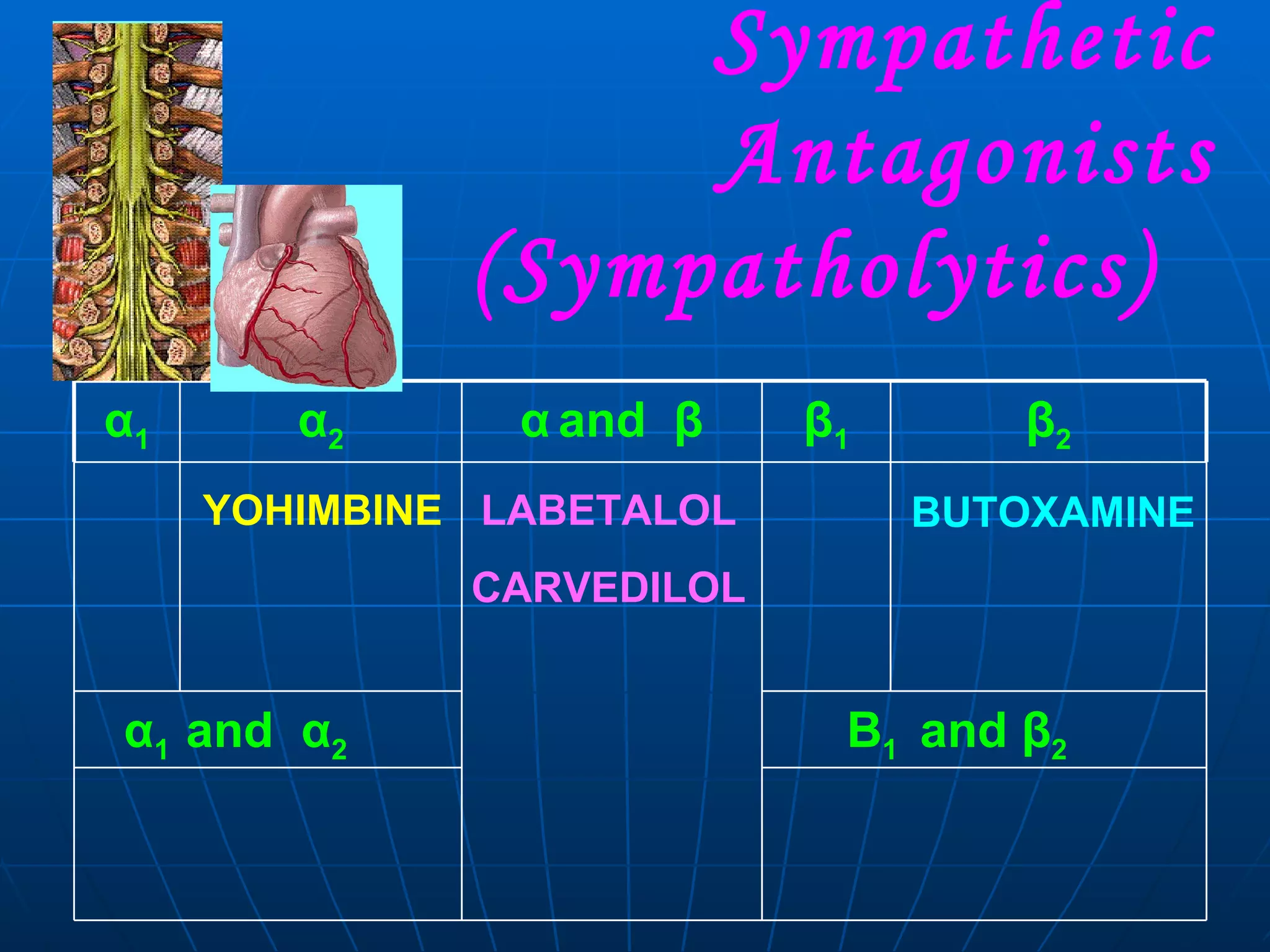
The document discusses the central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, and autonomic nervous system. It describes the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. It provides details on the neurotransmitters, receptors, and typical locations involved in neurotransmission within the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. It also lists some common effector organs and the actions mediated by stimulation or blockade of receptors in these divisions.