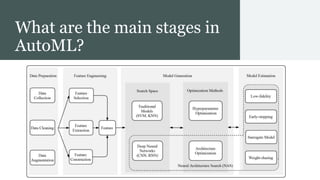
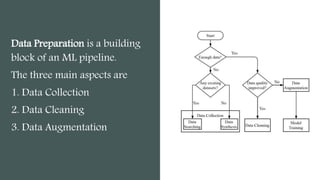
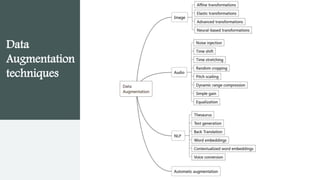
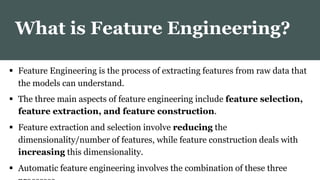
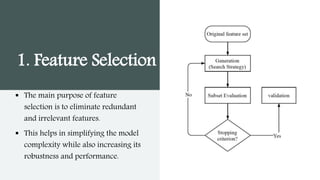
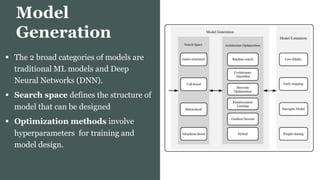
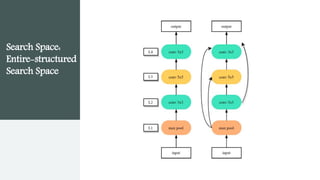
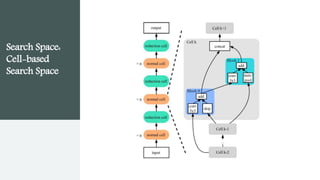
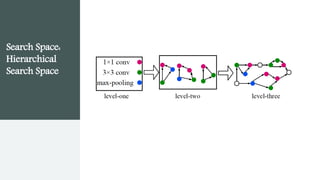
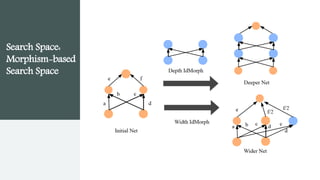
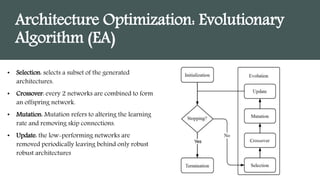
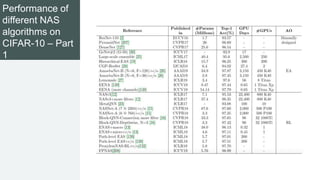
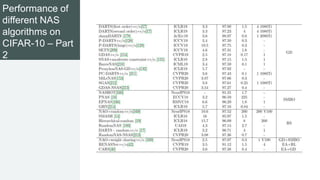
This document provides an overview of AutoML. It discusses how AutoML aims to automate the machine learning process to make ML accessible even for non-experts. The document outlines the main stages in an AutoML system, including data preparation, feature engineering, model generation, and model evaluation. It describes techniques used in each stage like data cleaning, feature selection, neural architecture search, and early stopping. The document also notes some open problems in AutoML like improving performance on NLP tasks and increasing reproducibility.