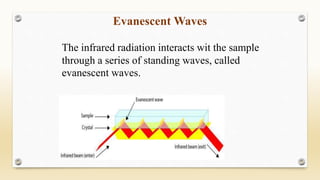
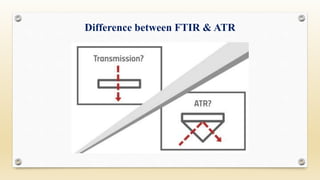
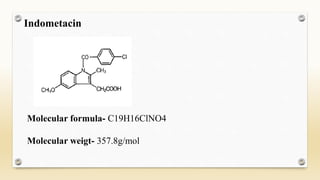
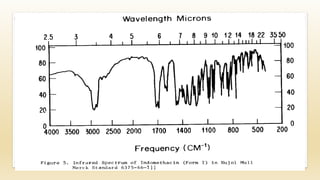
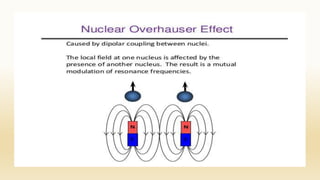
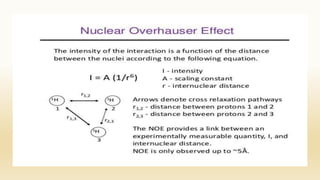
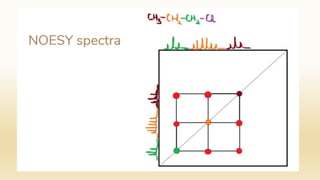
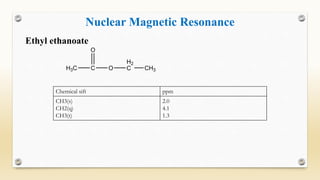
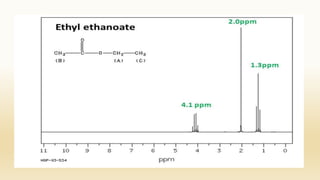
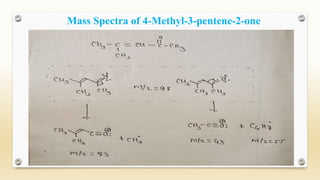
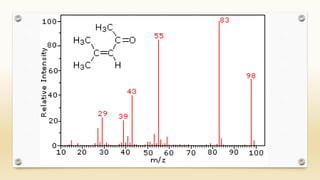
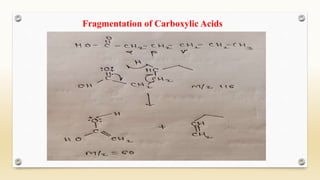
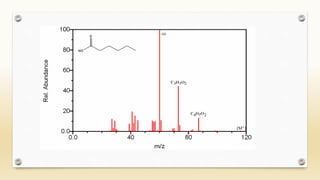
The document discusses techniques for interpreting organic compounds using infrared (IR), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and mass spectrometry. It elaborates on attenuated total reflectance (ATR) as a method for analyzing samples in various states without preparation and highlights various applications in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries. Additionally, it outlines the noesy technique in NMR for determining the proximity of protons and explains the ring rule for calculating unsaturation in organic compounds.