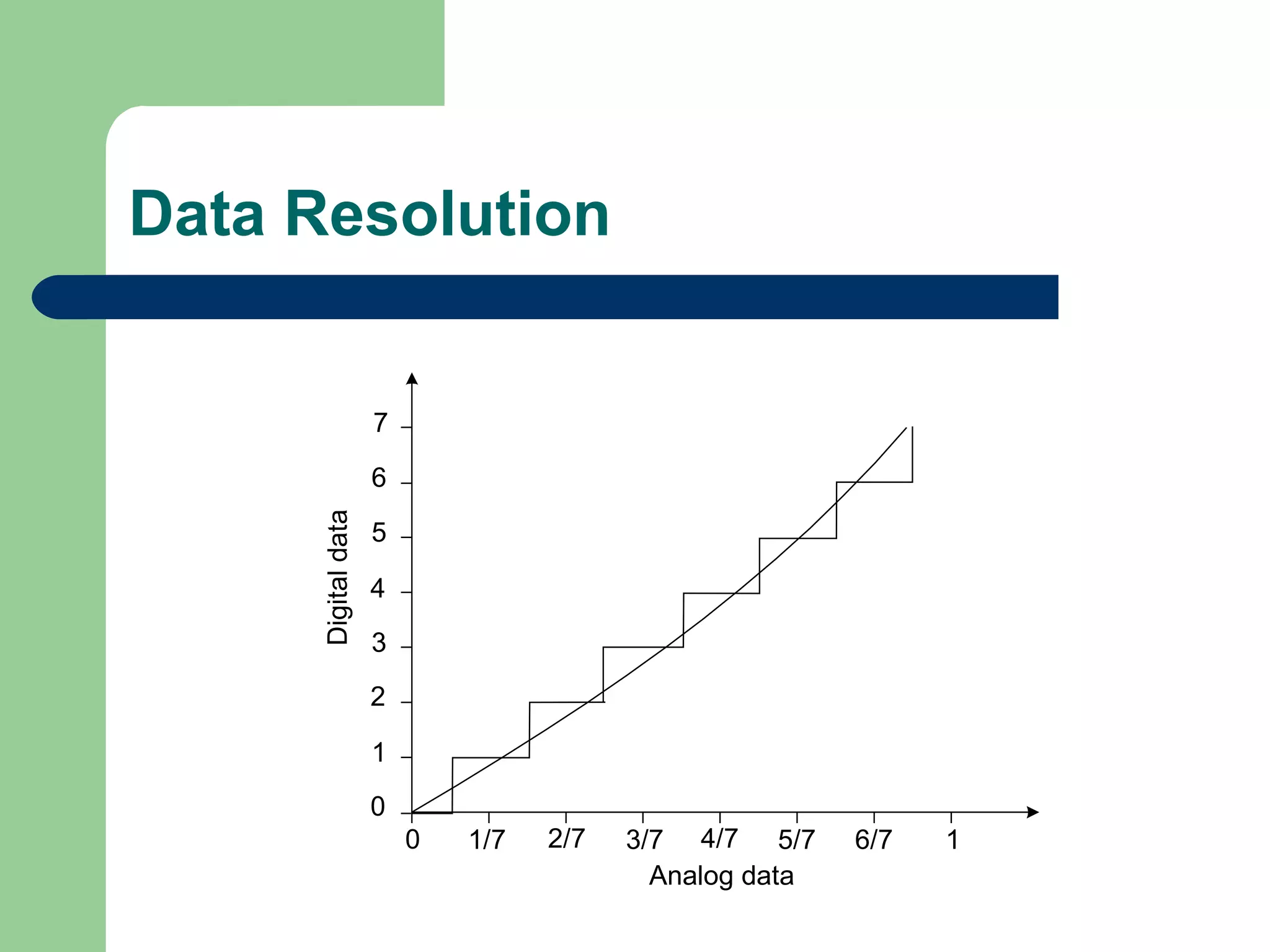
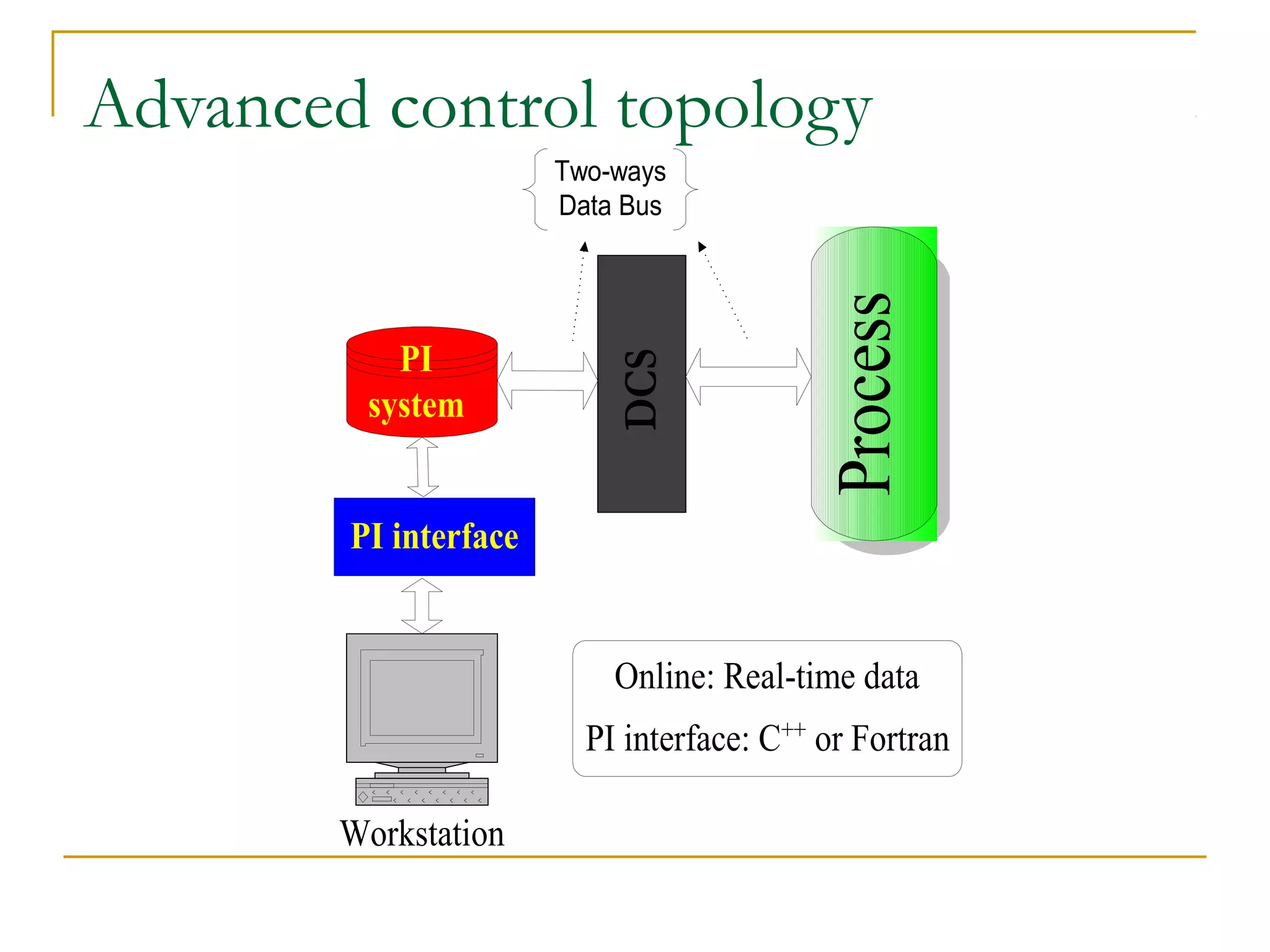
This document discusses distributed control systems (DCS). It begins by defining DCS as a collection of hardware and instrumentation that provides an infrastructure for implementing advanced control algorithms. It then provides a brief history of control hardware from pneumatic to analog to digital implementations. The advantages of digital systems like precision, flexibility, and lower costs are highlighted. Key elements of a DCS like local control units, data acquisition units, and communication networks are described. Additional advantages of DCS like access to process information and flexibility to modify control configurations are also noted.