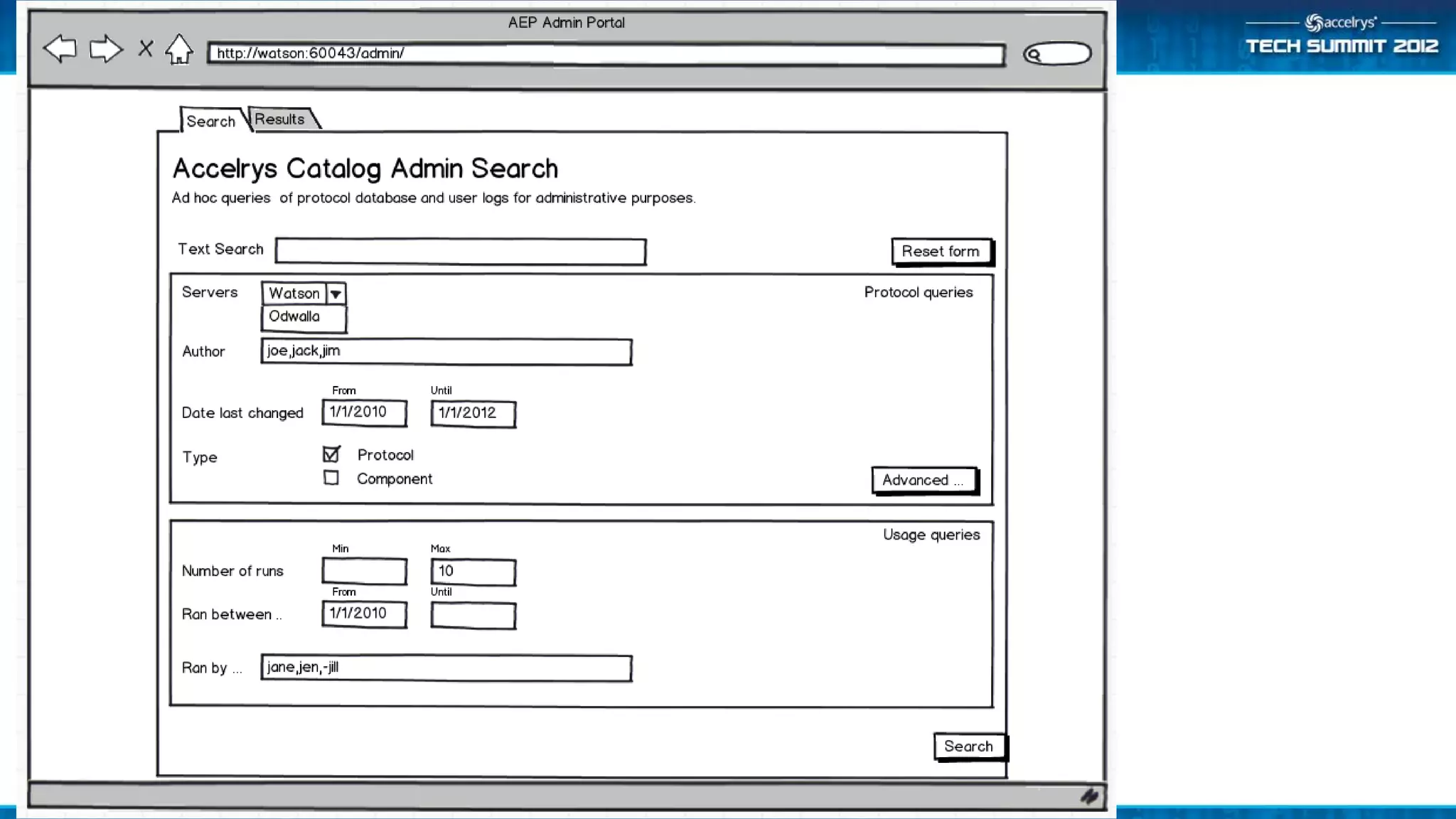
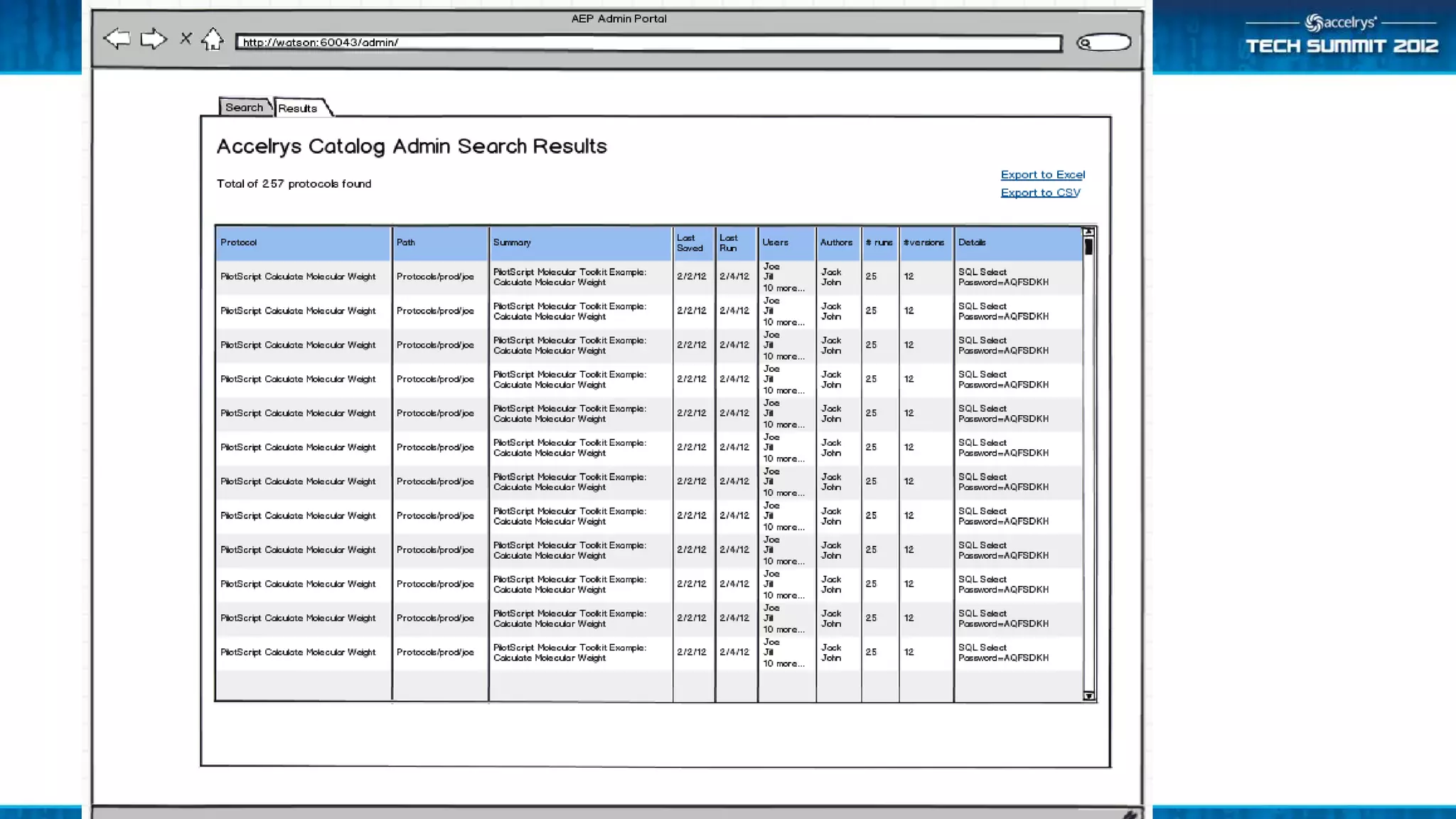
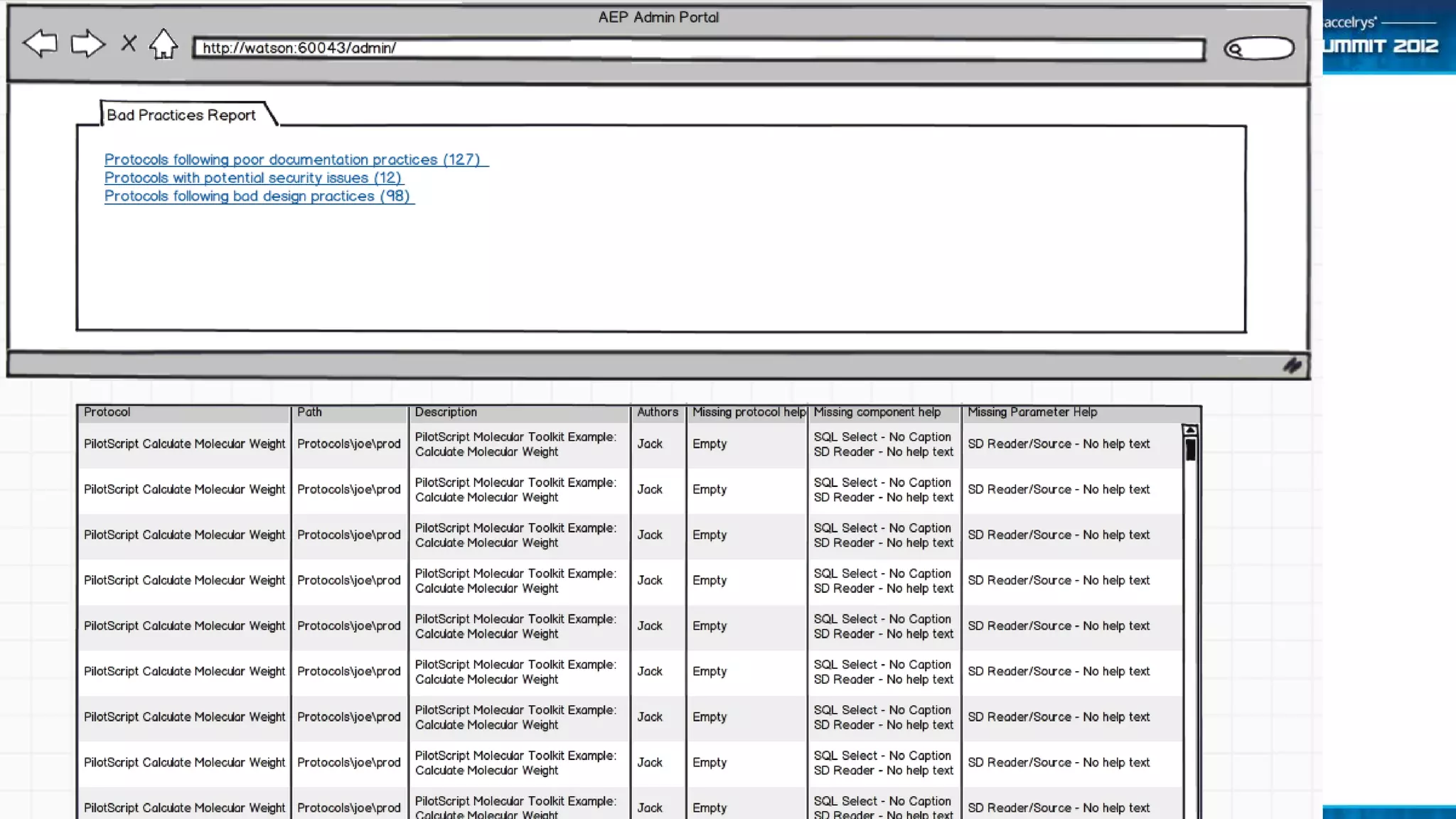
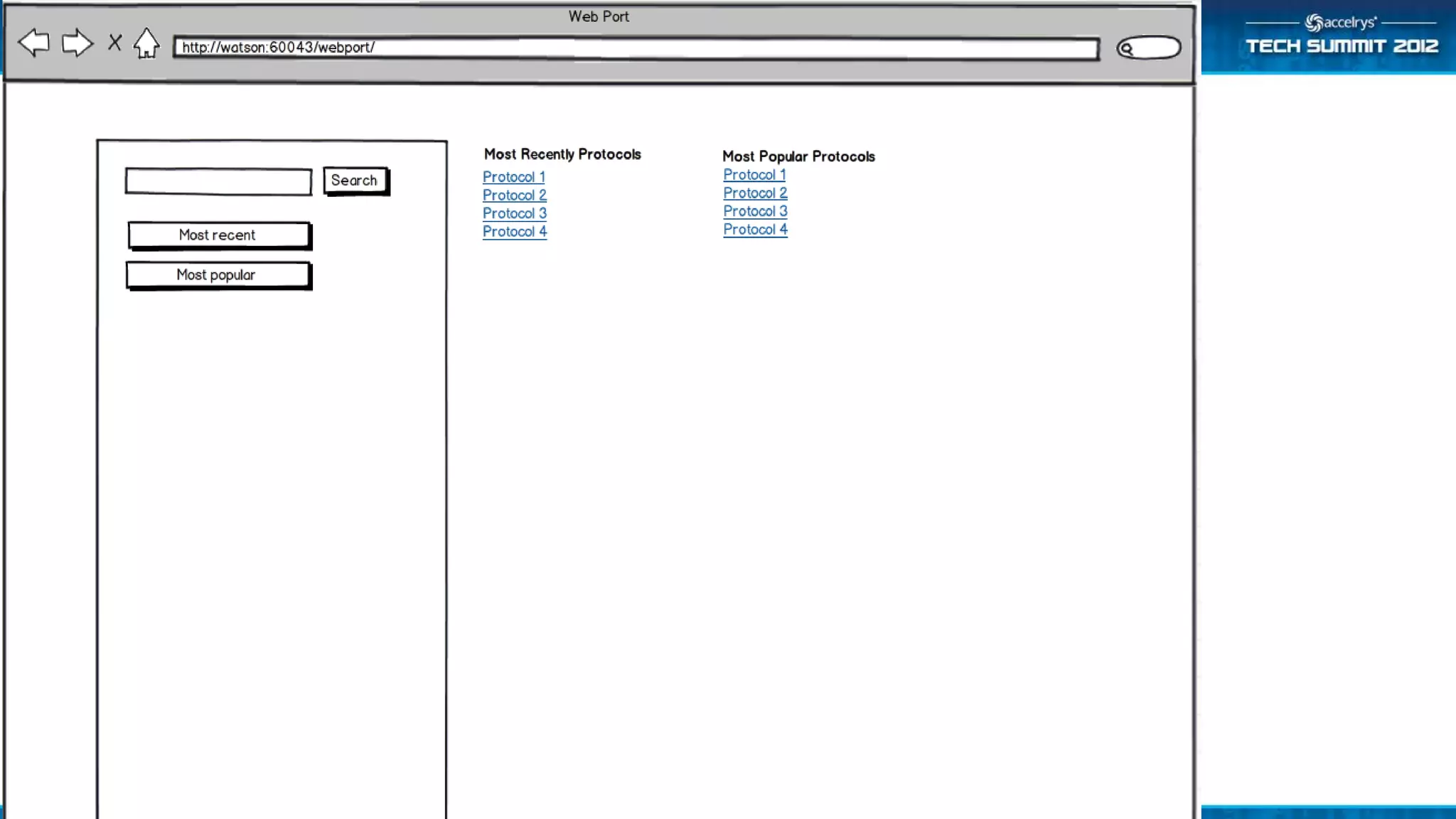
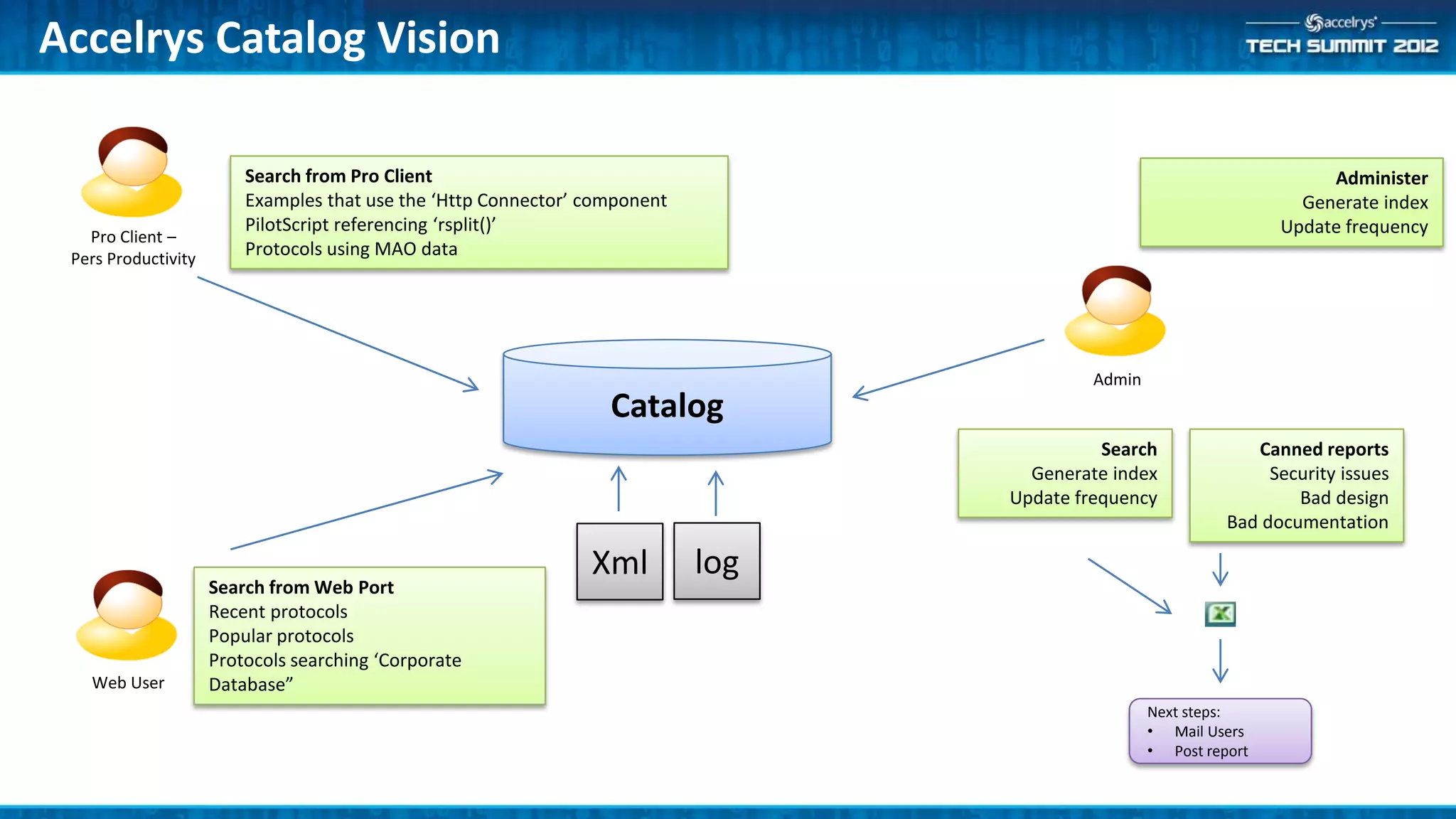
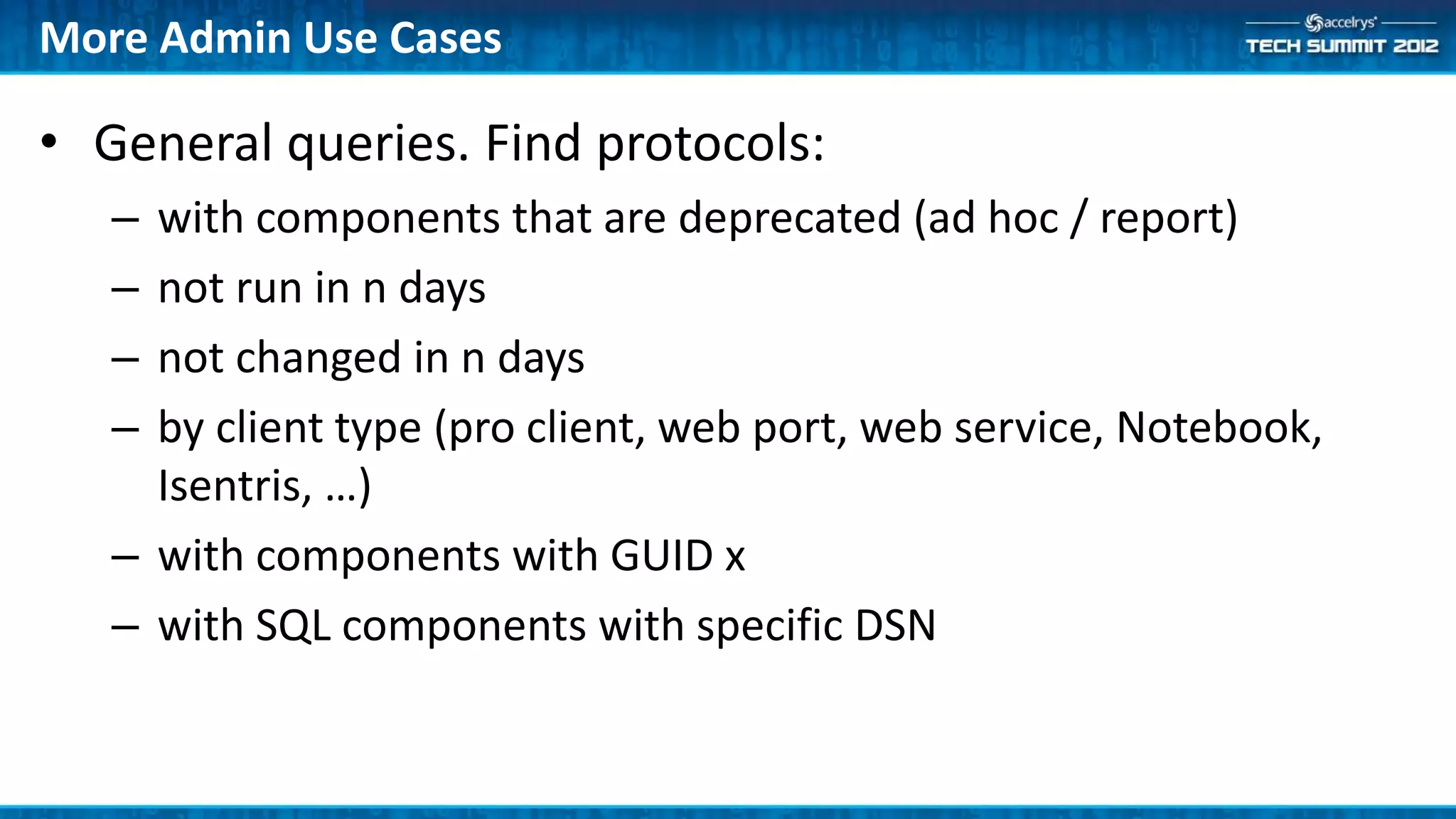
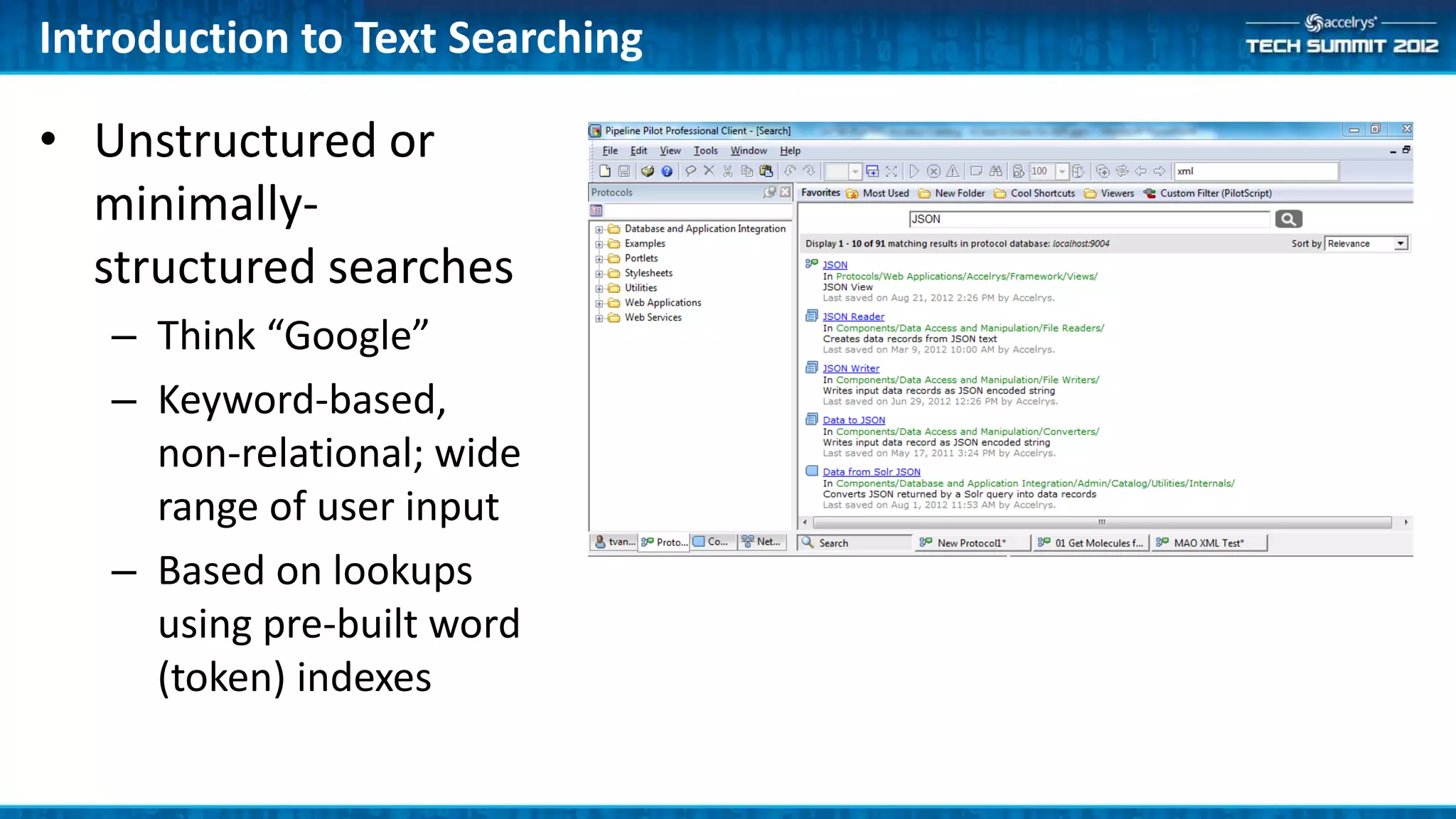
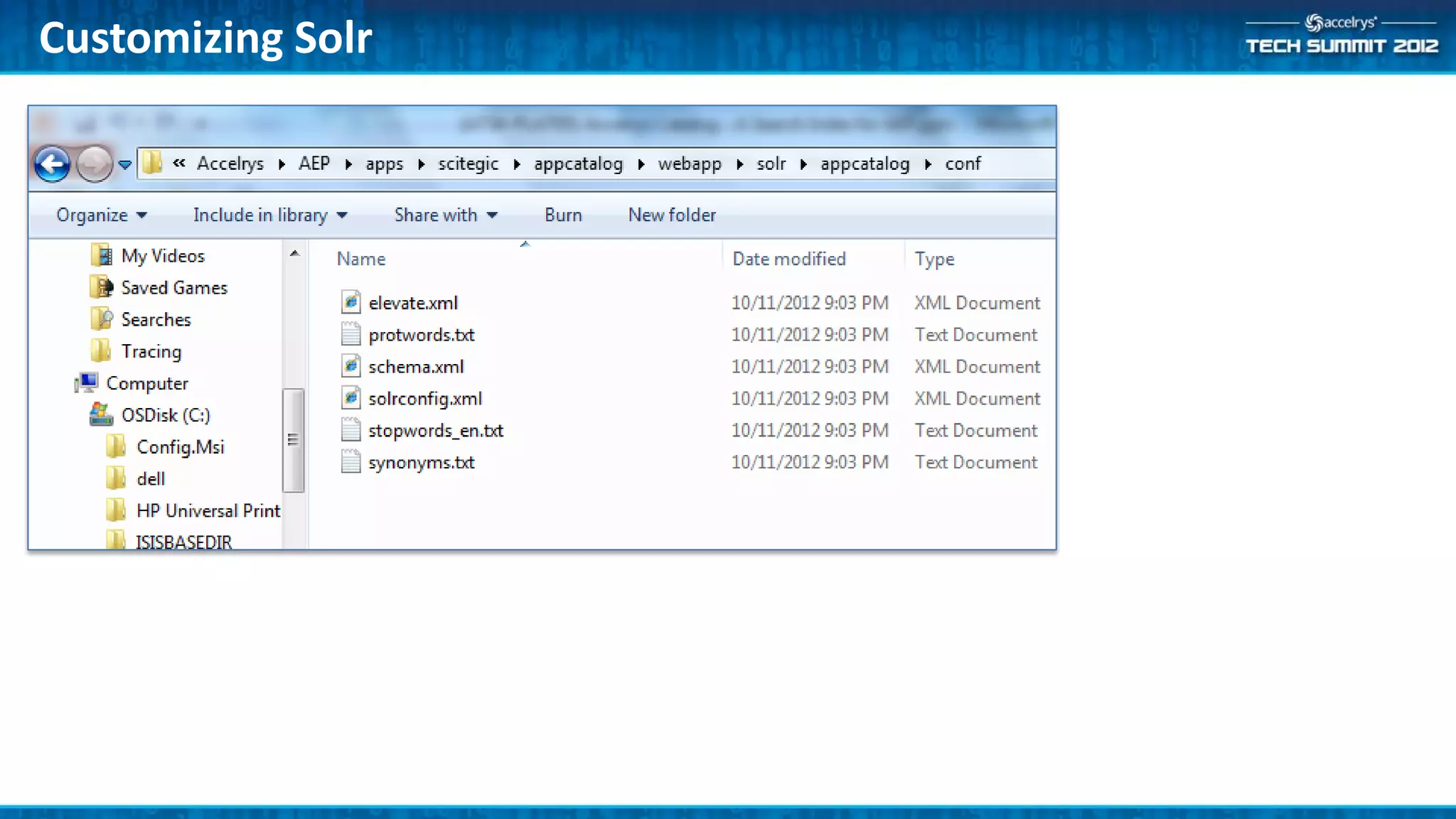
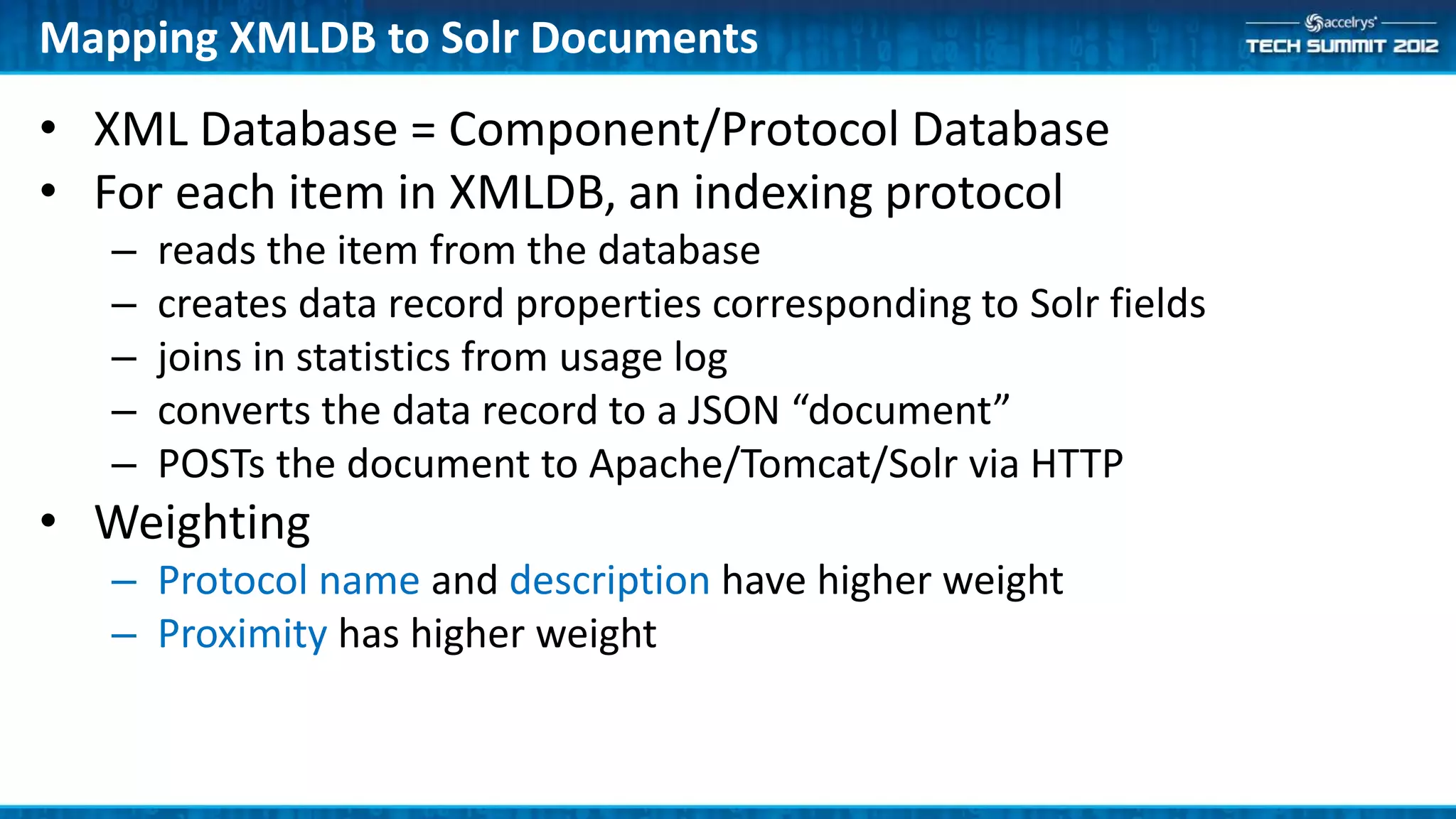
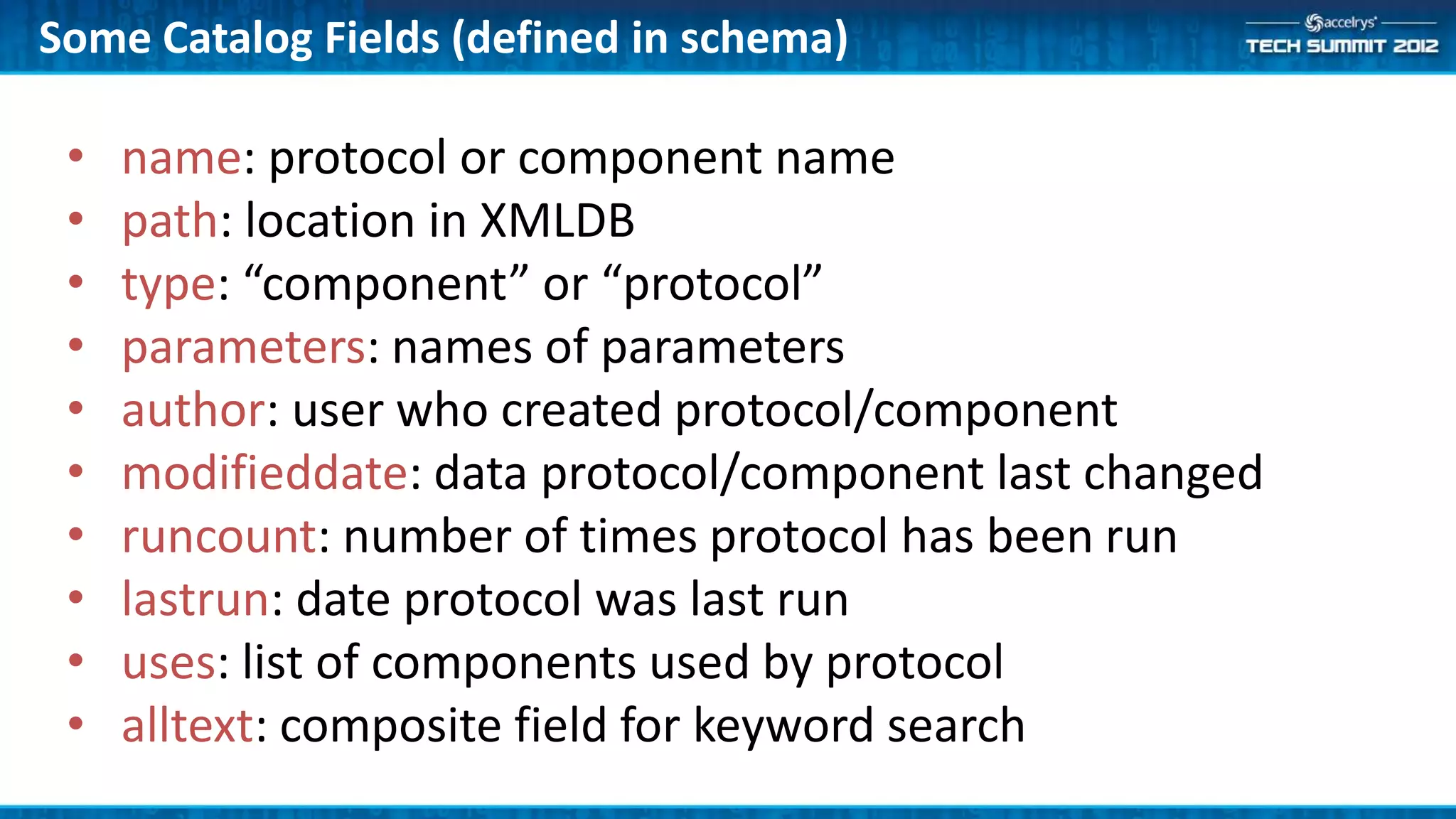
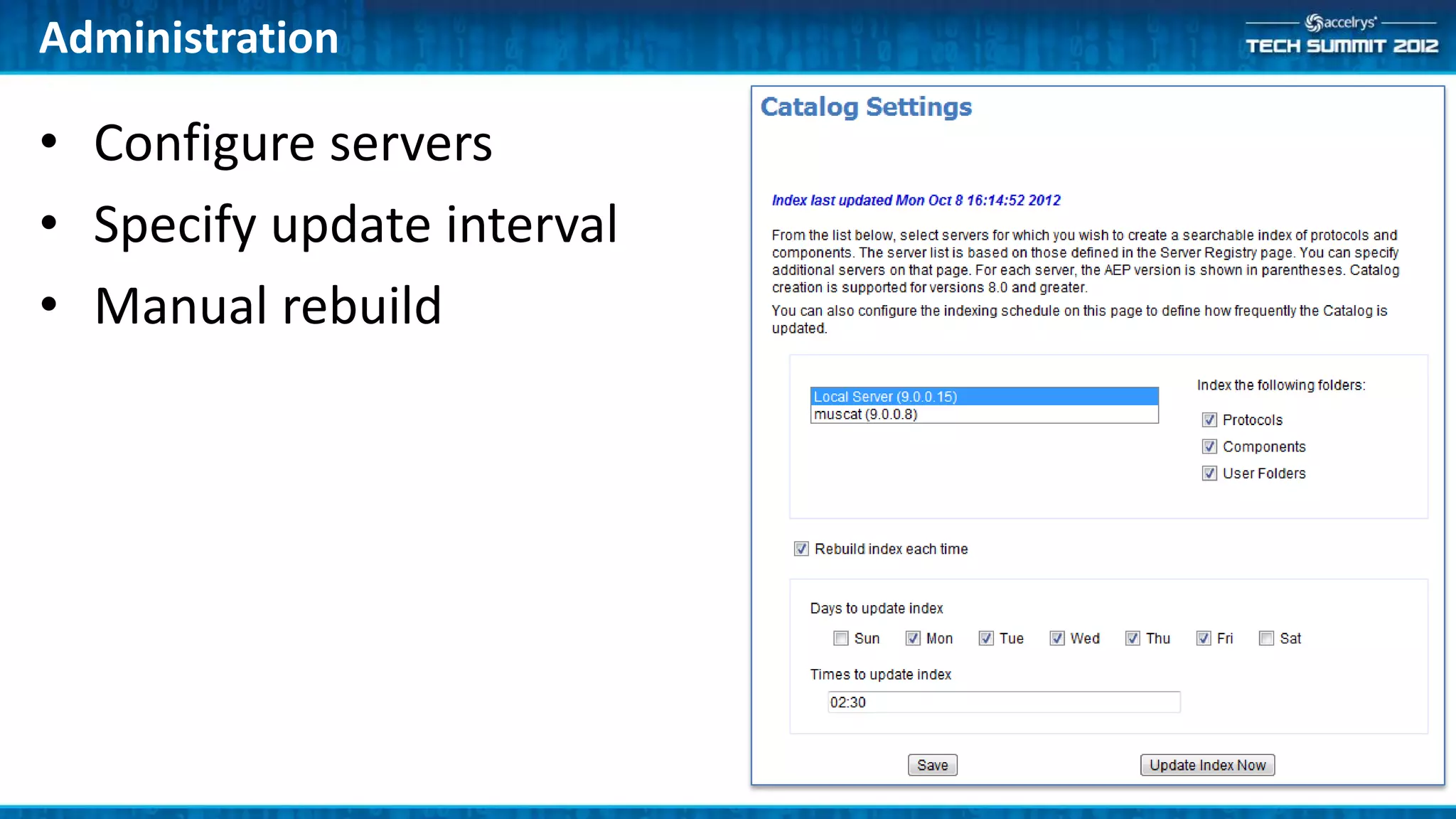
The Accelrys Catalog is an advanced search technology that outlines its deployment architecture and administration features, including Solr search indexing and text searching strategies. It addresses common design and documentation issues while providing various administrative use cases and examples for effective protocol management. Users are encouraged to engage in beta testing and begin preparing for an upgrade to version 9.0.











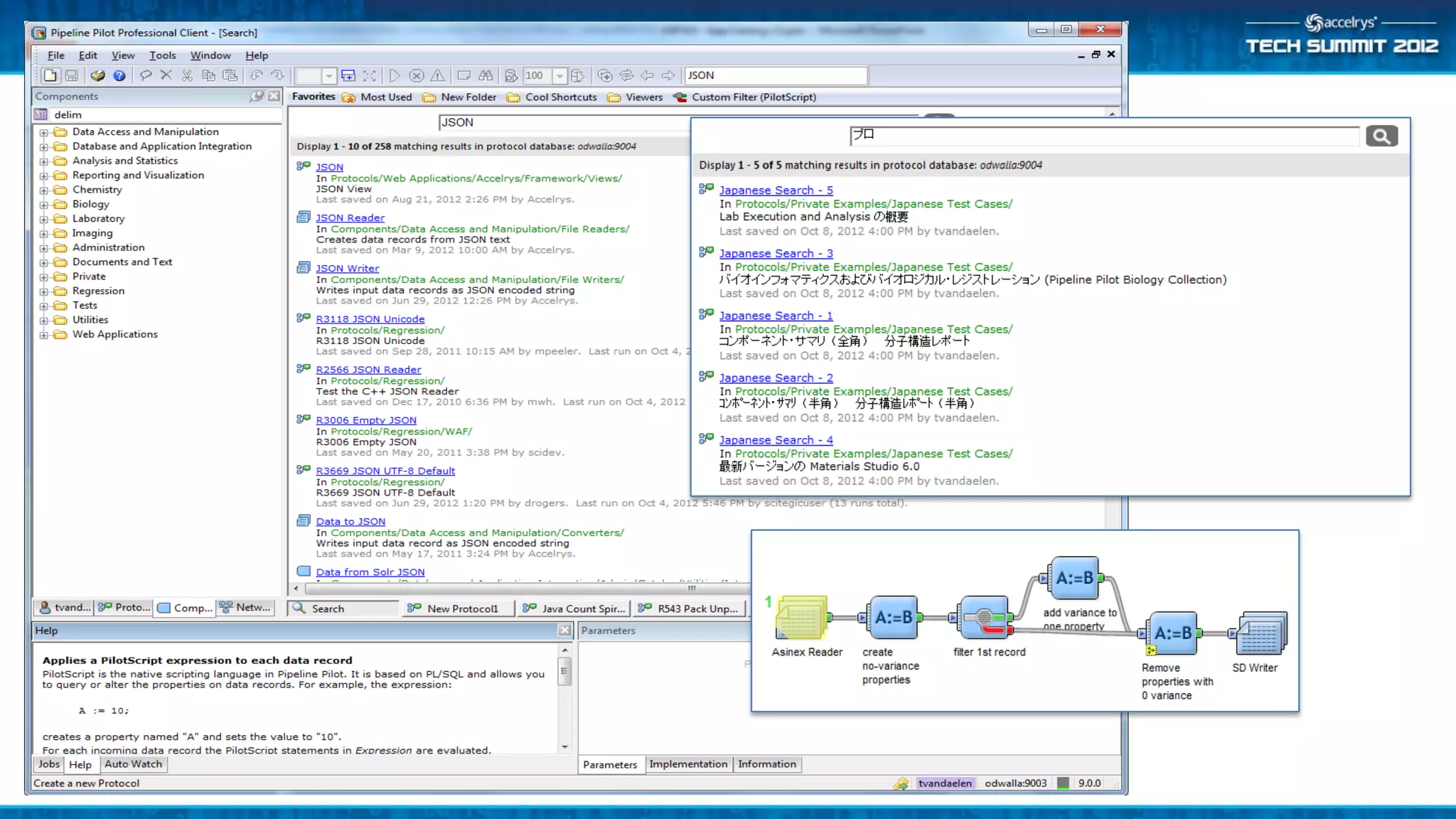
![Example Queries
• MAO type:"Component“
– Any components referencing ‘MAO’
• uses:"Xml Reader" -author:Accelrys
– Components/protocols that have an xml reader and are not
authored by Accelrys
• lastrun:[*TO NOW-6MONTH]
– Last run at least six months prior
• runcount:0
– Never been run](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ats4-plat05accelryscatalog-asearchindexforaep-121024035817-phpapp02/75/ATS4-PLAT05-Accelrys-Catalog-A-Search-Index-for-AEP-21-2048.jpg)