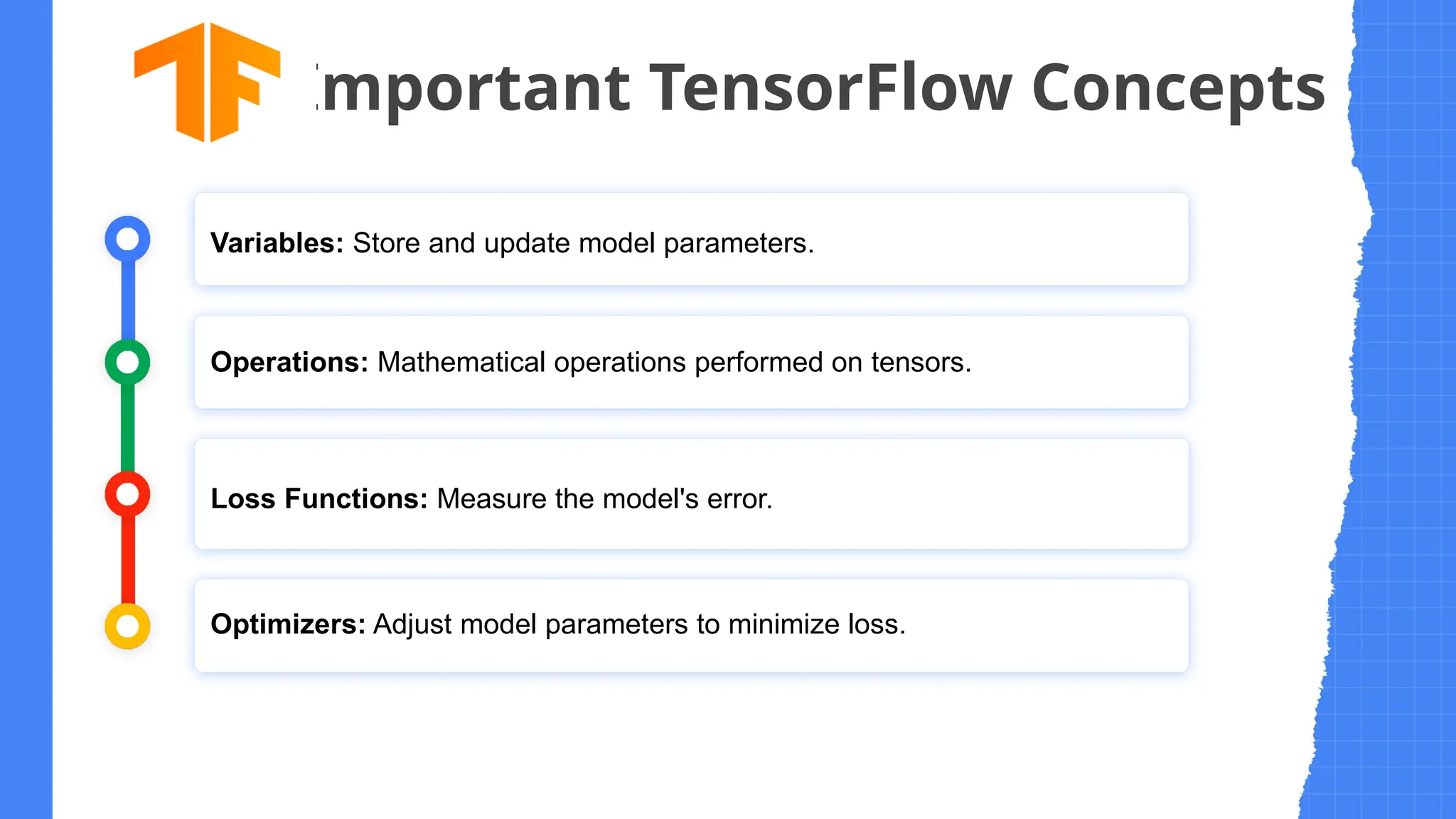
The document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI) and its subset, machine learning (ML), explaining their definitions, differences, and applications. It outlines the machine learning life cycle, types of ML, popular algorithms, and introduces neural networks and deep learning. Additionally, it covers TensorFlow, an open-source ML library by Google, highlighting its features, concepts, and applications in various domains.