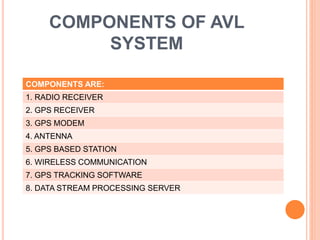
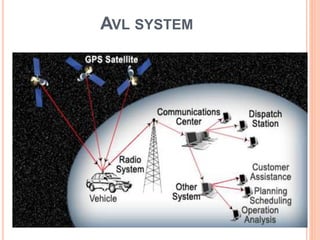
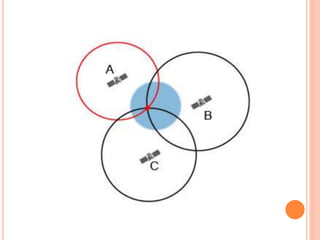
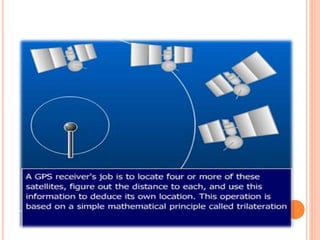
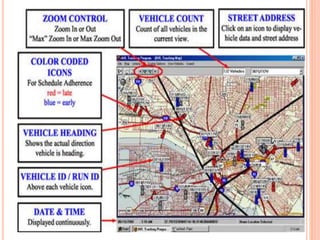
An automatic vehicle locator (AVL) system uses GPS technology to remotely track the location of vehicles. It has several components, including a radio receiver, GPS receiver, GPS modem, antenna, GPS base station, and GPS tracking software. The GPS system uses satellites to calculate a vehicle's position via trilateration. An AVL system allows fleet managers to monitor vehicle locations in real-time and ensure efficient operations, and can also be used for passenger information systems, asset tracking, and covert surveillance. While GPS provides very accurate location data, some factors like atmospheric delays and signal multipath can introduce errors.