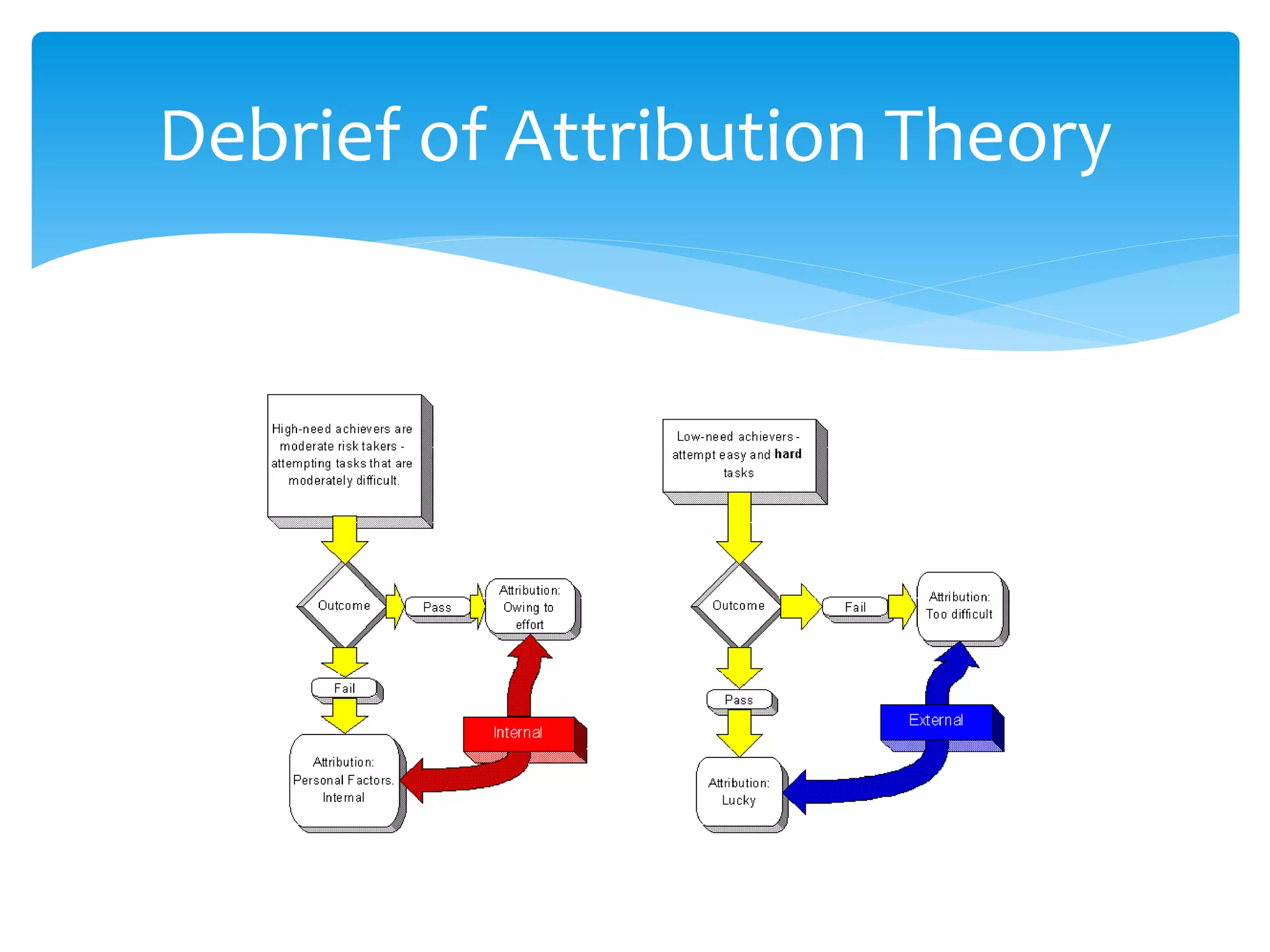
Attribution theory deals with how people make causal explanations for events. It examines what information people use to form causal judgments. Attribution theory seeks to explain cognitive processes like perception, memory, reasoning, and judgment. Specifically, it concerns how people attribute causes to their own and others' behaviors. Attribution theory originated with Fritz Heider, who identified internal characteristics and external factors as the two categories for explaining events. Later, Julian Rotter examined perceptions of control over events, and Bernard Weiner described how attributions influence motivation and learning behaviors. Understanding attribution theory can help improve learning by changing attributions that hinder motivation.