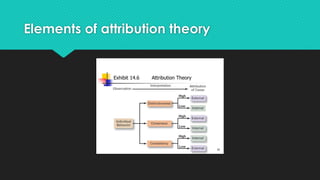
Attribution theory in psychology explores how individuals interpret the causes of their experiences, categorizing them as either internal (personal factors) or external (environmental influences). It aims to provide cognitive control over one’s surroundings, helping to explain behavior and bring predictability to life. Key elements include distinctiveness, consensus, and consistency, as well as the process of perception, judgment, and attribution, highlighting errors like the fundamental attribution error where personal character is over-emphasized in others' actions.