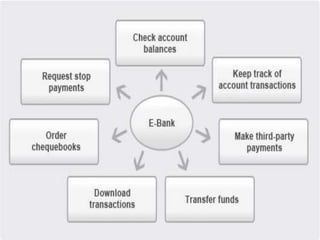
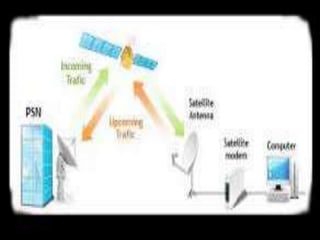
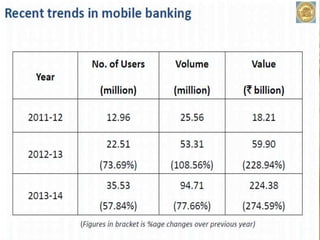
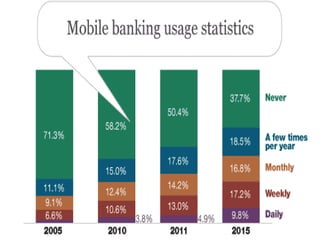
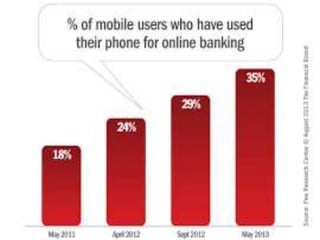
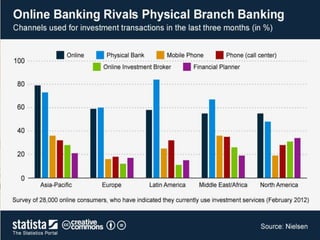
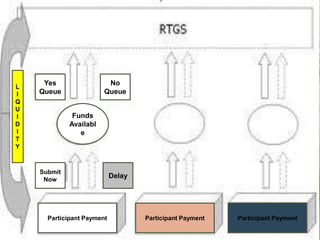
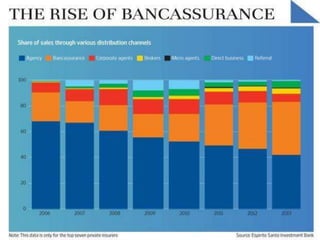
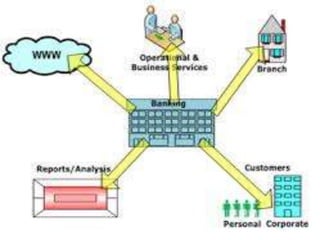
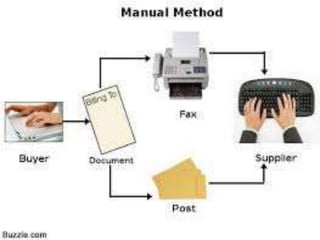
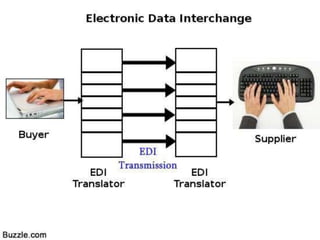
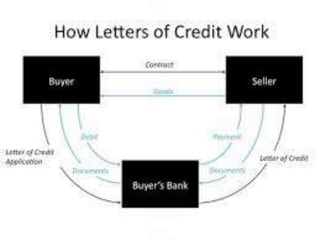
This document summarizes the history and development of the Indian banking system. It discusses the establishment of early banks in India such as the Bank of Calcutta in 1806. It also describes the functions of banks and various technological innovations that have eased banking like ATMs, credit cards, and electronic banking. The latest trends in Indian banking discussed include universal banking, globalization of banking, and use of technologies like satellite banking, phone banking, online banking, and real time gross settlement. Risk management and customer relationship management have also become increasingly important in Indian banks.