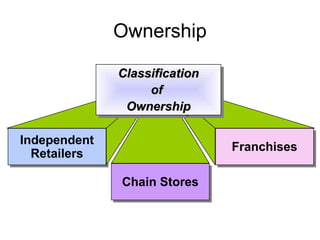
This document discusses different types of retail institutions and ownership structures, including independent retailers, chain stores, and franchises. It then covers various types of retailing like food retailers, general merchandise retailers, non-store retailers, and service retailing. Food retailers discussed include conventional supermarkets, superstores, supercenters, warehouse supermarkets, and convenience stores. General merchandise retailers mentioned are department stores, discount stores, specialty stores, category specialists/killers, home improvement centers, and warehouse clubs. The document also touches on non-store retailing like catalogue, direct mail, direct sell, TV home shopping, and vending machines.