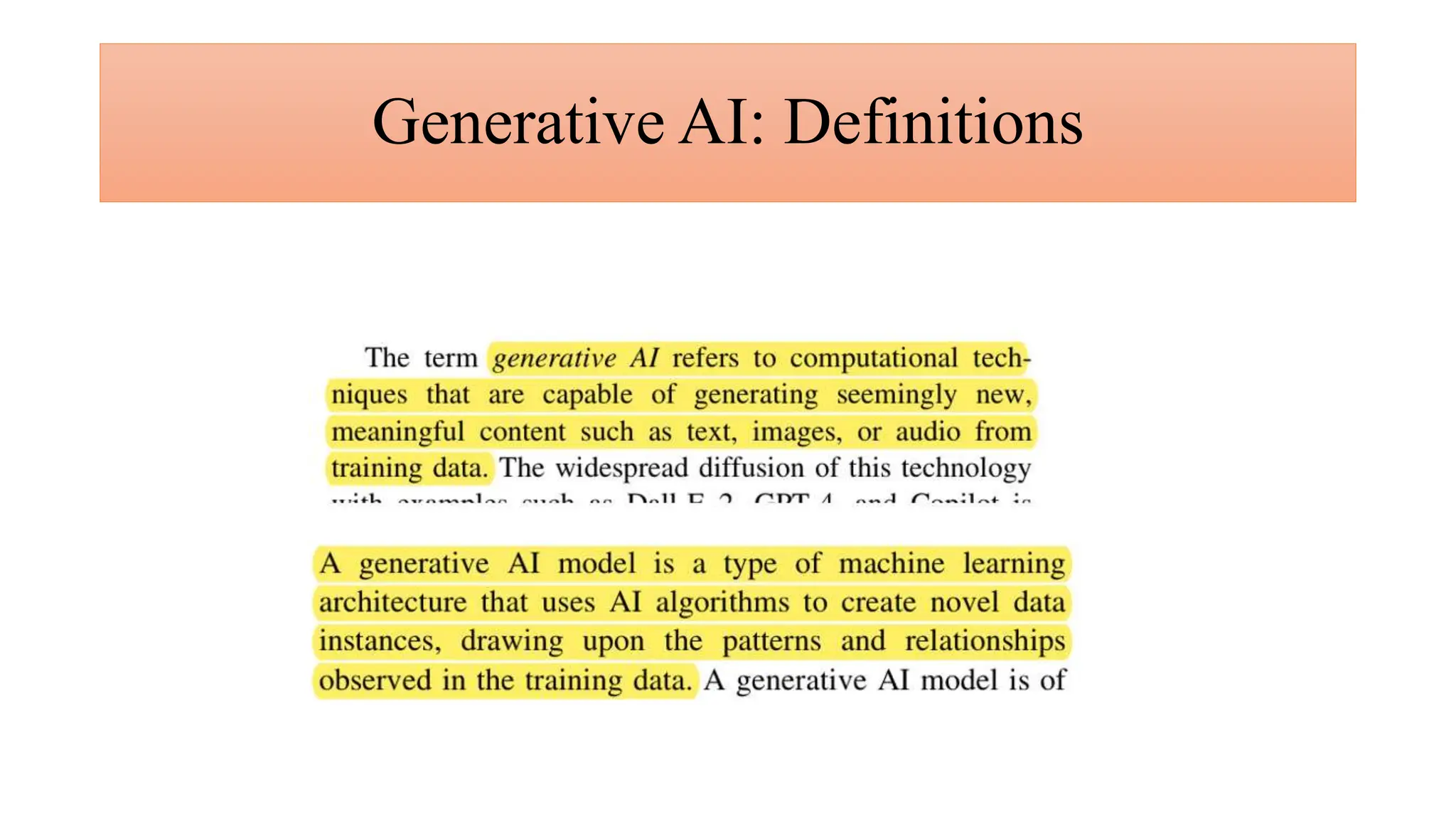
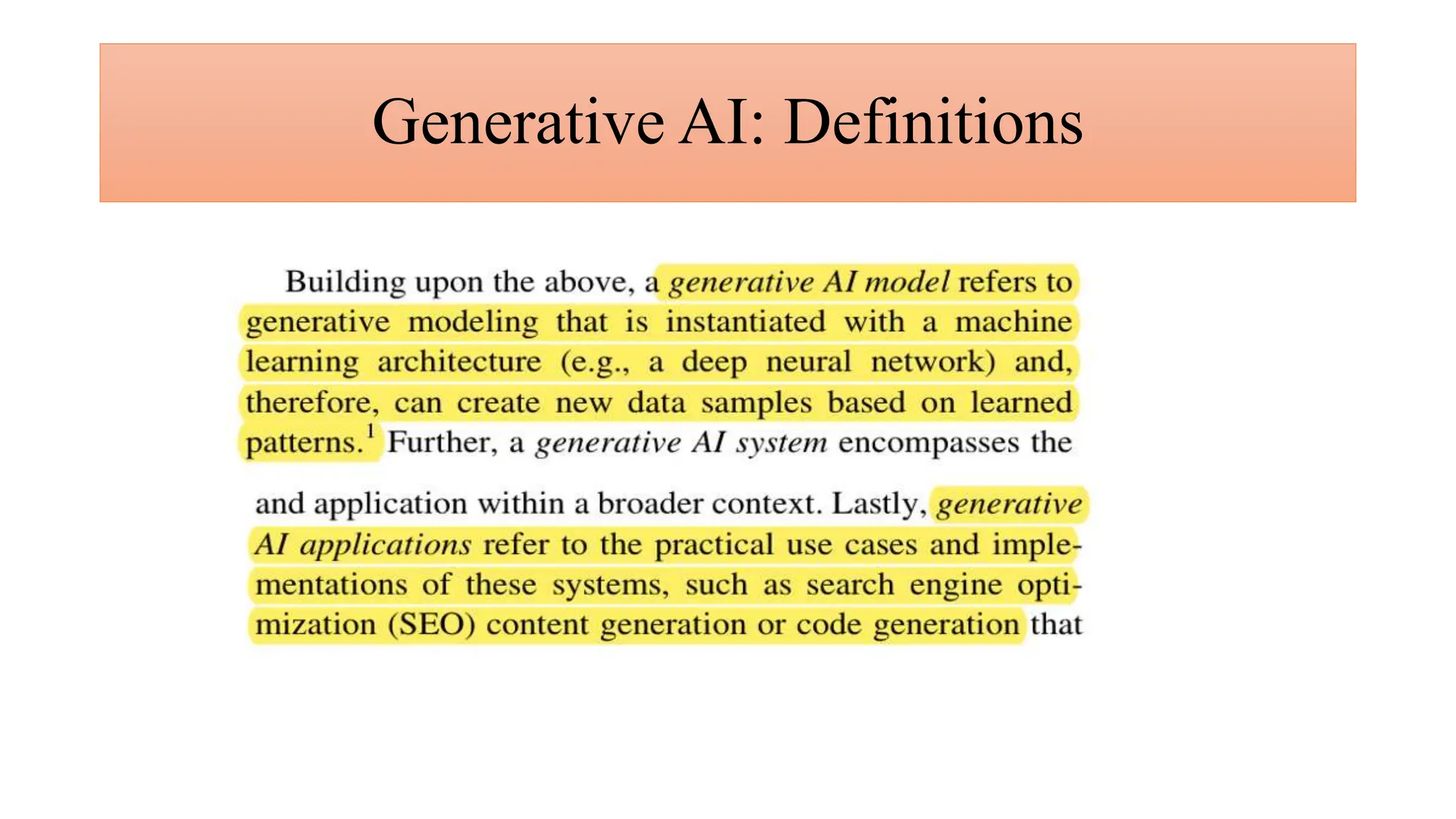
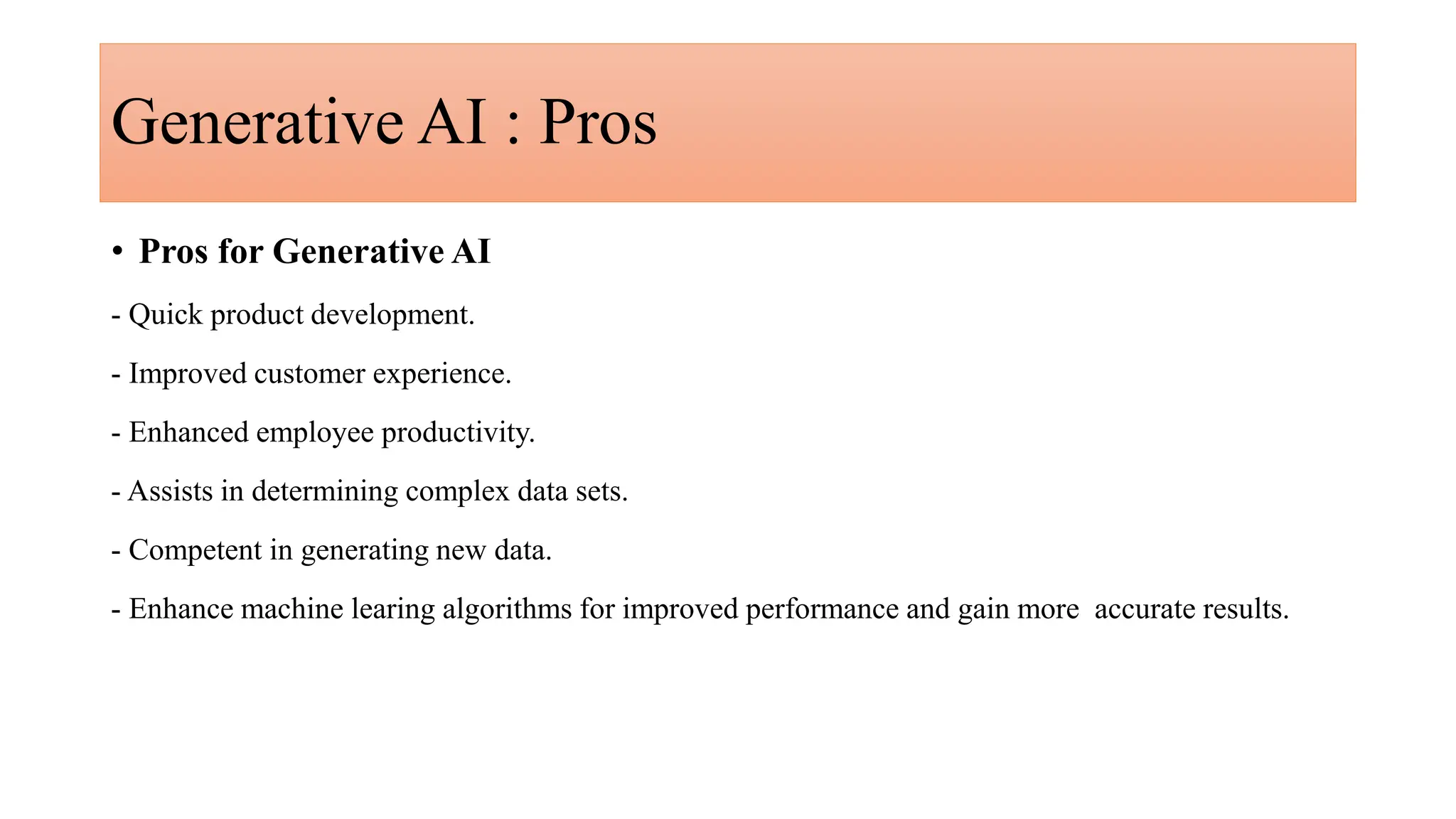
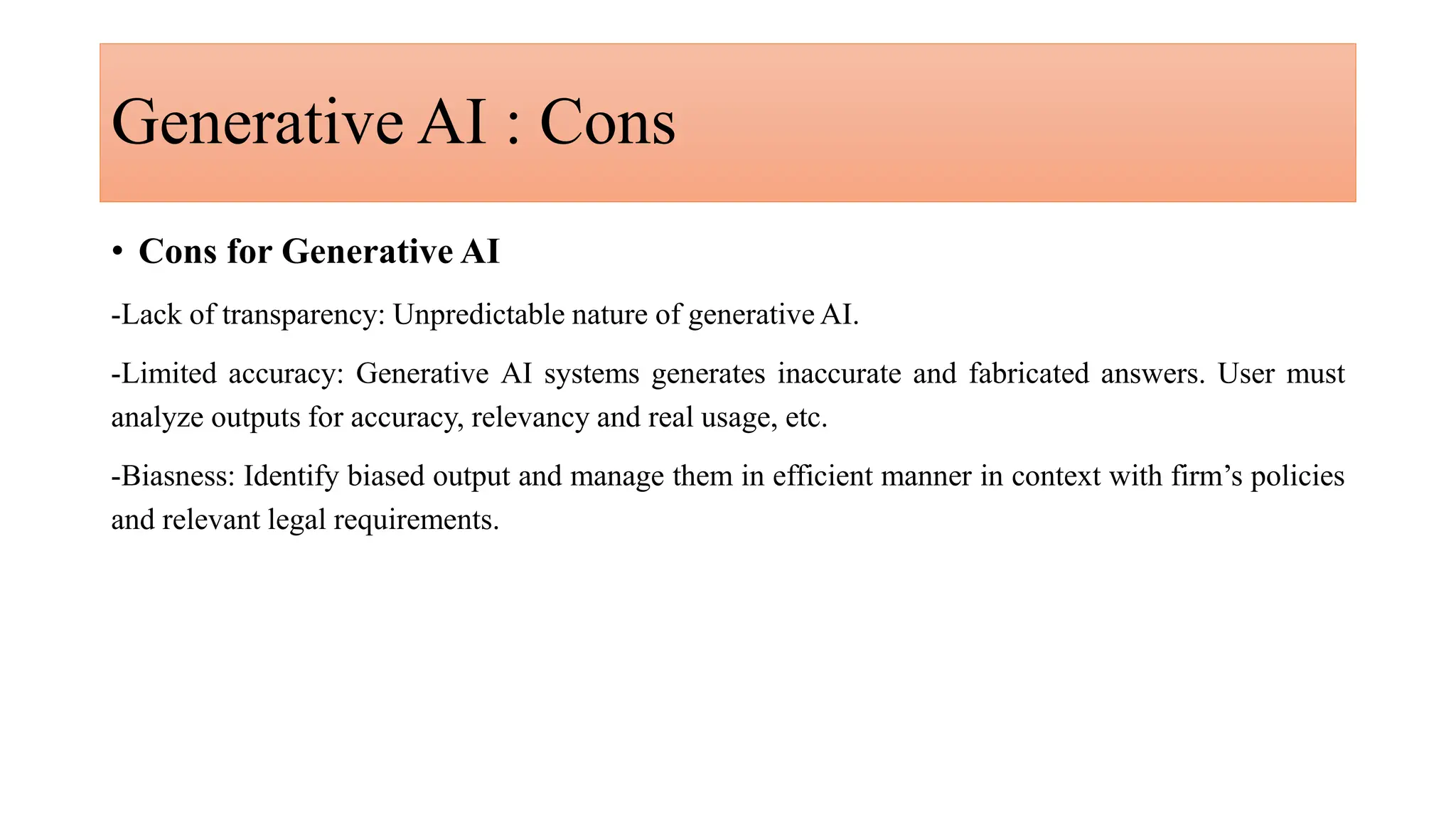
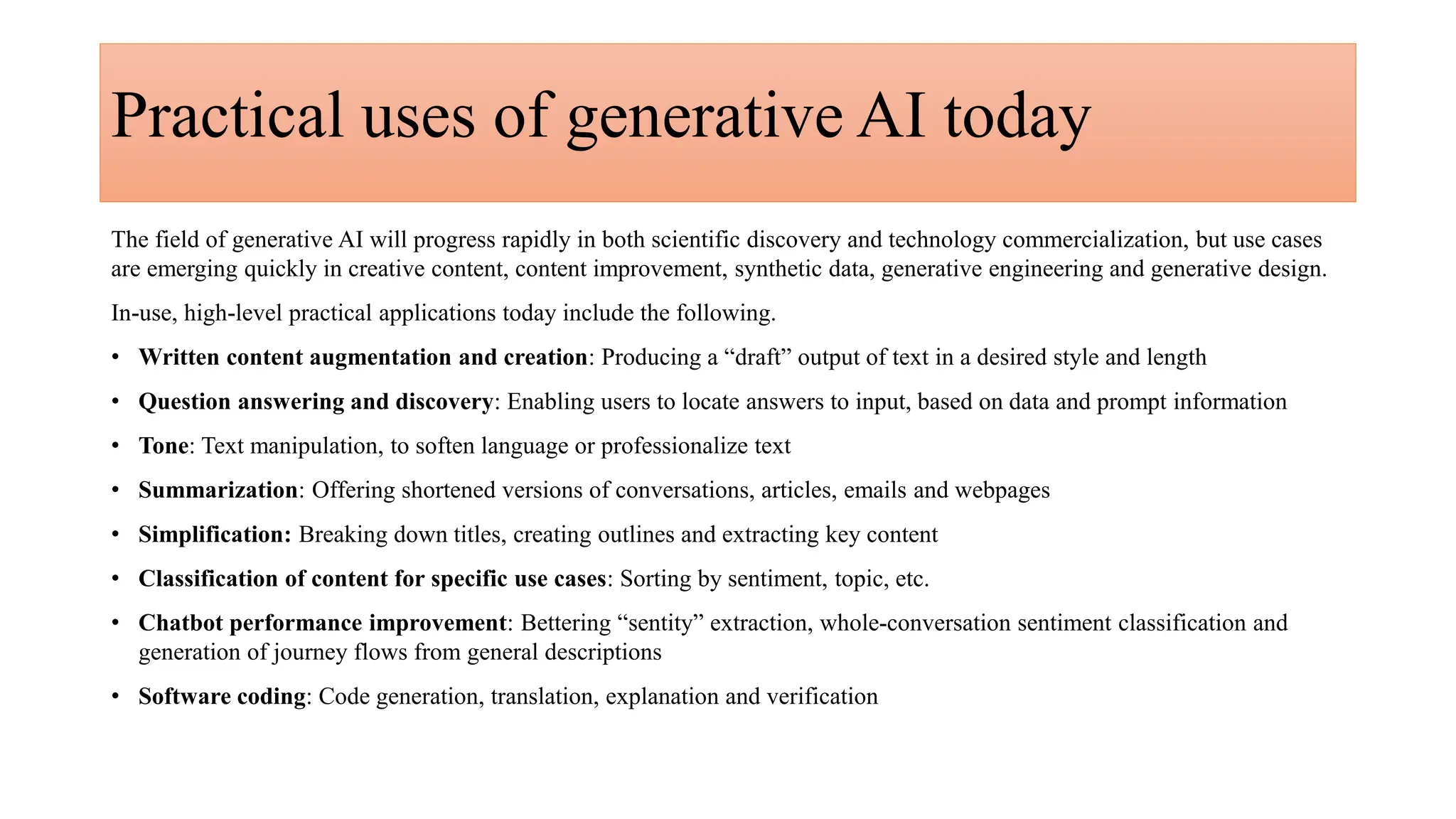
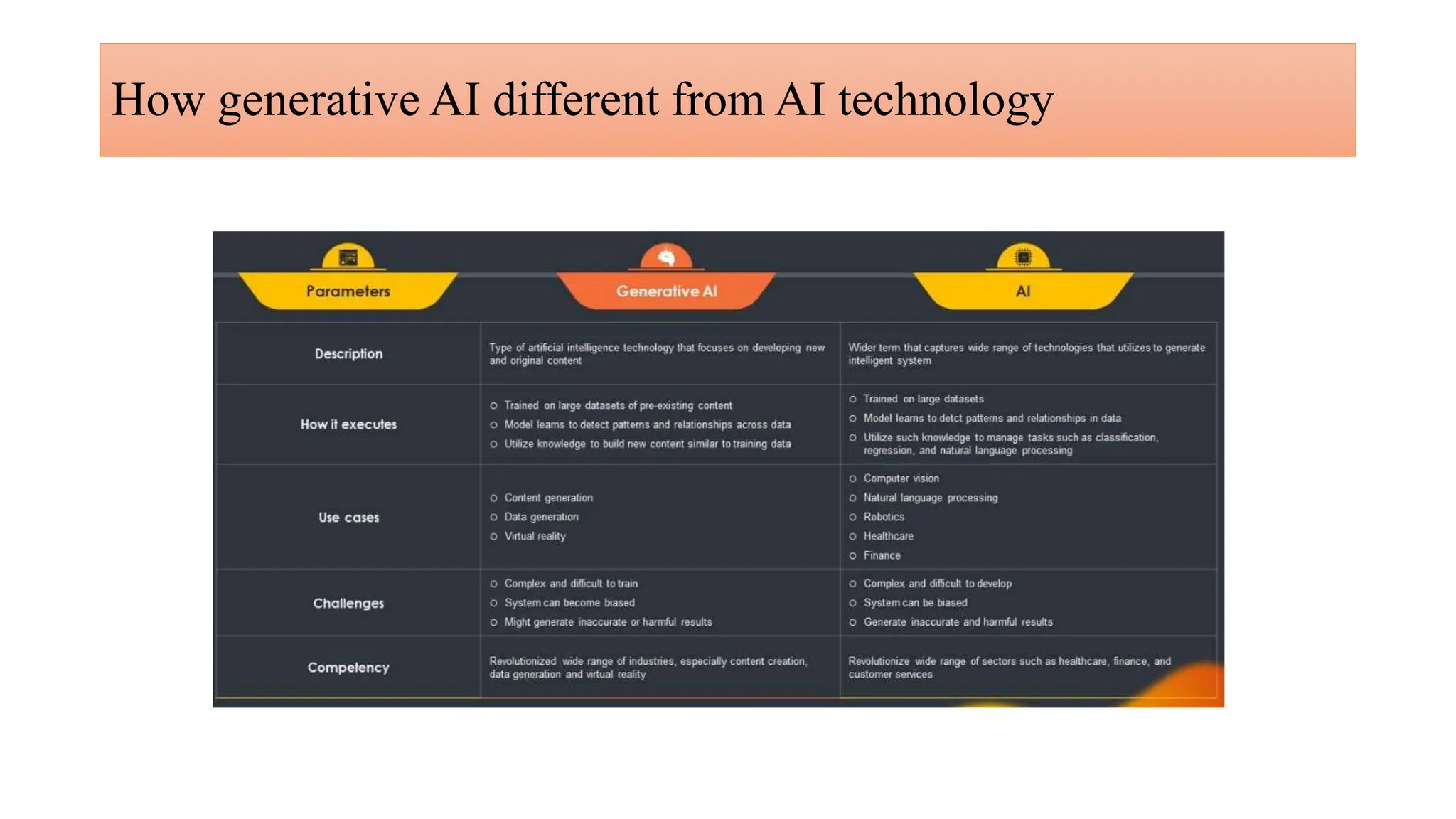
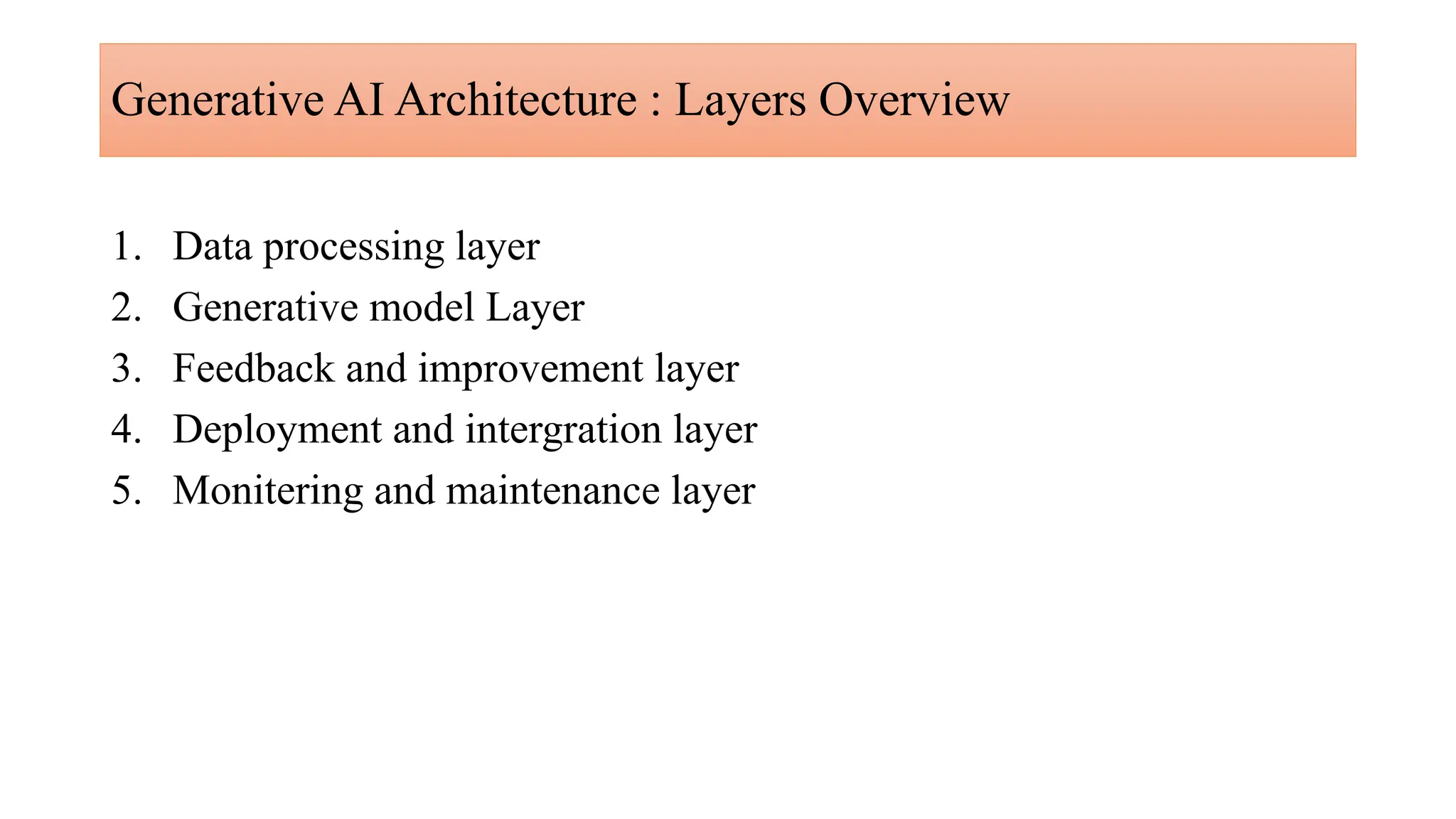
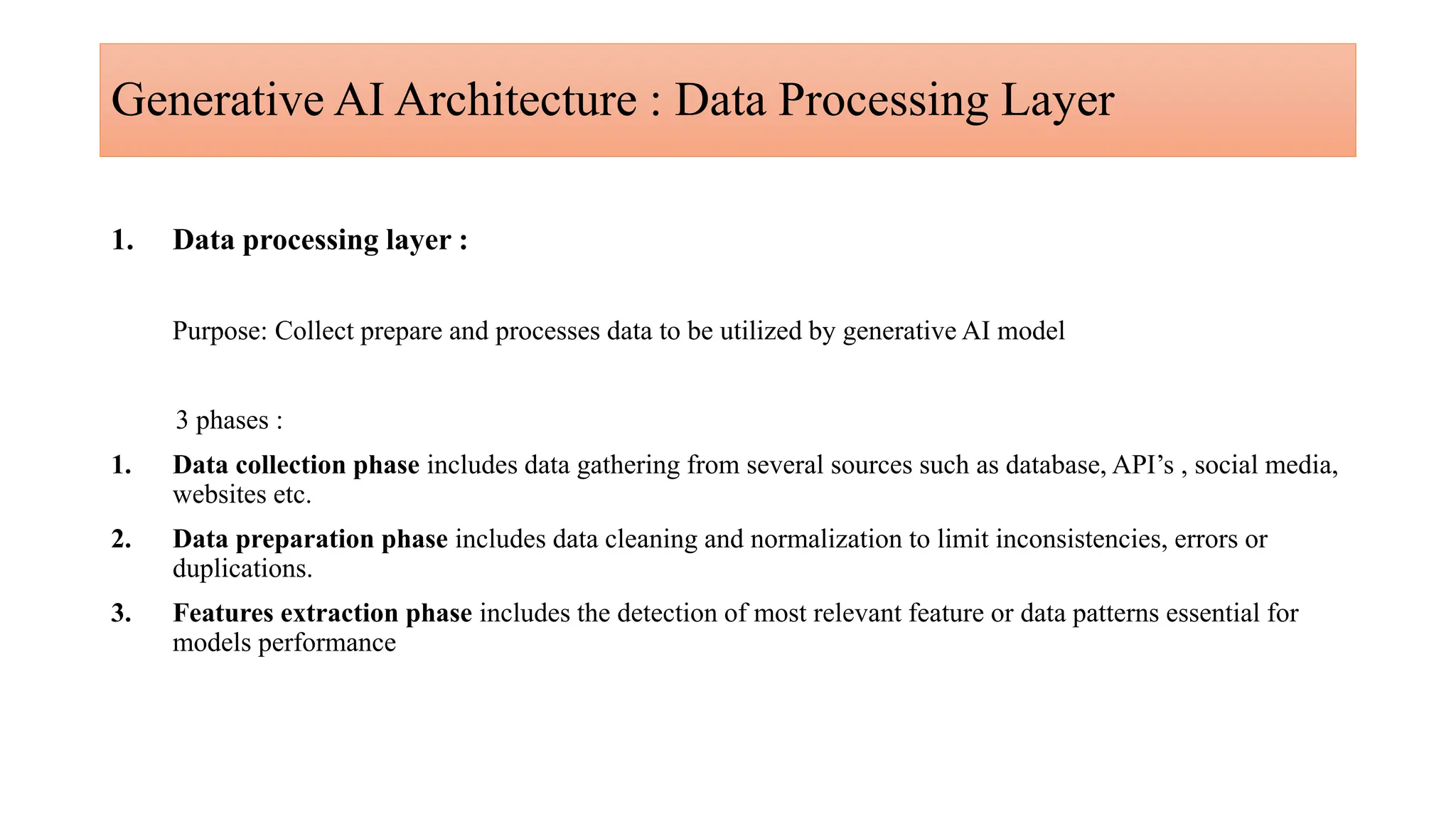
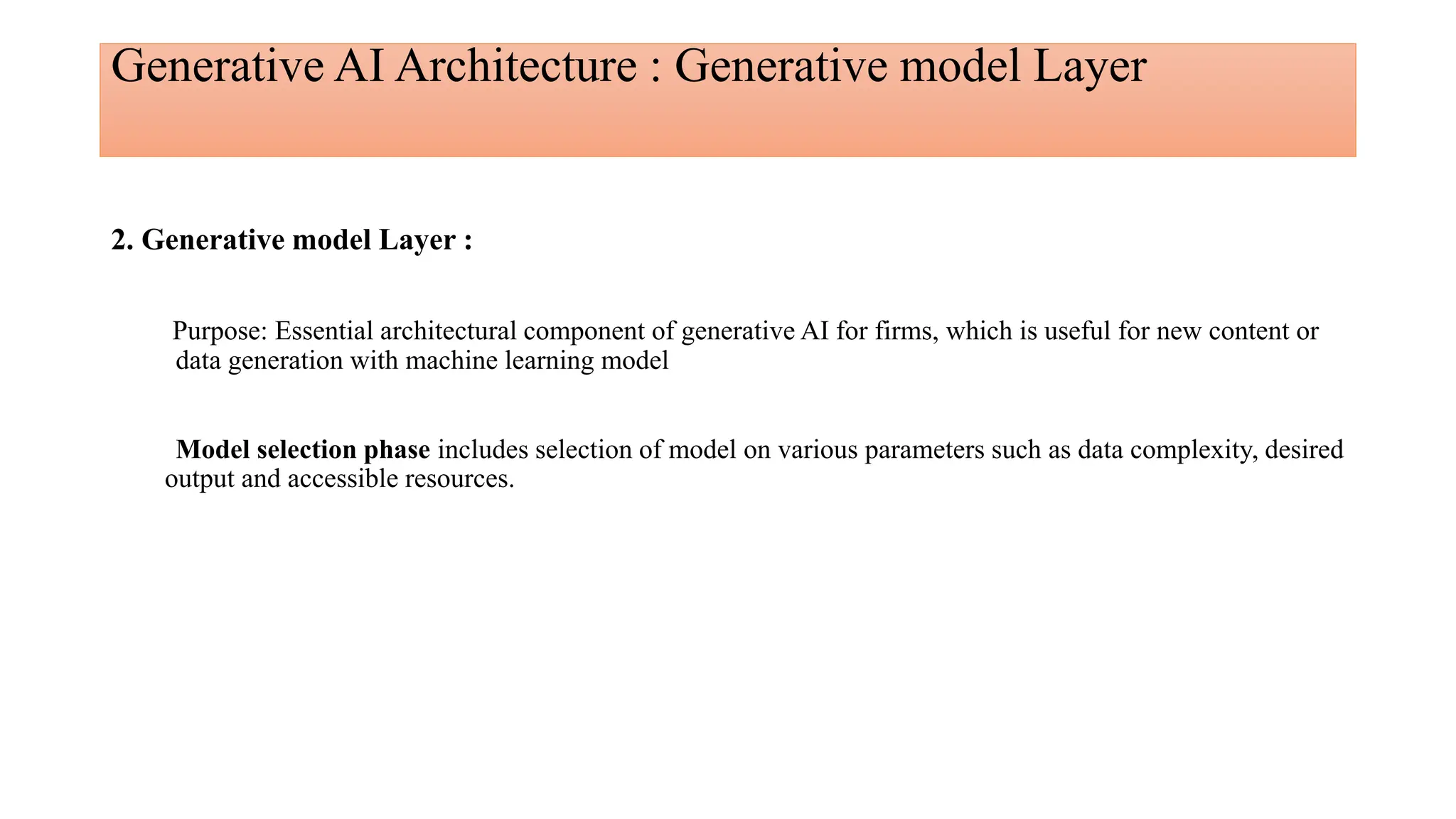
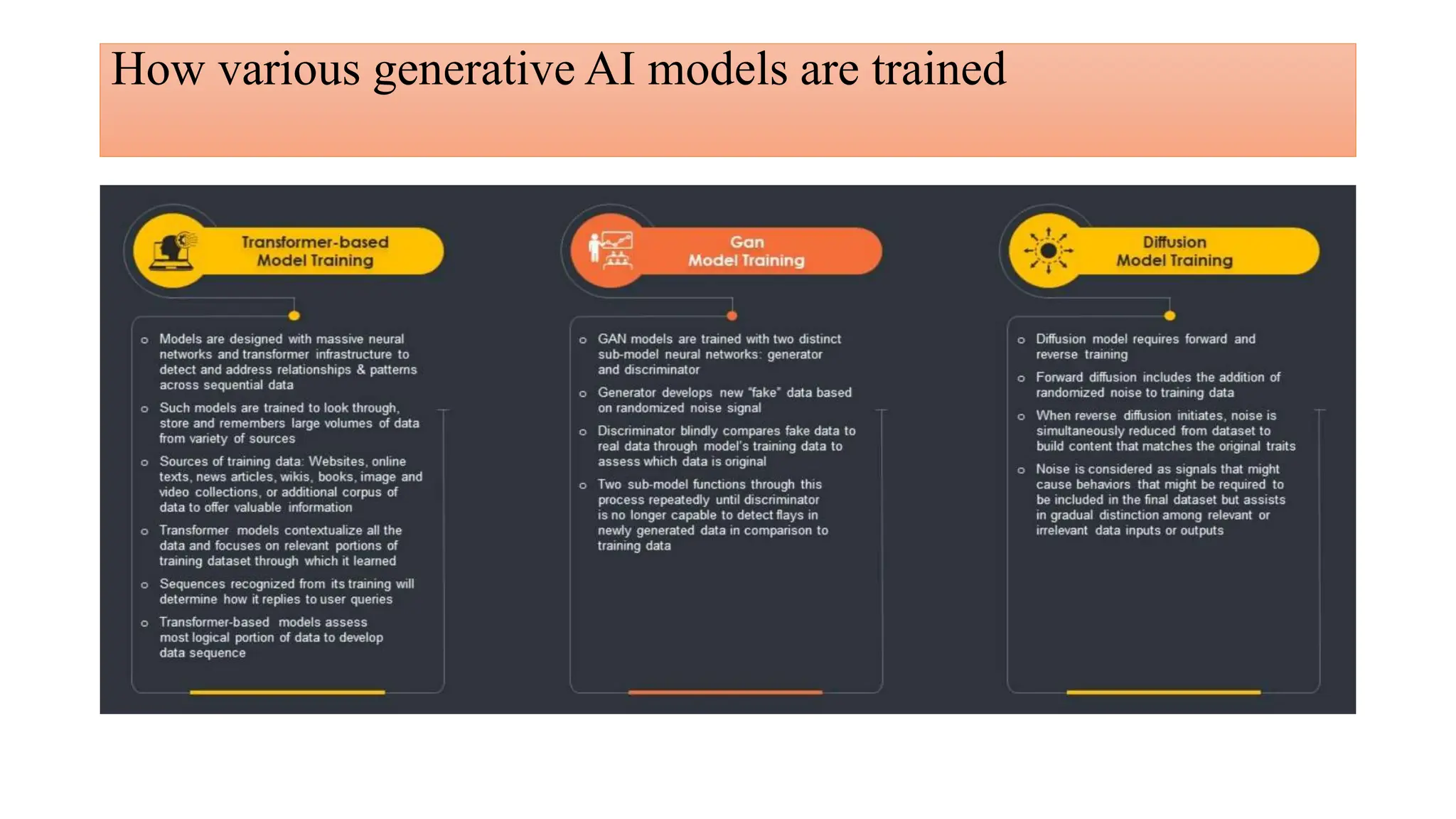
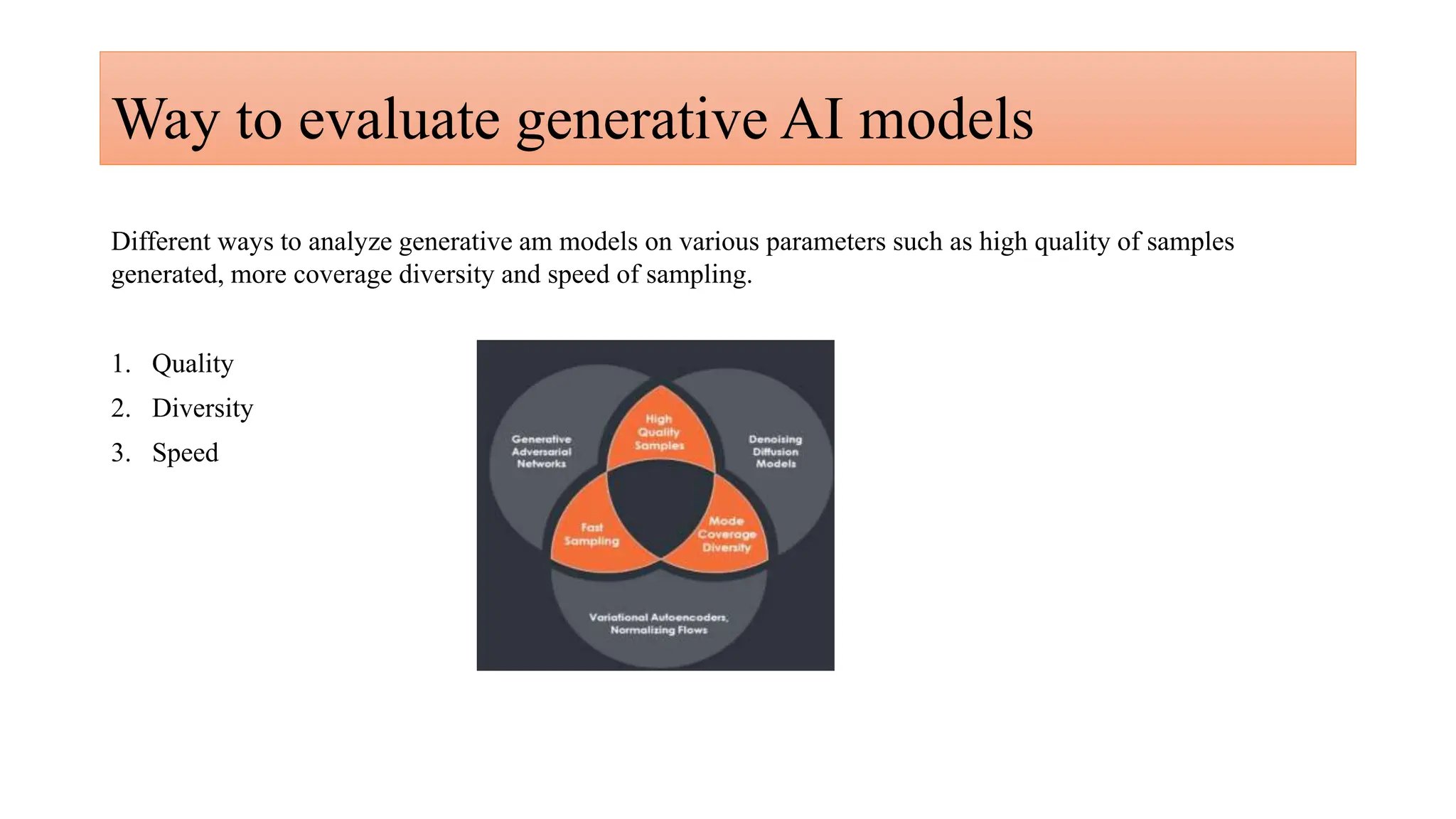
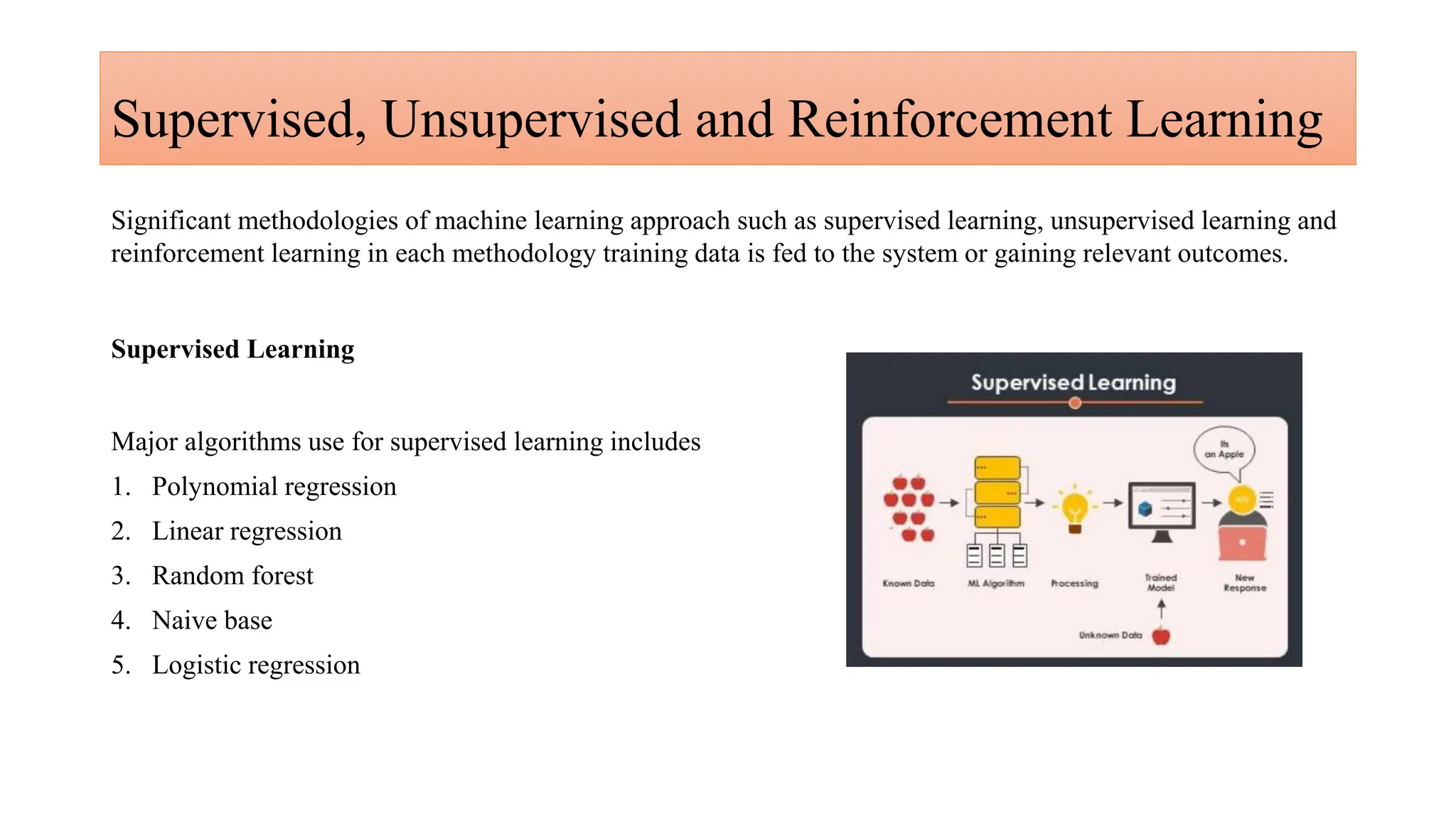
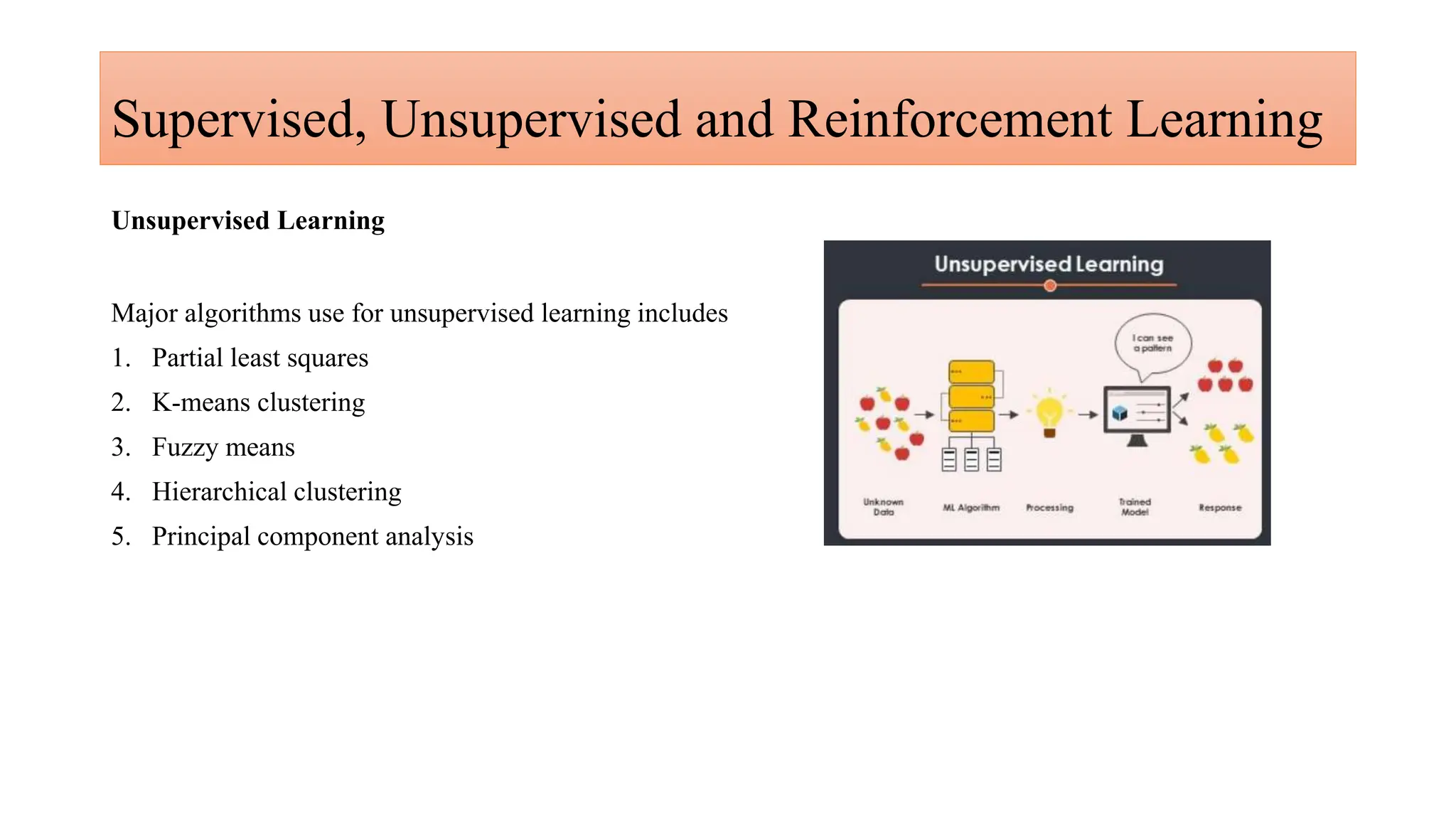
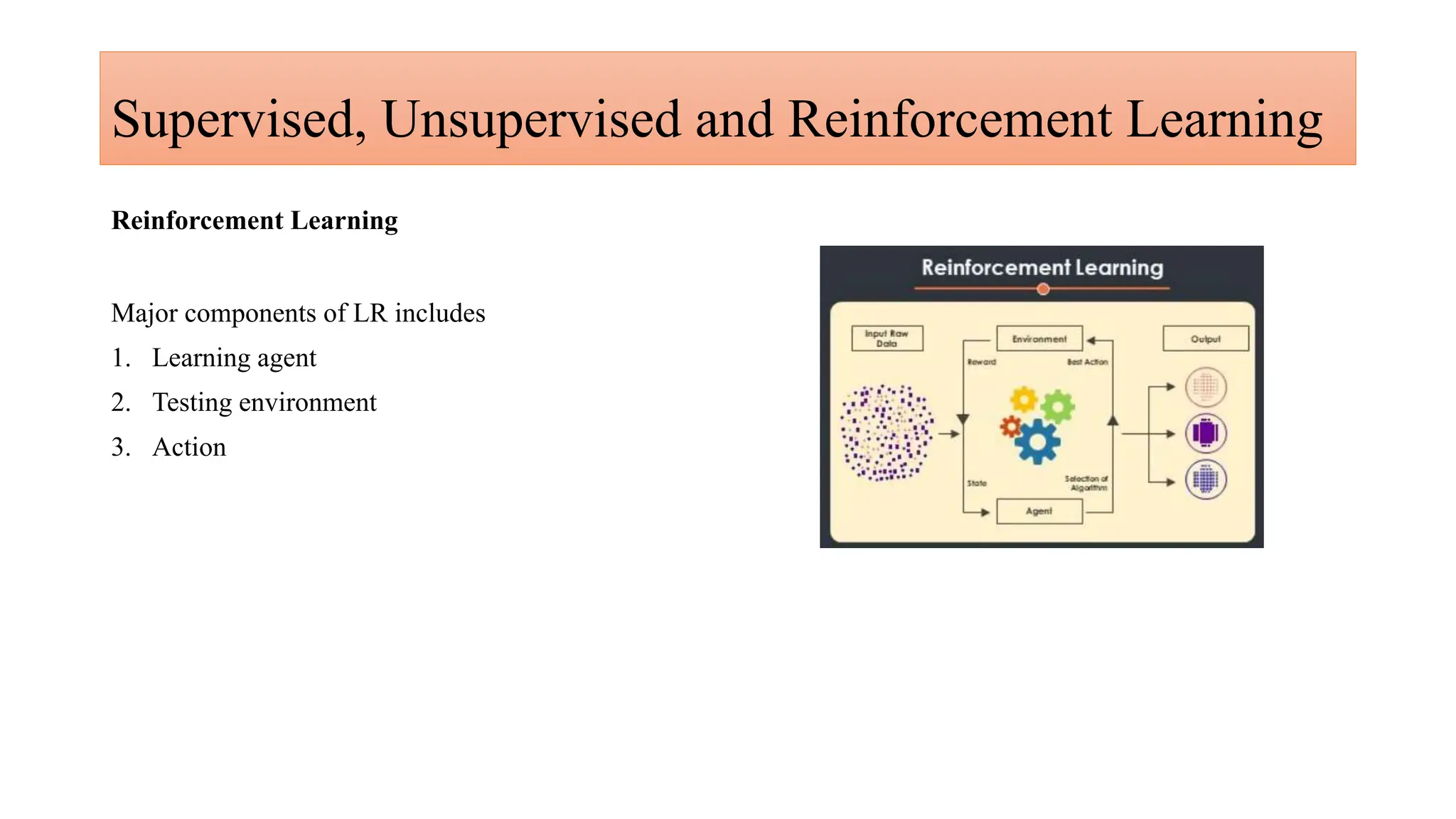
Generative AI is a technology that creates content such as images, videos, speech, and text by predicting the next element based on trained datasets. It offers advantages like quick product development and improved customer experience, but also presents challenges such as lack of transparency and risk of bias. Different industries, including pharmaceuticals and marketing, are increasingly utilizing generative AI to enhance processes and discover new products.